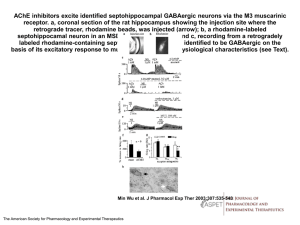
Coding of Visual Information in the Retina Coding of Light d D k and
... Problem: how does one cell code for yp of information? two types A neuron can only vary its frequency of action potentials. If the cone’s response indicates brightness then it cannot signal for brightness, color. ...
... Problem: how does one cell code for yp of information? two types A neuron can only vary its frequency of action potentials. If the cone’s response indicates brightness then it cannot signal for brightness, color. ...
Biology Cells unit: LT8 Review
... Put the images in the correct order to represent the sodiumpotassium pump. The first one is already labeled #1. ...
... Put the images in the correct order to represent the sodiumpotassium pump. The first one is already labeled #1. ...
Motor Neuron - papbiobellaire
... Stimulus - environmental change which causes a response; usually a form of energy a) radiant (heat, light) d) sound b) electrical e) chemical c) pressure ...
... Stimulus - environmental change which causes a response; usually a form of energy a) radiant (heat, light) d) sound b) electrical e) chemical c) pressure ...
31.1 The Neuron Functions of the Nervous System and external
... us that is required to start an impulse in a neuron is called its threshold. At the end of the axon, impulses can be transmitted to the next neuron. The point at which a neuron transfers an impulse to another cell is called a synapse. When an impulse arrives ves at the synapse, neurotransmitters,, c ...
... us that is required to start an impulse in a neuron is called its threshold. At the end of the axon, impulses can be transmitted to the next neuron. The point at which a neuron transfers an impulse to another cell is called a synapse. When an impulse arrives ves at the synapse, neurotransmitters,, c ...
Parts of the Brain - University of Peradeniya
... Histology of cerebral cortex Principal neurons connect with other neurons in CNS in 3 ways I. Projection neurons/fibers (subcortical areas such as thalamus, corpus striatum, brain stem & spinal cord) II. Association neurons/fibers (connects cortical neurons in same hemisphere) III. Comissural neuro ...
... Histology of cerebral cortex Principal neurons connect with other neurons in CNS in 3 ways I. Projection neurons/fibers (subcortical areas such as thalamus, corpus striatum, brain stem & spinal cord) II. Association neurons/fibers (connects cortical neurons in same hemisphere) III. Comissural neuro ...
Ch02
... Transmitting Information Across the Gap • Synapse is the small space between neurons • Neurotransmitters are: – released by the presynaptic neuron from vesicles. – received by the postsynaptic neuron on receptor sites. – matched like a key to a lock into specific receptor sites. – used as triggers ...
... Transmitting Information Across the Gap • Synapse is the small space between neurons • Neurotransmitters are: – released by the presynaptic neuron from vesicles. – received by the postsynaptic neuron on receptor sites. – matched like a key to a lock into specific receptor sites. – used as triggers ...
Chapter 17:
... Messages are relayed throughout the body via electrochemical messages from the brain or through chemical messengers – hormones (hormones require more time than nervous transmission but are long lasting) There are more nerve cells in the body than there are visible stars in the Milky Way! 1 cm3 of br ...
... Messages are relayed throughout the body via electrochemical messages from the brain or through chemical messengers – hormones (hormones require more time than nervous transmission but are long lasting) There are more nerve cells in the body than there are visible stars in the Milky Way! 1 cm3 of br ...
File - firestone falcons
... called axons, which cause chemicals called neurotransmitters to be released at junctions called synapses. • A cell that receives a synaptic signal may be excited, inhibited, or otherwise modulated. ...
... called axons, which cause chemicals called neurotransmitters to be released at junctions called synapses. • A cell that receives a synaptic signal may be excited, inhibited, or otherwise modulated. ...
Nervous System
... function. Physical effects include increased body temperature, heart rate, and blood pressure. Psychological effects include perceptual and thought distortions, hallucinations, delusions, and rapid mood swings. ...
... function. Physical effects include increased body temperature, heart rate, and blood pressure. Psychological effects include perceptual and thought distortions, hallucinations, delusions, and rapid mood swings. ...
Prac T12 - studylib.net
... Action potentials occur in all neurons if a stimulus is applied that lowers the membrane potential. When a stimulus is applied it triggers an action potential in the membrane. A hyperpolarized membrane always results in the production of an action potential. During the relative refractory period, a ...
... Action potentials occur in all neurons if a stimulus is applied that lowers the membrane potential. When a stimulus is applied it triggers an action potential in the membrane. A hyperpolarized membrane always results in the production of an action potential. During the relative refractory period, a ...
a study of axonal protein trafficking in neuronal networks via the
... express fluorescent proteins in neurons. Preliminary results show that the neurons can be polarized with their soma and axons being compartmentalized into different fluidically isolated microenvironments. When chemical stimulation was applied to axonal chamber, anterograde migration of expressed flu ...
... express fluorescent proteins in neurons. Preliminary results show that the neurons can be polarized with their soma and axons being compartmentalized into different fluidically isolated microenvironments. When chemical stimulation was applied to axonal chamber, anterograde migration of expressed flu ...
Cheng, P. T. ond J. E. Willis. Glucose-6-
... glycylglycine buffer, pH 8.0, per gmm wet weight of cells. The buffer was added slowly over o period of IO minutes with continued grinding. The resulting mixture was stirred for one hour at room temperature and centrifuged ot 13,000 x g for 20 minutes to yield the crude extract used in this study. R ...
... glycylglycine buffer, pH 8.0, per gmm wet weight of cells. The buffer was added slowly over o period of IO minutes with continued grinding. The resulting mixture was stirred for one hour at room temperature and centrifuged ot 13,000 x g for 20 minutes to yield the crude extract used in this study. R ...
Q 1
... • A29: • Using twin experiments, scientists have discovered that if one identical male twin has an addiction, the other twin is 50% more likely to have an addiction as well. • A deficiency in dopamine receptors also causes an increased susceptibility to addiction. • If a child is surrounded by drug ...
... • A29: • Using twin experiments, scientists have discovered that if one identical male twin has an addiction, the other twin is 50% more likely to have an addiction as well. • A deficiency in dopamine receptors also causes an increased susceptibility to addiction. • If a child is surrounded by drug ...
CNS DEVELOPMENT - University of Kansas Medical Center
... grow processes (axons) that will form a new outer layer: Marginal layer. The marginal layer is also located beneath the external limiting membrane. The marginal layer will form the white matter of the spinal cord and the brain. The mantle layer forms the gray matter of the brain and spinal cord (exc ...
... grow processes (axons) that will form a new outer layer: Marginal layer. The marginal layer is also located beneath the external limiting membrane. The marginal layer will form the white matter of the spinal cord and the brain. The mantle layer forms the gray matter of the brain and spinal cord (exc ...
CNS: Brain and Spinal Cord
... subarachnoid space and circulates. At arachnoid villi, it enters dural sinuses and drains into the jugular veins. D. The blood brain barrier- capillaries that enter the neural part of the brain (as opposed to the choroid plexuses of the ventricles) contain an endothelium in which simple squamous cel ...
... subarachnoid space and circulates. At arachnoid villi, it enters dural sinuses and drains into the jugular veins. D. The blood brain barrier- capillaries that enter the neural part of the brain (as opposed to the choroid plexuses of the ventricles) contain an endothelium in which simple squamous cel ...
Readings to Accompany “Nerves” Worksheet (adapted from France
... nerve can stop signals to and from the central nervous system, causing impaired muscle function and loss of (or abnormal) sensation in the injured area. When a nerve is cut, both the nerve and its insulating myelin sheath are disrupted. Compression or tensile injuries can cause nerve fibers to break ...
... nerve can stop signals to and from the central nervous system, causing impaired muscle function and loss of (or abnormal) sensation in the injured area. When a nerve is cut, both the nerve and its insulating myelin sheath are disrupted. Compression or tensile injuries can cause nerve fibers to break ...
Channelrhodopsin

Channelrhodopsins are a subfamily of retinylidene proteins (rhodopsins) that function as light-gated ion channels. They serve as sensory photoreceptors in unicellular green algae, controlling phototaxis: movement in response to light. Expressed in cells of other organisms, they enable light to control electrical excitability, intracellular acidity, calcium influx, and other cellular processes. Channelrhodopsin-1 (ChR1) and Channelrhodopsin-2 (ChR2) from the model organism Chlamydomonas reinhardtii are the first discovered channelrhodopsins. Variants have been cloned from other algal species, and more are expected.