Brain(annotated)
... In addition to tool-making (which is an intelligent, learned behavior, not extinctive), birds have displayed many other intelligent behaviors. Some parrots have learned to use (very simple) language, that is to say, they use words in context and in simple phrases (not mere mimicry). Birds lack a co ...
... In addition to tool-making (which is an intelligent, learned behavior, not extinctive), birds have displayed many other intelligent behaviors. Some parrots have learned to use (very simple) language, that is to say, they use words in context and in simple phrases (not mere mimicry). Birds lack a co ...
* Certain neurons in the brain have receptors (opioid receptors) for
... and withdrawal symptoms are no longer evident. • Drugs that lead to dependence act on the “pleasure circuit” in the brain called the VTA, nucleus accumbens and prefrontal cortex. ...
... and withdrawal symptoms are no longer evident. • Drugs that lead to dependence act on the “pleasure circuit” in the brain called the VTA, nucleus accumbens and prefrontal cortex. ...
48 - Groupfusion.net
... 4) The vesicles release neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft 5)The neurotransmitter binds to the receptor portion of ligand-gated ion channels in the postsynaptic membrane, opening the channels. In the synapse illustrated here, both Na+ and K+ can diffuse through the channels 6) The neurotransmi ...
... 4) The vesicles release neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft 5)The neurotransmitter binds to the receptor portion of ligand-gated ion channels in the postsynaptic membrane, opening the channels. In the synapse illustrated here, both Na+ and K+ can diffuse through the channels 6) The neurotransmi ...
2014 chemical signal..
... post-synaptic cell, glutamate receptors, such as the NMDA receptor, bind glutamate and are activated. - (NMDA (N-methyl D-aspartate) Calcium flux through NMDARs is thought to play a critical role in synaptic plasticity, a cellular mechanism for learning and memory. ...
... post-synaptic cell, glutamate receptors, such as the NMDA receptor, bind glutamate and are activated. - (NMDA (N-methyl D-aspartate) Calcium flux through NMDARs is thought to play a critical role in synaptic plasticity, a cellular mechanism for learning and memory. ...
electrochemical impulse
... threshold level before the signal will be sent. This threshold is important for it prevents small changes that don’t have an effect from sending a signal to the brain. Without the threshold, the sensory neurons would send signals continuously which would overwhelm the brain. • Once the threshold lev ...
... threshold level before the signal will be sent. This threshold is important for it prevents small changes that don’t have an effect from sending a signal to the brain. Without the threshold, the sensory neurons would send signals continuously which would overwhelm the brain. • Once the threshold lev ...
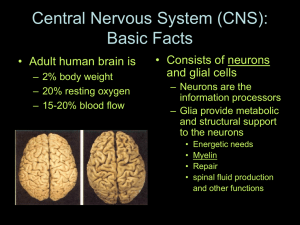
Central Nervous System (CNS): Basic Facts
... Central Nervous System (CNS): Basic Facts • Adult human brain is – 2% body weight – 20% resting oxygen – 15-20% blood flow ...
... Central Nervous System (CNS): Basic Facts • Adult human brain is – 2% body weight – 20% resting oxygen – 15-20% blood flow ...
File
... Presynaptic neuron- sends signal Postsynaptic neuron- receives signal How does this happen? The arrival of an action potential at an axon’s terminal triggers the release of NEUROTRANSMITTERS- chemicals that transmit information from one neuron to another Collected together in little sacks ...
... Presynaptic neuron- sends signal Postsynaptic neuron- receives signal How does this happen? The arrival of an action potential at an axon’s terminal triggers the release of NEUROTRANSMITTERS- chemicals that transmit information from one neuron to another Collected together in little sacks ...
The Nervous System
... Key Concepts and Important Terms • Nervous systems function in sensory input, integration, and motor output. • The nervous system is composed of neurons and supporting cells. • Membrane potentials arise from differences in ion concentrations between a cell’s contents and the extracellular fluid. • ...
... Key Concepts and Important Terms • Nervous systems function in sensory input, integration, and motor output. • The nervous system is composed of neurons and supporting cells. • Membrane potentials arise from differences in ion concentrations between a cell’s contents and the extracellular fluid. • ...
Chapter 9: Nervous System guide—Please complete these notes on
... 6. Action potential that results causes a bioelectric current that stimulates adjacent portions of membrane 7. Wave of action potentials travels axon as nerve impulse ...
... 6. Action potential that results causes a bioelectric current that stimulates adjacent portions of membrane 7. Wave of action potentials travels axon as nerve impulse ...
7. Describe what membrane potential is, and how
... - occur when excitatory synapses release a neurotransmitter that opens gated channels allowing Na+ to enter the cell and K+ to leave (depolarization) • IPSP inhibitory postsynaptic potentials - occur when neurotransmitters released from inhibitory synapses bind to receptors that open ion gates, wh ...
... - occur when excitatory synapses release a neurotransmitter that opens gated channels allowing Na+ to enter the cell and K+ to leave (depolarization) • IPSP inhibitory postsynaptic potentials - occur when neurotransmitters released from inhibitory synapses bind to receptors that open ion gates, wh ...
Physiology 1B
... The point of contact at which impulses are passed from one cell to another are known as Synapse ...
... The point of contact at which impulses are passed from one cell to another are known as Synapse ...
Migraine Visual Aura
... The pain of migraine headache is thought to have a neurogenic basis. Migraine involves dysfunction of brain-stem pathways that normally modulate sensory input. The key pathways for the pain are the trigeminovascular input from the meningeal vessels, which passes through the trigeminal ganglion and s ...
... The pain of migraine headache is thought to have a neurogenic basis. Migraine involves dysfunction of brain-stem pathways that normally modulate sensory input. The key pathways for the pain are the trigeminovascular input from the meningeal vessels, which passes through the trigeminal ganglion and s ...
Neurons - Holterman
... 4. The sodium-potassium pump pushes 3 Na and 2 K against their concentration gradients using 1 ATP. It restores and maintains the resting potential by pushing more Na out of neuron and pushing more K into neuron. (But overall, it pushes more positive charges out of the cell than it brings in.) 5. T ...
... 4. The sodium-potassium pump pushes 3 Na and 2 K against their concentration gradients using 1 ATP. It restores and maintains the resting potential by pushing more Na out of neuron and pushing more K into neuron. (But overall, it pushes more positive charges out of the cell than it brings in.) 5. T ...
The Nervous System
... The Spinal Cord and Reflexes (simple, automatic response to sensory stimuli) ...
... The Spinal Cord and Reflexes (simple, automatic response to sensory stimuli) ...
Unit 3 - Mayfield City Schools
... -stimulate the firing of messages vs. slowing the transmission of neural messages -gap between the terminal buttons of one neuron and the dendrites of another neuron -location of neurotransmitter entry -released by terminal buttons -chemical messengers -bind the receptors on subsequent dendrites -ca ...
... -stimulate the firing of messages vs. slowing the transmission of neural messages -gap between the terminal buttons of one neuron and the dendrites of another neuron -location of neurotransmitter entry -released by terminal buttons -chemical messengers -bind the receptors on subsequent dendrites -ca ...
Neurons and Neurotransmitters
... neurotransmitters are either Agonists or Antagonists. There are currently at least 50 identified neurotransmitters. Agonists – increase the effects of a neurotransmitter, makes more of it, or stops the minimizing of it Antagonist – slows down neurotransmitters either because they destroy or inhibit ...
... neurotransmitters are either Agonists or Antagonists. There are currently at least 50 identified neurotransmitters. Agonists – increase the effects of a neurotransmitter, makes more of it, or stops the minimizing of it Antagonist – slows down neurotransmitters either because they destroy or inhibit ...
No Slide Title
... reflex may not be produced, however if several small pinches are rapidly applied they trigger a reflex. This is called temporal summation. ...
... reflex may not be produced, however if several small pinches are rapidly applied they trigger a reflex. This is called temporal summation. ...
The nervous system - Sonoma Valley High School
... Action potential - When an impulse is sent the charge reverses inside the cell – it becomes positive Threshold – the amount of stimulus required to activate the neuron ...
... Action potential - When an impulse is sent the charge reverses inside the cell – it becomes positive Threshold – the amount of stimulus required to activate the neuron ...
neuron
... • If enough kids go from sad to happy when the beautiful air whooshes in, they have reached the “threshold.” If/when this threshold is reached, they start getting rambunctious ("action potential"). • After having wasted their energy being rambunctious, there's a short time ("refractory period") befo ...
... • If enough kids go from sad to happy when the beautiful air whooshes in, they have reached the “threshold.” If/when this threshold is reached, they start getting rambunctious ("action potential"). • After having wasted their energy being rambunctious, there's a short time ("refractory period") befo ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.