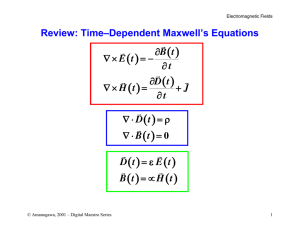
Review: Time–Dependent Maxwell`s Equations D t E t B t H t = ε = µ
... convenient reference is a zero potential at an infinite distance. In the result above for the electrostatic work, we could set a zero potential at the initial point of the path, so that φ(a)=0. Either choice of potential reference would give the same potential ...
... convenient reference is a zero potential at an infinite distance. In the result above for the electrostatic work, we could set a zero potential at the initial point of the path, so that φ(a)=0. Either choice of potential reference would give the same potential ...
Influence of atmospheric electric fields on the radio
... in the radial direction to the shower axis [12,13]. The total emission observed at ground level is the coherent sum of both components. Because the two components are polarized in different directions, they are added constructively or destructively depending on the positions of the observer relative ...
... in the radial direction to the shower axis [12,13]. The total emission observed at ground level is the coherent sum of both components. Because the two components are polarized in different directions, they are added constructively or destructively depending on the positions of the observer relative ...
Pair production in counter-propagating laser beams
... 1.3. PROBING STRONG WAVES AND STRONG FIELDS ...
... 1.3. PROBING STRONG WAVES AND STRONG FIELDS ...
7.2 Angular Momentum
... When no net external torque acts on a closed system, the total angular momentum of the system does not change. Skaters, gymnasts, dancers, and divers use conservation of angular momentum. For example, a diver changes from a pike position to an extended position at the end of a flip. This extension o ...
... When no net external torque acts on a closed system, the total angular momentum of the system does not change. Skaters, gymnasts, dancers, and divers use conservation of angular momentum. For example, a diver changes from a pike position to an extended position at the end of a flip. This extension o ...
Quantum electrodynamics with 1D artificial atoms
... transitions with large dipole moments and relatively decoherence-free spin states. Additionally, nanostructures may be formed in the host GaAs to efficiently interface the QD to an optical field. Ultimately, a QD can be made to interact with just a single optical mode, which constitutes an artificia ...
... transitions with large dipole moments and relatively decoherence-free spin states. Additionally, nanostructures may be formed in the host GaAs to efficiently interface the QD to an optical field. Ultimately, a QD can be made to interact with just a single optical mode, which constitutes an artificia ...
Phenomenology Beyond the Standard Model
... The Stakes in the Higgs Search • How is gauge symmetry broken? • Is there any elementary scalar field? • Would have caused phase transition in the Universe when it was about 10-12 seconds old • May have generated then the matter in the Universe: electroweak baryogenesis • A related inflaton might h ...
... The Stakes in the Higgs Search • How is gauge symmetry broken? • Is there any elementary scalar field? • Would have caused phase transition in the Universe when it was about 10-12 seconds old • May have generated then the matter in the Universe: electroweak baryogenesis • A related inflaton might h ...
Potential Structure and of a Plasma Hole in a Rotating Magnetized
... Electric field in magnetized plasmas drives a rotating motion by E B drift, giving rise to macroscopic structures such as vortices. Structure formation in magnetized plasmas attracts many researchers, and a large number of theoretical and simulation studies have been performed. Recently spontaneou ...
... Electric field in magnetized plasmas drives a rotating motion by E B drift, giving rise to macroscopic structures such as vortices. Structure formation in magnetized plasmas attracts many researchers, and a large number of theoretical and simulation studies have been performed. Recently spontaneou ...
Terahertz driven intraband dynamics of excitons in nanorods Fredrik Sy
... used to passivate the nanorods. A full set of dynamical equations were then constructed from Heisenberg’s equation of motion, and were used to model the excitonic correlations as a function of time. Transmittance and absorbance were calculated for different nanorod orientations and electric field s ...
... used to passivate the nanorods. A full set of dynamical equations were then constructed from Heisenberg’s equation of motion, and were used to model the excitonic correlations as a function of time. Transmittance and absorbance were calculated for different nanorod orientations and electric field s ...
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Spring 2014
... where a† and a are a raising and a lowering operator of photons respectively, and N is a photon number operator. In the absence of coupling, the eigenstates of the uncoupled Hamiltonian or the bare states are simply a ground or excited state with photons. For example, the bare states can be labeled ...
... where a† and a are a raising and a lowering operator of photons respectively, and N is a photon number operator. In the absence of coupling, the eigenstates of the uncoupled Hamiltonian or the bare states are simply a ground or excited state with photons. For example, the bare states can be labeled ...
Spacetime algebra as a powerful tool for electromagnetism
... for photons, respectively. [47, 52–58, 74]. (Akin to this, the spin and orbital angularmomentum contributions of gluon fields in QCD are currently considered as measurable in spite of the field-theory restrictions [88].) Similarly, the local momentum density of the electromagnetic field (as well as ...
... for photons, respectively. [47, 52–58, 74]. (Akin to this, the spin and orbital angularmomentum contributions of gluon fields in QCD are currently considered as measurable in spite of the field-theory restrictions [88].) Similarly, the local momentum density of the electromagnetic field (as well as ...
Quantum vacuum thruster

A quantum vacuum plasma thruster (or Q-thruster) is a proposed type of spacecraft thruster that would work in part by acting on the virtual particles produced by quantum vacuum fluctuations. This was proposed as a possible model for an engine that could produce thrust without carrying its own propellant. Some physicists working with microwave resonant cavity thrusters think that they might be the first examples of such an engine.























