dx cx dx and x - Cameron University
... 5.2 State the differences at the molecular level between an ideal gas and a van der Waals gas 5.3 Define and apply the terms thermal expansivity and isothermal compressibility 6.1 Evaluate definite integrals such as: ...
... 5.2 State the differences at the molecular level between an ideal gas and a van der Waals gas 5.3 Define and apply the terms thermal expansivity and isothermal compressibility 6.1 Evaluate definite integrals such as: ...
315.pdf
... the broad maximum in resistivity, such as that Coqblin, observed in CePdSb at 150 K, is associated with the combined eff'ect of the crystalline electric fields on the localized 4f moments and Kondo-type interaction. This theory also predicts different ln(T) regions (or different Kondo temperatures) ...
... the broad maximum in resistivity, such as that Coqblin, observed in CePdSb at 150 K, is associated with the combined eff'ect of the crystalline electric fields on the localized 4f moments and Kondo-type interaction. This theory also predicts different ln(T) regions (or different Kondo temperatures) ...
Foam Drainage: Microscale Flow in an Ideal Isolated System
... leading to more tailored foam control ...
... leading to more tailored foam control ...
on Plasma-Wall Interactions
... breakdown/arc voltage. - Plasma can support sufficiently large arc current to form the spot, for example, by evaporating of wall materials or producing thermionic or field emission. • Unipolar arcs also occur when walls are made from micro-engineered material with complex surface architecture. They ...
... breakdown/arc voltage. - Plasma can support sufficiently large arc current to form the spot, for example, by evaporating of wall materials or producing thermionic or field emission. • Unipolar arcs also occur when walls are made from micro-engineered material with complex surface architecture. They ...
Heat flow direction
... Though we all have a feel for temperature (‘like when we are feeling hot’); in the context of TD temperature is technical term with ‘deep meaning’. As we know (from a commons sense perspective) that temperature is a measure of the ‘intensity of heat’. ‘Heat flows’ (energy is transferred as heat) ...
... Though we all have a feel for temperature (‘like when we are feeling hot’); in the context of TD temperature is technical term with ‘deep meaning’. As we know (from a commons sense perspective) that temperature is a measure of the ‘intensity of heat’. ‘Heat flows’ (energy is transferred as heat) ...
Basics of Thermodynamics
... Though we all have a feel for temperature (‘like when we are feeling hot’); in the context of TD temperature is technical term with ‘deep meaning’. As we know (from a commons sense perspective) that temperature is a measure of the ‘intensity of heat’. ‘Heat flows’ (energy is transferred as heat) ...
... Though we all have a feel for temperature (‘like when we are feeling hot’); in the context of TD temperature is technical term with ‘deep meaning’. As we know (from a commons sense perspective) that temperature is a measure of the ‘intensity of heat’. ‘Heat flows’ (energy is transferred as heat) ...
Nanogel Nanosecond Photonic Crystal Optical Switching
... photonic crystals possess one-dimensional periodic modulations in their optical dielectric constant.1 This creates a diffracting structure that prevents transmission of light meeting the Bragg condition. These devices can be used as optical filters. High rejection efficiencies occur for thin films o ...
... photonic crystals possess one-dimensional periodic modulations in their optical dielectric constant.1 This creates a diffracting structure that prevents transmission of light meeting the Bragg condition. These devices can be used as optical filters. High rejection efficiencies occur for thin films o ...
Particle-in-Cell Plasma Simulation Model: Properties and Applications δ f R. D. Sydora
... system when the initial condition is chosen sufficiently close to F(v). Linear theory, however, does not account for particle trapping effects and the long-time behavior of Landau damping leads to a removal of the decay. In fact, recent numerical simulations of the 1D Vlasov-Poisson system indicate ...
... system when the initial condition is chosen sufficiently close to F(v). Linear theory, however, does not account for particle trapping effects and the long-time behavior of Landau damping leads to a removal of the decay. In fact, recent numerical simulations of the 1D Vlasov-Poisson system indicate ...
Inorganic Physical Methods
... these can be tuned over a wide range of frequencies are available, so spectra are commonly recorded using a broad-band source, whose output contains all frequencies of interest. The problem then becomes how to separate out the information about intensities at each frequency from the overall transmis ...
... these can be tuned over a wide range of frequencies are available, so spectra are commonly recorded using a broad-band source, whose output contains all frequencies of interest. The problem then becomes how to separate out the information about intensities at each frequency from the overall transmis ...
Temperature gradients due to adiabatic plasma
... As the ions get accelerated through the diverging section of the magnetic nozzle their density decreases which the electrons must match to maintain quasineutrality. But the electron pressure gradient must continue to balance the electric field which requires the electron temperature to decrease as w ...
... As the ions get accelerated through the diverging section of the magnetic nozzle their density decreases which the electrons must match to maintain quasineutrality. But the electron pressure gradient must continue to balance the electric field which requires the electron temperature to decrease as w ...
Chapter 3: Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter
... Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different masses. Isotopes will have the same number of protons and electrons, but will differ in the number of neutrons. Tin has the most isotopes (10) For example, Hydrogen has 3 isotopes: ...
... Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different masses. Isotopes will have the same number of protons and electrons, but will differ in the number of neutrons. Tin has the most isotopes (10) For example, Hydrogen has 3 isotopes: ...
Chapter 3: Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter
... Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different masses. Isotopes will have the same number of protons and electrons, but will differ in the number of neutrons. Tin has the most isotopes (10) For example, Hydrogen has 3 isotopes: ...
... Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different masses. Isotopes will have the same number of protons and electrons, but will differ in the number of neutrons. Tin has the most isotopes (10) For example, Hydrogen has 3 isotopes: ...
Theory for an order-driven disruption of the liquid state in water
... seeming contradiction to this result, another study that simulated a range of similar systems has reported a less surprising electrostrictive increase in particle density upon application of the field 关Bratko et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129, 2504 共2007兲兴. In this work, we attempt to reconcile these co ...
... seeming contradiction to this result, another study that simulated a range of similar systems has reported a less surprising electrostrictive increase in particle density upon application of the field 关Bratko et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129, 2504 共2007兲兴. In this work, we attempt to reconcile these co ...
QUANTUM SPIN GLASSES Heiko Rieger and A. Peter Young
... even finite temperature properties are characterized by strong crossover effects between a quantum critical and classical regions. Thus the properties of such zero temperature transitions become experimentally accessible, which motivates the study these new universality classes. The prominent featur ...
... even finite temperature properties are characterized by strong crossover effects between a quantum critical and classical regions. Thus the properties of such zero temperature transitions become experimentally accessible, which motivates the study these new universality classes. The prominent featur ...
Simulations of Si and SiO2 Etching in SF6+O2 Plasma
... SF6 to 1.0 at 50% O2 content in the feed, and the number of oxygen atoms per silicon increases from 0 for pure SF6 to 1.7 at 50% O2 . The thickness of the SiOx Fy layer monotonically increases with the increase of O2 content in the feed. At the trench bottom the SiOx Fy layer is very thin due to int ...
... SF6 to 1.0 at 50% O2 content in the feed, and the number of oxygen atoms per silicon increases from 0 for pure SF6 to 1.7 at 50% O2 . The thickness of the SiOx Fy layer monotonically increases with the increase of O2 content in the feed. At the trench bottom the SiOx Fy layer is very thin due to int ...
Document
... The discharge formation time () has been obtained as a function of the gas pressure. • The normalization Eeff p vs. pτ predicted by the simple theory holds only at very high pressures. • At low pressures, the discharge formation time is independent of Erf0 and . ...
... The discharge formation time () has been obtained as a function of the gas pressure. • The normalization Eeff p vs. pτ predicted by the simple theory holds only at very high pressures. • At low pressures, the discharge formation time is independent of Erf0 and . ...
State of matter

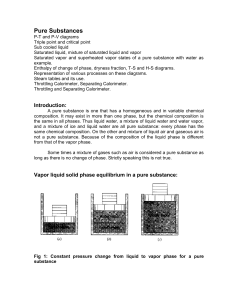
In physics, a state of matter is one of the distinct forms that matter takes on. Four states of matter are observable in everyday life: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. Many other states are known, such as Bose–Einstein condensates and neutron-degenerate matter, but these only occur in extreme situations such as ultra cold or ultra dense matter. Other states, such as quark–gluon plasmas, are believed to be possible but remain theoretical for now. For a complete list of all exotic states of matter, see the list of states of matter.Historically, the distinction is made based on qualitative differences in properties. Matter in the solid state maintains a fixed volume and shape, with component particles (atoms, molecules or ions) close together and fixed into place. Matter in the liquid state maintains a fixed volume, but has a variable shape that adapts to fit its container. Its particles are still close together but move freely. Matter in the gaseous state has both variable volume and shape, adapting both to fit its container. Its particles are neither close together nor fixed in place. Matter in the plasma state has variable volume and shape, but as well as neutral atoms, it contains a significant number of ions and electrons, both of which can move around freely. Plasma is the most common form of visible matter in the universe.The term phase is sometimes used as a synonym for state of matter, but a system can contain several immiscible phases of the same state of matter (see Phase (matter) for more discussion of the difference between the two terms).