09 Stoichiometry WS Stoichiometry WS
... If 1.23 g of lead nitrate are consumed, what is the mass of the potassium nitrate produced? 10. A car battery produces electrical energy with the following chemical reaction: Pb(s) + PbO2(s) + 2H2SO4(aq) 2PbSO4(s) + 2H2O(l) If the battery loses 340. g of lead in this reaction, how many moles of lead ...
... If 1.23 g of lead nitrate are consumed, what is the mass of the potassium nitrate produced? 10. A car battery produces electrical energy with the following chemical reaction: Pb(s) + PbO2(s) + 2H2SO4(aq) 2PbSO4(s) + 2H2O(l) If the battery loses 340. g of lead in this reaction, how many moles of lead ...
File - Varsity Field
... Q7. Ammonium sulphate reacts with sodium hydroxide: Q8. Rhodocrosite, a red mineral, consists largely of manganese II carbonate. Write an equation for the reaction of the mineral with hydrochloric acid. Name the products. Q9. Sodium sulphite and acetic acid react. Q10. Write a balanced, net ionic eq ...
... Q7. Ammonium sulphate reacts with sodium hydroxide: Q8. Rhodocrosite, a red mineral, consists largely of manganese II carbonate. Write an equation for the reaction of the mineral with hydrochloric acid. Name the products. Q9. Sodium sulphite and acetic acid react. Q10. Write a balanced, net ionic eq ...
2005 - NESACS
... II. A central atom of a molecule has a lone pairs of electrons on it. III. The molecule's electronic geometry and molecular geometry are the same. (A) (B) (C) (D) ...
... II. A central atom of a molecule has a lone pairs of electrons on it. III. The molecule's electronic geometry and molecular geometry are the same. (A) (B) (C) (D) ...
NZIC 2012 - Rangiora High School
... Since HA is a strong acid, it reacts completely with water giving a 0.1 mol L–1 solution, so its conductivity will be high. HA + H2O A– + H3O+ Since HB is a weak acid, reaction with water is incomplete giving a solution that is ~ 10–3 mol L–1 in ions so its conductivity will be lower than that of ...
... Since HA is a strong acid, it reacts completely with water giving a 0.1 mol L–1 solution, so its conductivity will be high. HA + H2O A– + H3O+ Since HB is a weak acid, reaction with water is incomplete giving a solution that is ~ 10–3 mol L–1 in ions so its conductivity will be lower than that of ...
Wet Chemical Etching
... law of mass action, at given temperature and pressure, the product [H3O+].[OH-] always keeps constant. Therefore, with [OH-] increasing, the H3O+-concentration drops thus increasing the pH-value. Corresponding to acids, the strength of a base as aqueous solution can be defined as follows: ...
... law of mass action, at given temperature and pressure, the product [H3O+].[OH-] always keeps constant. Therefore, with [OH-] increasing, the H3O+-concentration drops thus increasing the pH-value. Corresponding to acids, the strength of a base as aqueous solution can be defined as follows: ...
Hydrolysis of Phytic Acid by Microwave Treatment: Application to
... determination through phosphate analysis. The analytical reaction selected for phosphate determination in this work has the advantage that after 45 min, the final absorbance is not dependent on the nature of the acid used and its concentration. Nevertheless, the kinetics of heteropoly acid formation ...
... determination through phosphate analysis. The analytical reaction selected for phosphate determination in this work has the advantage that after 45 min, the final absorbance is not dependent on the nature of the acid used and its concentration. Nevertheless, the kinetics of heteropoly acid formation ...
PowerPoint
... 4 Ag(CN)2-(aq) + OH -(aq) Add 4 OH- to balance charge. Since there hydrogen is absent on the reactant side, add 2 H2O to balance the hydrogen and oxygen. ...
... 4 Ag(CN)2-(aq) + OH -(aq) Add 4 OH- to balance charge. Since there hydrogen is absent on the reactant side, add 2 H2O to balance the hydrogen and oxygen. ...
Science Notes on Physical and Chemical Properties
... Example – Tear a piece of paper into 10-15 pieces. The shape and size have changed, but its still paper Example – Change of state = physical change…add energy to ice and you get a liquid…add more energy and you get a gas…all physical changes as it is still water Example – Dissolving things is a phys ...
... Example – Tear a piece of paper into 10-15 pieces. The shape and size have changed, but its still paper Example – Change of state = physical change…add energy to ice and you get a liquid…add more energy and you get a gas…all physical changes as it is still water Example – Dissolving things is a phys ...
Practical Exercises in Physical Chemistry
... thermostat at 18 0C for 5 min. Then, add 4 ml of the Solution 1, shake the flask and fill with the mixture the measuring cell. Remember, you should note the time at the moment when you add the Solution 1 into the flask – it is the time moment t = 0 of your measurements. Fix the cell in the chamber a ...
... thermostat at 18 0C for 5 min. Then, add 4 ml of the Solution 1, shake the flask and fill with the mixture the measuring cell. Remember, you should note the time at the moment when you add the Solution 1 into the flask – it is the time moment t = 0 of your measurements. Fix the cell in the chamber a ...
exam review - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... dissolved in water and diluted to a final volume of 200.0 mL. b) Determine the volume of commercial grade nitric acid (15.8 mol/L HNO 3) that is needed to prepare 100.0 mL of 3.00 mol/L HNO3. c) Rubbing alcohol is commonly used as an antiseptic for small cuts. It is sold as a 23% (v/v) solution of i ...
... dissolved in water and diluted to a final volume of 200.0 mL. b) Determine the volume of commercial grade nitric acid (15.8 mol/L HNO 3) that is needed to prepare 100.0 mL of 3.00 mol/L HNO3. c) Rubbing alcohol is commonly used as an antiseptic for small cuts. It is sold as a 23% (v/v) solution of i ...
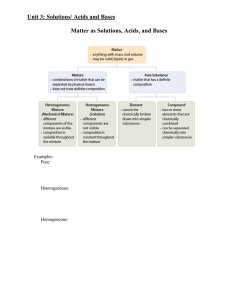
Outline for Unit 1 Solutions, Acid/Base, and Gases
... Strong base: completely (100%) dissociates into hydroxide (OH-) ions when dissolved in water. All oxides and hydroxides of the alkali metals and alkaline earths – group 1 and 2 are strong bases. (some are not very soluble in water but what does dissolve will ...
... Strong base: completely (100%) dissociates into hydroxide (OH-) ions when dissolved in water. All oxides and hydroxides of the alkali metals and alkaline earths – group 1 and 2 are strong bases. (some are not very soluble in water but what does dissolve will ...
AS Paper 1 Practice Paper 12 - A
... containing iodide ions. Write the simplest ionic equation for the reaction that occurs. Observation ................................................................................................. ...
... containing iodide ions. Write the simplest ionic equation for the reaction that occurs. Observation ................................................................................................. ...
Quantities, Units, Symbols and Nomenclature used in
... Fe3+ (aq), Fe2+ (aq) | Pt Oxidant and reductant are in the same phase. An inert electrode is used. The vertical line represents a phase boundary. Equilibrium Constant, K Constants will be dimensionless, ie have no units, in keeping with current IUPAC conventions. They will include: Kc Ka Kw Ks ...
... Fe3+ (aq), Fe2+ (aq) | Pt Oxidant and reductant are in the same phase. An inert electrode is used. The vertical line represents a phase boundary. Equilibrium Constant, K Constants will be dimensionless, ie have no units, in keeping with current IUPAC conventions. They will include: Kc Ka Kw Ks ...
CHAPTER 15 ACIDS AND BASES
... At pH 1.00 the concentration of hydrogen ion is 0.10 M (Why only two significant figures?) This will tend to suppress the ionization of the weak acid (LeChatelier's principle, Section 14.5). The extra hydrogen ion shifts the position of equilibrium in the direction of the un-ionized acid, and to two ...
... At pH 1.00 the concentration of hydrogen ion is 0.10 M (Why only two significant figures?) This will tend to suppress the ionization of the weak acid (LeChatelier's principle, Section 14.5). The extra hydrogen ion shifts the position of equilibrium in the direction of the un-ionized acid, and to two ...
No Slide Title
... below. The series are listed in descending order of chemical reactivity, with the most active metals and halogens at the top (the elements most likely to undergo oxidation). Any metal on the list will replace the ions of those metals (to undergo reduction) that appear anywhere underneath it on the l ...
... below. The series are listed in descending order of chemical reactivity, with the most active metals and halogens at the top (the elements most likely to undergo oxidation). Any metal on the list will replace the ions of those metals (to undergo reduction) that appear anywhere underneath it on the l ...
Semester 1 Final Exam
... Unit conversions should be shown using dimensional analysis, showing how all units cancel out. Work for problems involving formulas should follow the I.E.S.A. form. 1. A particular compound containing only chlorine and oxygen is 52.56% chlorine by mass. The molar mass of the compound is found to ...
... Unit conversions should be shown using dimensional analysis, showing how all units cancel out. Work for problems involving formulas should follow the I.E.S.A. form. 1. A particular compound containing only chlorine and oxygen is 52.56% chlorine by mass. The molar mass of the compound is found to ...
9. The Copigmentation Interactions between Strawberry
... temperature at heating and at cooling. Obtained results confirmed that the interaction between pigment:copigment complex was destroyed at heating to 50 oC”and with following cooling to 20oC was not seen reversibility of the copigmentation process. Practical applications The copigmentation process co ...
... temperature at heating and at cooling. Obtained results confirmed that the interaction between pigment:copigment complex was destroyed at heating to 50 oC”and with following cooling to 20oC was not seen reversibility of the copigmentation process. Practical applications The copigmentation process co ...
2017 Chemistry Exam Review Compounds and Reactions 1. Know
... 39. Draw water molecules to show how, based on their polarity, they cling together. What properties of water does this “clinginess” cause? 40. Draw water molecules to show how, based on their polarity, they dissolve table salt (NaCl) by surrounding Na+ cations and Cl- anions. 41. What kind of substa ...
... 39. Draw water molecules to show how, based on their polarity, they cling together. What properties of water does this “clinginess” cause? 40. Draw water molecules to show how, based on their polarity, they dissolve table salt (NaCl) by surrounding Na+ cations and Cl- anions. 41. What kind of substa ...
Matter and Measurement
... chloride and sodium carbonate are mixed. First write the chemical formulas of the reactants aqueous Calcium chloride: CaCl2(aq) aqueous sodium carbonate: Na2CO3(aq) Next, determine what the products of the reaction will be and which product is the precipitate. The products of this reaction are: NaCl ...
... chloride and sodium carbonate are mixed. First write the chemical formulas of the reactants aqueous Calcium chloride: CaCl2(aq) aqueous sodium carbonate: Na2CO3(aq) Next, determine what the products of the reaction will be and which product is the precipitate. The products of this reaction are: NaCl ...
Quantitative Microscale Hydrogenation of Vegetable Oils
... through the Tygon tubing or the septum. The loss is typically in the range of 2 to 3 mL. This could be taken into account by having students work in pairs with each pair running both a “real” hydrogenation and a control with everything except the oil. While this and fluctuating ambient lab temperatu ...
... through the Tygon tubing or the septum. The loss is typically in the range of 2 to 3 mL. This could be taken into account by having students work in pairs with each pair running both a “real” hydrogenation and a control with everything except the oil. While this and fluctuating ambient lab temperatu ...