Slide ()
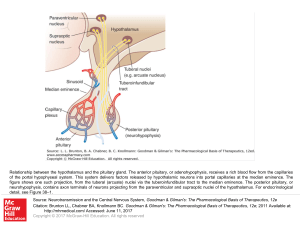
... Relationship between the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland. The anterior pituitary, or adenohypophysis, receives a rich blood flow from the capillaries of the portal hypophyseal system. This system delivers factors released by hypothalamic neurons into portal capillaries at the median eminence. T ...
... Relationship between the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland. The anterior pituitary, or adenohypophysis, receives a rich blood flow from the capillaries of the portal hypophyseal system. This system delivers factors released by hypothalamic neurons into portal capillaries at the median eminence. T ...
Action potential - Solon City Schools
... Inhibition and Excitation Excitation – the process of making the neuron receiving neurotransmitters more likely to generate an action potential (fire) Inhibition – the process of making the neuron receiving neurotransmitters less likely to generate an action potential ...
... Inhibition and Excitation Excitation – the process of making the neuron receiving neurotransmitters more likely to generate an action potential (fire) Inhibition – the process of making the neuron receiving neurotransmitters less likely to generate an action potential ...
Intro-ANN - Computer Science
... (popularly known as Moore's Law). Intel has kept that pace for nearly 40 years. ...
... (popularly known as Moore's Law). Intel has kept that pace for nearly 40 years. ...
LSU Seminar Neuroscience Center of Excellence
... effects on visual function, including loss of visual responsiveness to the deprived eye, reduced visual acuity, and loss of tuning to many stimulus characteristics. These changes occur faster than remodeling of thalamocortical axons, but the intracortical plasticity mechanisms that underlie them are ...
... effects on visual function, including loss of visual responsiveness to the deprived eye, reduced visual acuity, and loss of tuning to many stimulus characteristics. These changes occur faster than remodeling of thalamocortical axons, but the intracortical plasticity mechanisms that underlie them are ...
NeuralNets
... • Neurons communicate by receiving signals on their dendrites. Adding these signals and firing off a new signal along the axon if the total input exceeds a threshold. • The axon connects to new dendrites through synapses which can learn how much signal is transmitted. • McCulloch and Pitt (’43) buil ...
... • Neurons communicate by receiving signals on their dendrites. Adding these signals and firing off a new signal along the axon if the total input exceeds a threshold. • The axon connects to new dendrites through synapses which can learn how much signal is transmitted. • McCulloch and Pitt (’43) buil ...
29.2 Neurons - Cloudfront.net
... • Neurons transmit information in the form of electrical and chemical impulses – When a neuron is stimulated, it produces an electrical signal (action potential) within that neuron – Before it can move to the next cell it changes into a chemical signal (neurotransmitter) ...
... • Neurons transmit information in the form of electrical and chemical impulses – When a neuron is stimulated, it produces an electrical signal (action potential) within that neuron – Before it can move to the next cell it changes into a chemical signal (neurotransmitter) ...
Nervous Systems II PPT
... allows the giant squid to have near simultaneous contraction of its mantel, due to its ability to speed up transmission to its farthest parts from the CNS. ...
... allows the giant squid to have near simultaneous contraction of its mantel, due to its ability to speed up transmission to its farthest parts from the CNS. ...
Essential Questions and Vocabulary
... How is the cerebral cortex organized? What experimental methods are used to study brain function? What are the differences between the right and left hemispheres? VOCABULARY: Biological psychology, neuron, dendrite, axon, myelin sheath, action potential, threshold, synapse, neurotransmitters, ...
... How is the cerebral cortex organized? What experimental methods are used to study brain function? What are the differences between the right and left hemispheres? VOCABULARY: Biological psychology, neuron, dendrite, axon, myelin sheath, action potential, threshold, synapse, neurotransmitters, ...
Electro acupuncture activates glutamatergic neurons in
... ARC and vlPAG, retrograde dye was injected into rats’ vlPAG. The retrograde dye was absorbed by the axons in vlPAG, and then traveled to the cell body of the neuron. Detecting cell labeling in the ARC shows the neuron projection between ARC and vlPAG. The rats were then separated into two groups, an ...
... ARC and vlPAG, retrograde dye was injected into rats’ vlPAG. The retrograde dye was absorbed by the axons in vlPAG, and then traveled to the cell body of the neuron. Detecting cell labeling in the ARC shows the neuron projection between ARC and vlPAG. The rats were then separated into two groups, an ...
neurons
... then back to electrical impulse • Neurotransmitter may excite or inhibit the next neuron ...
... then back to electrical impulse • Neurotransmitter may excite or inhibit the next neuron ...
Nervous System & Endocrine System
... • Nerve Cells – The main part of the nervous system – The human body contains numerous nerve cells – Nerve cells are called neurons – Neurons are similar to electrical wires and carry messages along long, thin strands – They can reach up to a meter in length – A nerve is a bunch of neurons bunched t ...
... • Nerve Cells – The main part of the nervous system – The human body contains numerous nerve cells – Nerve cells are called neurons – Neurons are similar to electrical wires and carry messages along long, thin strands – They can reach up to a meter in length – A nerve is a bunch of neurons bunched t ...
Neuro Physiology 1
... recording a serious of peaks in the compound action potential which is shown in the adjacent diagram. ...
... recording a serious of peaks in the compound action potential which is shown in the adjacent diagram. ...
Central Nervous System (CNS)
... the outside under resting conditions due to distribution of ions controlled by Na+/K+ pump that require ATP • Nerve impulse starts when the membrane of the nerve depolarizes due to some stimulus, chemical, temp. changes, mechanical, etc…. • Depolarization is caused by the influx of Na+ which causes ...
... the outside under resting conditions due to distribution of ions controlled by Na+/K+ pump that require ATP • Nerve impulse starts when the membrane of the nerve depolarizes due to some stimulus, chemical, temp. changes, mechanical, etc…. • Depolarization is caused by the influx of Na+ which causes ...
The Nervous System
... have been felt, tasted, and touched with the sensory neurons into responses that the body recognizes. This process is accomplished by the brain. ...
... have been felt, tasted, and touched with the sensory neurons into responses that the body recognizes. This process is accomplished by the brain. ...
Migraine Visual Aura
... The pain of migraine headache is thought to have a neurogenic basis. Migraine involves dysfunction of brain-stem pathways that normally modulate sensory input. The key pathways for the pain are the trigeminovascular input from the meningeal vessels, which passes through the trigeminal ganglion and s ...
... The pain of migraine headache is thought to have a neurogenic basis. Migraine involves dysfunction of brain-stem pathways that normally modulate sensory input. The key pathways for the pain are the trigeminovascular input from the meningeal vessels, which passes through the trigeminal ganglion and s ...
Product Information N2 Supplement (100X)
... v. Add 5 mL 100X NEAA 3. Add N2 Supplement to 1X final concentration. 4. Add FGF2 (GSR‐2001) to 20 ng/mL. For some applications you may also add EGF to 20 ng/mL. 5. The complete 1X N2 medium can be stored at 4°C for up to three weeks. To preserve FGF2 activity, avoid repeatedly warming the med ...
... v. Add 5 mL 100X NEAA 3. Add N2 Supplement to 1X final concentration. 4. Add FGF2 (GSR‐2001) to 20 ng/mL. For some applications you may also add EGF to 20 ng/mL. 5. The complete 1X N2 medium can be stored at 4°C for up to three weeks. To preserve FGF2 activity, avoid repeatedly warming the med ...
An Herbalist`s View of the Nervous System
... Antispasmodic – relieves smooth muscle spasms Antistress – reduces stressful feelings or actions Anxiolytic – reduces anxiety or nervousness Calmative – promotes a feeling of calm, relaxation Excitant – agent eliciting excitation of specific body functions, i.e. Cerebral or motor Hypnotic – induces ...
... Antispasmodic – relieves smooth muscle spasms Antistress – reduces stressful feelings or actions Anxiolytic – reduces anxiety or nervousness Calmative – promotes a feeling of calm, relaxation Excitant – agent eliciting excitation of specific body functions, i.e. Cerebral or motor Hypnotic – induces ...
Review Material 2011
... Peripheral nerves--fibrous tissue. "Fiber" consists of axon and myelin sheath. In longitudinal section, fibers appear "wavy". Often have "dull" appearance due to presence of myelin, as apposed to "shiny" appearance of smooth muscle. In cross section look for axons surrounded by palely staining myeli ...
... Peripheral nerves--fibrous tissue. "Fiber" consists of axon and myelin sheath. In longitudinal section, fibers appear "wavy". Often have "dull" appearance due to presence of myelin, as apposed to "shiny" appearance of smooth muscle. In cross section look for axons surrounded by palely staining myeli ...
Rabbit anti-Phosphoserine 608 Retinoblastoma Protein
... www.invitrogen.com). By use of these products you accept the terms and conditions of all applicable Limited Use Label Licenses. Unless otherwise indicated, these products are for research use only and are not intended for human or animal diagnostic, therapeutic or commercial use. ...
... www.invitrogen.com). By use of these products you accept the terms and conditions of all applicable Limited Use Label Licenses. Unless otherwise indicated, these products are for research use only and are not intended for human or animal diagnostic, therapeutic or commercial use. ...
Neurons and Glial Cells
... Like other cells, each neuron has a cell body (or soma) that contains a nucleus, smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, and other cellular components. ...
... Like other cells, each neuron has a cell body (or soma) that contains a nucleus, smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, and other cellular components. ...
ppt - Castle High School
... These receptors allow Na+ and K+ to flow through, and the increase in Na+ depolarizes the membrane. If it reaches threshold, more Na+ voltagegated channels are activated and an action potential is generated. ...
... These receptors allow Na+ and K+ to flow through, and the increase in Na+ depolarizes the membrane. If it reaches threshold, more Na+ voltagegated channels are activated and an action potential is generated. ...
Channelrhodopsin

Channelrhodopsins are a subfamily of retinylidene proteins (rhodopsins) that function as light-gated ion channels. They serve as sensory photoreceptors in unicellular green algae, controlling phototaxis: movement in response to light. Expressed in cells of other organisms, they enable light to control electrical excitability, intracellular acidity, calcium influx, and other cellular processes. Channelrhodopsin-1 (ChR1) and Channelrhodopsin-2 (ChR2) from the model organism Chlamydomonas reinhardtii are the first discovered channelrhodopsins. Variants have been cloned from other algal species, and more are expected.























