The effect of neural synchronization on information transmission
... nonlinear Poisson (LNP) cascade. The LNP neurons were tuned to 16 orientations and projected nonspecifically to 20% of the neurons in the receiver layer. We assumed that the stimulus was a sequence of drifting gratings with random orientations. In response to stimuli, the network displayed transient ...
... nonlinear Poisson (LNP) cascade. The LNP neurons were tuned to 16 orientations and projected nonspecifically to 20% of the neurons in the receiver layer. We assumed that the stimulus was a sequence of drifting gratings with random orientations. In response to stimuli, the network displayed transient ...
Cells of the Nervous System
... Neurons are specialized cells for the reception, conduction, and transmission of electrochemical signals Many sizes and shapes ~100 billion neurons ...
... Neurons are specialized cells for the reception, conduction, and transmission of electrochemical signals Many sizes and shapes ~100 billion neurons ...
Document
... – events are reproduced at different points along the axon membrane positive charges can depolarize the next region of the membrane to threshold ...
... – events are reproduced at different points along the axon membrane positive charges can depolarize the next region of the membrane to threshold ...
- Describe the roles of the different types of glial cells
... after it has been released and facilitate its quick removal from the synapse. This is important as NT concentrations can rise from nM to mM following an AP and some NTs like glutamate can cause excitotoxicity and need to be quickly removed. Some rely on conc gradients of other substances. Family 1 t ...
... after it has been released and facilitate its quick removal from the synapse. This is important as NT concentrations can rise from nM to mM following an AP and some NTs like glutamate can cause excitotoxicity and need to be quickly removed. Some rely on conc gradients of other substances. Family 1 t ...
Neuron Labeling WS
... The long fiber that carries the nerve impulses. A bundle of axons. The connection between adjacent neurons. The chemical secreted into the gap between neurons at a synapse. A rapid automatic response to a stimulus. The covering of fatty material that speeds up the passage of nerve impulses. The stru ...
... The long fiber that carries the nerve impulses. A bundle of axons. The connection between adjacent neurons. The chemical secreted into the gap between neurons at a synapse. A rapid automatic response to a stimulus. The covering of fatty material that speeds up the passage of nerve impulses. The stru ...
Biology and Behaviour 40s
... encode this information into electrochemical messages that are transmitted by sensory neurons. • Interneurons connect various neurons within the brain and spinal cord. • The simplest type of neural pathway is a monosynaptic (single connection) reflex pathway, like the knee-jerk reflex. When the doct ...
... encode this information into electrochemical messages that are transmitted by sensory neurons. • Interneurons connect various neurons within the brain and spinal cord. • The simplest type of neural pathway is a monosynaptic (single connection) reflex pathway, like the knee-jerk reflex. When the doct ...
Nociceptive system
... glucose and cuprum level in plasma, activation of hemostasis. • It considered to cause the majority of both visceral and biochemical reactions by excitation of sympathetic nervous system, which is presented by neurons of hypothalamus, hypophisis and cells in medullar substance of adrenal glands. ...
... glucose and cuprum level in plasma, activation of hemostasis. • It considered to cause the majority of both visceral and biochemical reactions by excitation of sympathetic nervous system, which is presented by neurons of hypothalamus, hypophisis and cells in medullar substance of adrenal glands. ...
Fundamentals of the Nervous System and
... Neurotransmitters mediate graded potentials on the postsynaptic cell that may be excitatory or inhibitory. ...
... Neurotransmitters mediate graded potentials on the postsynaptic cell that may be excitatory or inhibitory. ...
Slide ()
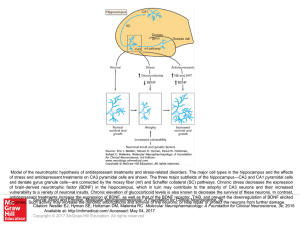
... Model of the neurotrophic hypothesis of antidepressant treatments and stress-related disorders. The major cell types in the hippocampus and the effects of stress and antidepressant treatments on CA3 pyramidal cells are shown. The three major subfields of the hippocampus—CA3 and CA1 pyramidal cells a ...
... Model of the neurotrophic hypothesis of antidepressant treatments and stress-related disorders. The major cell types in the hippocampus and the effects of stress and antidepressant treatments on CA3 pyramidal cells are shown. The three major subfields of the hippocampus—CA3 and CA1 pyramidal cells a ...
Nervous tissue is composed of two types of cells, neurons and glial
... glia, are known to play a supporting role for nervous tissue. Ongoing research pursues an expanded role that glial cells might play in signaling, but neurons are still considered the basis of this function. Neurons are important, but without glial support they would not be able to perform their func ...
... glia, are known to play a supporting role for nervous tissue. Ongoing research pursues an expanded role that glial cells might play in signaling, but neurons are still considered the basis of this function. Neurons are important, but without glial support they would not be able to perform their func ...
File
... synapses to make it more efficient During adolescence your brain has a major tidy-up and gets rid of lots of ...
... synapses to make it more efficient During adolescence your brain has a major tidy-up and gets rid of lots of ...
The Nervous System
... -Original stimulation must be above threshold level in order for an impulse to be started (all or nothing) Transmission of impulses between neurons -Communication between cells occurs at synapses (gap between axon and neighboring dendrite) -Pre-synaptic cells contain synaptic vesicles which contain ...
... -Original stimulation must be above threshold level in order for an impulse to be started (all or nothing) Transmission of impulses between neurons -Communication between cells occurs at synapses (gap between axon and neighboring dendrite) -Pre-synaptic cells contain synaptic vesicles which contain ...
The Biology of Mind Chapter 2 PowerPoint
... other neurons, muscles, or glands? ANSWER A. B. C. D. ...
... other neurons, muscles, or glands? ANSWER A. B. C. D. ...
CHAPTER 4 STRUCTURE AND CELL BIOLOGY OF THE NEURON
... The cell body contains the nucleus and other organelles. It is the maintenance center of the neuron. It contains the cell's genetic material as well as the molecular machinery for synthesizing different chemical substances used for information transfer to other neurons, for maintenance and repair of ...
... The cell body contains the nucleus and other organelles. It is the maintenance center of the neuron. It contains the cell's genetic material as well as the molecular machinery for synthesizing different chemical substances used for information transfer to other neurons, for maintenance and repair of ...
Chapter 13: The Nervous System
... The synapse is a small space between neurons or between neurons and effectors. This space contains small vesicles containing transmitter chemicals. Chemicals are released from end plates as nerve impulses move along the axon. Transmitter chemicals are released from presynaptic neuron and diff ...
... The synapse is a small space between neurons or between neurons and effectors. This space contains small vesicles containing transmitter chemicals. Chemicals are released from end plates as nerve impulses move along the axon. Transmitter chemicals are released from presynaptic neuron and diff ...
brainbeebootcamp 2017
... Dendrite – receives input Soma (cell body) – cell organelles Axon – conducts electrical impulse (action potential) Myelin: “insulation” for axon Node of Ranvier = gap in myelin Nerve terminal – contains neurotransmitter vesicles Synapse – communication with next neuron ...
... Dendrite – receives input Soma (cell body) – cell organelles Axon – conducts electrical impulse (action potential) Myelin: “insulation” for axon Node of Ranvier = gap in myelin Nerve terminal – contains neurotransmitter vesicles Synapse – communication with next neuron ...
Chapter 03: Neuroscience and behaviour PowerPoint
... – Emotional functions of the frontal lobes – He lived after the accident, but with unfortunate changes to personality ...
... – Emotional functions of the frontal lobes – He lived after the accident, but with unfortunate changes to personality ...
General design of the nervous system
... The somatic nervous system includes all nerves controlling the muscular system and external sensory receptors. External sense organs (including skin) are receptors. Muscle fibers and gland cells are effectors (since they prerform the functions dictated by the nerve signals). The autonomous nervous s ...
... The somatic nervous system includes all nerves controlling the muscular system and external sensory receptors. External sense organs (including skin) are receptors. Muscle fibers and gland cells are effectors (since they prerform the functions dictated by the nerve signals). The autonomous nervous s ...
COMPUTATIONAL INTELLIGENCE Medical Diagnostic Systems
... impulses originate in the cell body, and are propagated along the axon, which may have one or more branches. This axon, which is folded for diagrammatic purposes, would be a centimeter long at actual size. Some axons are more than a meter long. The axon’s terminal branches form synapses with as many ...
... impulses originate in the cell body, and are propagated along the axon, which may have one or more branches. This axon, which is folded for diagrammatic purposes, would be a centimeter long at actual size. Some axons are more than a meter long. The axon’s terminal branches form synapses with as many ...
Nervous System Introduction
... • - cell winds around axon, inside its own layers, piling up layers of lipid/protein cell membranes • - one Schwann cell associates with and myelinates a segment of only one axon • - Schwann cell, myelin, axon are all surrounded by a basement membrane (covers whole unit) • - help to buffer excess ex ...
... • - cell winds around axon, inside its own layers, piling up layers of lipid/protein cell membranes • - one Schwann cell associates with and myelinates a segment of only one axon • - Schwann cell, myelin, axon are all surrounded by a basement membrane (covers whole unit) • - help to buffer excess ex ...
Introduction to the Nervous System Guided Notes are masses of
... (2) _____________ neurons - Efferent neurons that make up efferent component of the PNS; carry instructions from the CNS to the peripheral effectors. (1) ________________ motor neurons – innervate skeletal muscle (conscious control – Somatic Nervous System) (2) _____________ motor neurons – innervat ...
... (2) _____________ neurons - Efferent neurons that make up efferent component of the PNS; carry instructions from the CNS to the peripheral effectors. (1) ________________ motor neurons – innervate skeletal muscle (conscious control – Somatic Nervous System) (2) _____________ motor neurons – innervat ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.