Modern Physics - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Isotopes of a given element correspond to nuclei with different numbers of neutrons. This results in a variety of different properties for the nuclei, including the obvious one of mass. The chemical behavior, however, is governed by the lectrons. All isotopes of a given element have the same number ...
... Isotopes of a given element correspond to nuclei with different numbers of neutrons. This results in a variety of different properties for the nuclei, including the obvious one of mass. The chemical behavior, however, is governed by the lectrons. All isotopes of a given element have the same number ...
Chapter 29
... • The volume of the nucleus (assumed to be spherical) is directly proportional to the total number of nucleons • This suggests that all nuclei have nearly the same density • Nucleons combine to form a nucleus as though they were tightly packed spheres ...
... • The volume of the nucleus (assumed to be spherical) is directly proportional to the total number of nucleons • This suggests that all nuclei have nearly the same density • Nucleons combine to form a nucleus as though they were tightly packed spheres ...
nuclear fission
... is shown in the diagram above. This reaction will proceed at high speed; the time for an emitted neutron to collide with another nucleus to produce a second fission is about 0.01 microsecond. ...
... is shown in the diagram above. This reaction will proceed at high speed; the time for an emitted neutron to collide with another nucleus to produce a second fission is about 0.01 microsecond. ...
fusion concepts
... The laser implosion process involves the following steps: 1. Atmosphere formation: Lasers or particle beams heat the surface of a fusion target in the direct drive concept, or heat the inside of a hohlraum chamber in the indirect drive concept using soft x rays, forming a plasma envelope. 2. Illumin ...
... The laser implosion process involves the following steps: 1. Atmosphere formation: Lasers or particle beams heat the surface of a fusion target in the direct drive concept, or heat the inside of a hohlraum chamber in the indirect drive concept using soft x rays, forming a plasma envelope. 2. Illumin ...
nuclear fusion
... It is very difficult to provide the necessary confinement time. Here two principally different methods are used. The first method is the inertial confinement by means of lasers in which extremely high density of the plasma is achieved (n ∼ 1025 cm-3) which allows one significant1y to reduce the conf ...
... It is very difficult to provide the necessary confinement time. Here two principally different methods are used. The first method is the inertial confinement by means of lasers in which extremely high density of the plasma is achieved (n ∼ 1025 cm-3) which allows one significant1y to reduce the conf ...
Chemical Reactions
... • The positive ions switch places to form two new compounds. • The reactants and products are always two molecules. AD + BC AC + BD “happy breakup” ...
... • The positive ions switch places to form two new compounds. • The reactants and products are always two molecules. AD + BC AC + BD “happy breakup” ...
Unit 7 Review
... A nucleus of the isotope xenon, Xe-131, is produced when a nucleus of the radioactive isotope iodine I-13 decays. (a) Explain the term isotopes. the nuclei of different isotopes of an element have the same number of protons; but different numbers of neutrons; ...
... A nucleus of the isotope xenon, Xe-131, is produced when a nucleus of the radioactive isotope iodine I-13 decays. (a) Explain the term isotopes. the nuclei of different isotopes of an element have the same number of protons; but different numbers of neutrons; ...
Nuclear Chemistry - Ector County ISD.
... During the fission of U235, three neutrons are released in addition to the two daughter atoms. If these released neutrons collide with nearby U235 nuclei, they can stimulate the fission of these atoms and start a self-sustaining nuclear chain reaction. This chain reaction is the basis of nuclear pow ...
... During the fission of U235, three neutrons are released in addition to the two daughter atoms. If these released neutrons collide with nearby U235 nuclei, they can stimulate the fission of these atoms and start a self-sustaining nuclear chain reaction. This chain reaction is the basis of nuclear pow ...
Review 2 key - Home [www.petoskeyschools.org]
... 6 What cloud shape does s, p, d and f (no shape needed for f) orbital have and how many electrons fit into each? s- sphere (2) ...
... 6 What cloud shape does s, p, d and f (no shape needed for f) orbital have and how many electrons fit into each? s- sphere (2) ...
Alpha Beta Fission Fusion
... During the fission of U235, three neutrons are released in addition to the two daughter atoms. If these released neutrons collide with nearby U235 nuclei, they can stimulate the fission of these atoms and start a self-sustaining nuclear chain reaction. This chain reaction is the basis of nuclear pow ...
... During the fission of U235, three neutrons are released in addition to the two daughter atoms. If these released neutrons collide with nearby U235 nuclei, they can stimulate the fission of these atoms and start a self-sustaining nuclear chain reaction. This chain reaction is the basis of nuclear pow ...
Document
... DEF1. Half-life is the time taken for the activity of the sample to fall to half its ...
... DEF1. Half-life is the time taken for the activity of the sample to fall to half its ...
Nuclear Chemistry PowerPoint
... stimulate the fission of these atoms and start a selfsustaining nuclear chain reaction. This chain reaction is the basis of nuclear power. As uranium atoms continue to split, a significant amount of energy is released from the reaction. The heat released during this reaction is harvested and used to ...
... stimulate the fission of these atoms and start a selfsustaining nuclear chain reaction. This chain reaction is the basis of nuclear power. As uranium atoms continue to split, a significant amount of energy is released from the reaction. The heat released during this reaction is harvested and used to ...
Objectives for Nuclear Chemistry
... Fission reactions result in the splitting of heavier nuclei into lighter ones. This is accomplished by hitting the large nucleus with a slow moving neutron, the nucleus absorbs the neutron and becomes unstable. The new unstable nucleus then breaks apart into fission fragments of elements of lighter ...
... Fission reactions result in the splitting of heavier nuclei into lighter ones. This is accomplished by hitting the large nucleus with a slow moving neutron, the nucleus absorbs the neutron and becomes unstable. The new unstable nucleus then breaks apart into fission fragments of elements of lighter ...
Ch 10 Nuclear Chemistry
... atomic nucleus emits charged particles and energy. • Radioisotope is short for radioactive isotopes, which is any atom containing an unstable nucleus. • Radioisotopes spontaneously change into other isotopes over time and is said to undergo nuclear ...
... atomic nucleus emits charged particles and energy. • Radioisotope is short for radioactive isotopes, which is any atom containing an unstable nucleus. • Radioisotopes spontaneously change into other isotopes over time and is said to undergo nuclear ...
Content Domain III: Chemistry—Atomic Theory and
... compared to equivalent masses of coal or oil. It also eliminates air pollutants. On the other hand, nuclear waste from fission creates disposal problems. Improper disposal underground might lead to radioactive contamination of water supplies. Sometimes two low-mass nuclei combine to form one nucleus ...
... compared to equivalent masses of coal or oil. It also eliminates air pollutants. On the other hand, nuclear waste from fission creates disposal problems. Improper disposal underground might lead to radioactive contamination of water supplies. Sometimes two low-mass nuclei combine to form one nucleus ...
File - Chemistry with Mr. Patmos
... Have atomic numbers above 92 undergo transmutation Do not occur in nature Have been synthesized in nuclear reactors or particle accelerators Are radioactive ...
... Have atomic numbers above 92 undergo transmutation Do not occur in nature Have been synthesized in nuclear reactors or particle accelerators Are radioactive ...
Physics 535 lectures notes: 1 * Sep 4th 2007
... a) Why did we observe the nuclear masses that we see? For instance, why was Helium four times more massive than hydrogen rather than twice? b) How did you bind the positively charged particles together when they should have a strong electromagnetic repulsion? c) How to explain other “radiation” emit ...
... a) Why did we observe the nuclear masses that we see? For instance, why was Helium four times more massive than hydrogen rather than twice? b) How did you bind the positively charged particles together when they should have a strong electromagnetic repulsion? c) How to explain other “radiation” emit ...
Mindfiesta Page 1 CHAPTER – 13 NUCLEI EXPERT`S TIPS : (1) An
... (47) The total life of a radioactive sample is infinite. (48) -ray spectrum is continuous in nature, while in -ray and -ray spectrum, the emitted energy has only discrete values. _ ...
... (47) The total life of a radioactive sample is infinite. (48) -ray spectrum is continuous in nature, while in -ray and -ray spectrum, the emitted energy has only discrete values. _ ...
Chapter-2-Human-Chemistry
... and bases reacting with one another • Dissociates itself into cations and anions when dissolved in water • Important for tissue strength, blood, and lymph ...
... and bases reacting with one another • Dissociates itself into cations and anions when dissolved in water • Important for tissue strength, blood, and lymph ...
1.1 Principles of nuclear fusion
... release of a large number of particles including among other a helium nuclei. However, it was soon revealed that this would not be a feasible way for power production. Even though the process also releases heat, much more energy is consumed for accelerating the particles. The deuteron beams lose the ...
... release of a large number of particles including among other a helium nuclei. However, it was soon revealed that this would not be a feasible way for power production. Even though the process also releases heat, much more energy is consumed for accelerating the particles. The deuteron beams lose the ...
Chemistry Terms
... daughter isotope The isotope into which a radioisotope transforms. A radioisotope can have several possible daughter isotopes, depending on the process by which it decays. halflife The amount of time necessary for half a sample of a radioisotope to decay to its daughter isotope. This is different fo ...
... daughter isotope The isotope into which a radioisotope transforms. A radioisotope can have several possible daughter isotopes, depending on the process by which it decays. halflife The amount of time necessary for half a sample of a radioisotope to decay to its daughter isotope. This is different fo ...
Chemistry Standard 2A-Nucleus Section 20.1
... 2. The attractive force between protons and neutrons in a nucleus caused by the strong nuclear force acts only Page answer is found ____________ a. outside the nucleus. c. only in unstable isotopes. b. over a very short distance. d. intermittently. 3. Radioactive materials have unstable a. electrons ...
... 2. The attractive force between protons and neutrons in a nucleus caused by the strong nuclear force acts only Page answer is found ____________ a. outside the nucleus. c. only in unstable isotopes. b. over a very short distance. d. intermittently. 3. Radioactive materials have unstable a. electrons ...
Nuclear Physics and Radioactivity
... element - a substance made of only one kind of atom. isotope - a form of an element which has a particular number of neutrons, that is, has the same atomic number but a different mass number than the other elements which occupy the same place on the periodic table. ...
... element - a substance made of only one kind of atom. isotope - a form of an element which has a particular number of neutrons, that is, has the same atomic number but a different mass number than the other elements which occupy the same place on the periodic table. ...
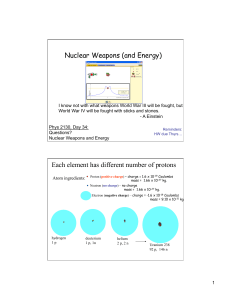
Nuclear Weapons (and Energy) Each element has different number
... goes down a bit but still have strong nuclear binding forces. Like putting a bunch of neutral people between one’s that find each other repulsive in same room… MORE STABLE SITUATION ...
... goes down a bit but still have strong nuclear binding forces. Like putting a bunch of neutral people between one’s that find each other repulsive in same room… MORE STABLE SITUATION ...
Nuclear fusion

In nuclear physics, nuclear fusion is a nuclear reaction in which two or more atomic nuclei come very close and then collide at a very high speed and join to form a new nucleus. During this process, matter is not conserved because some of the matter of the fusing nuclei is converted to photons (energy). Fusion is the process that powers active or ""main sequence"" stars.The fusion of two nuclei with lower masses than Iron-56 (which, along with Nickel-62, has the largest binding energy per nucleon) generally releases energy, while the fusion of nuclei heavier than iron absorbs energy. The opposite is true for the reverse process, nuclear fission. This means that fusion generally occurs for lighter elements only, and likewise, that fission normally occurs only for heavier elements. There are extreme astrophysical events that can lead to short periods of fusion with heavier nuclei. This is the process that gives rise to nucleosynthesis, the creation of the heavy elements during events such as supernova.Following the discovery of quantum tunneling by Friedrich Hund, in 1929 Robert Atkinson and Fritz Houtermans used the measured masses of light elements to predict that large amounts of energy could be released by fusing small nuclei. Building upon the nuclear transmutation experiments by Ernest Rutherford, carried out several years earlier, the laboratory fusion of hydrogen isotopes was first accomplished by Mark Oliphant in 1932. During the remainder of that decade the steps of the main cycle of nuclear fusion in stars were worked out by Hans Bethe. Research into fusion for military purposes began in the early 1940s as part of the Manhattan Project. Fusion was accomplished in 1951 with the Greenhouse Item nuclear test. Nuclear fusion on a large scale in an explosion was first carried out on November 1, 1952, in the Ivy Mike hydrogen bomb test.Research into developing controlled thermonuclear fusion for civil purposes also began in earnest in the 1950s, and it continues to this day. The present article is about the theory of fusion. For details of the quest for controlled fusion and its history, see the article Fusion power.








![Review 2 key - Home [www.petoskeyschools.org]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000860497_1-e3bea510ba504d09bc42d6f5e4936390-300x300.png)