Part 1: True/False
... C. Waking up in the middle of the night and writing unintelligible notes to himself D. Showing that 'stuff' dripping from the vagus nerve slows down the heart <––– E. Showing that heartbeat is controlled by vagus nerve 15. Neuropeptide Y is a peptide neurotransmitter. What can you say about this pep ...
... C. Waking up in the middle of the night and writing unintelligible notes to himself D. Showing that 'stuff' dripping from the vagus nerve slows down the heart <––– E. Showing that heartbeat is controlled by vagus nerve 15. Neuropeptide Y is a peptide neurotransmitter. What can you say about this pep ...
ppt
... • Action potentials can be divided into three phases: the resting or polarized state, depolarization, and ...
... • Action potentials can be divided into three phases: the resting or polarized state, depolarization, and ...
Instructor`s Answer Key
... 5. Damage to Broca’s area of the cortex produces speech difficulty without causing impairment in verbal comprehension (Broca’s aphasia). This evidence suggests that Broca’s area is involved in the motor control of speech. Damage to Wernicke’s area impairs language understanding, but not motor abili ...
... 5. Damage to Broca’s area of the cortex produces speech difficulty without causing impairment in verbal comprehension (Broca’s aphasia). This evidence suggests that Broca’s area is involved in the motor control of speech. Damage to Wernicke’s area impairs language understanding, but not motor abili ...
Slide 1
... because certain ions can cross at certain times but there is not a free exchange The opening and closing of specific ion channels can be controlled by chemical signals including neurotransmitter ...
... because certain ions can cross at certain times but there is not a free exchange The opening and closing of specific ion channels can be controlled by chemical signals including neurotransmitter ...
biology lecture notes chapter 2
... Ultimately, these can have several effects, one of which might be to increase many ion channels. 5. POSTSYNAPTIC POTENTIAL (PSP): (+) or (-) electrical charges move into the postsynaptic neuron, causing either: Womble AP Psychology Page 6 ...
... Ultimately, these can have several effects, one of which might be to increase many ion channels. 5. POSTSYNAPTIC POTENTIAL (PSP): (+) or (-) electrical charges move into the postsynaptic neuron, causing either: Womble AP Psychology Page 6 ...
consciousness
... by proposing that the division of labour is determined by the use to which visual information is to be put, once it has reached the striate cortex. They suggest that a ventral stream, terminating in the inferotemporal cortex, is involved in maintaining an enduring, viewpoint-independent, representat ...
... by proposing that the division of labour is determined by the use to which visual information is to be put, once it has reached the striate cortex. They suggest that a ventral stream, terminating in the inferotemporal cortex, is involved in maintaining an enduring, viewpoint-independent, representat ...
Unit Outline_Ch17 - Westgate Mennonite Collegiate
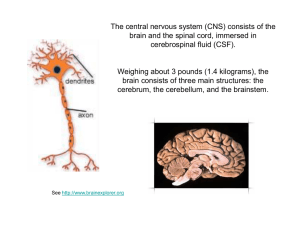
... The spinal cord and the brain make up the central nervous system (CNS). The Spinal Cord The spinal cord extends from the base of the brain through a large opening in the skull and into the vertebral canal. Structure of the Spinal Cord The spinal nerves project from the cord between the vertebrae. Fl ...
... The spinal cord and the brain make up the central nervous system (CNS). The Spinal Cord The spinal cord extends from the base of the brain through a large opening in the skull and into the vertebral canal. Structure of the Spinal Cord The spinal nerves project from the cord between the vertebrae. Fl ...
Slide ()
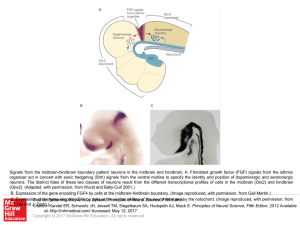
... Signals from the midbrain-hindbrain boundary pattern neurons in the midbrain and hindbrain. A. Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) signals from the isthmic organizer act in concert with sonic hedgehog (Shh) signals from the ventral midline to specify the identity and position of dopaminergic and serotone ...
... Signals from the midbrain-hindbrain boundary pattern neurons in the midbrain and hindbrain. A. Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) signals from the isthmic organizer act in concert with sonic hedgehog (Shh) signals from the ventral midline to specify the identity and position of dopaminergic and serotone ...
Spinal Cord and Reflex Act
... Label the following parts of a spinal cord on the cross-section diagram. a. white matter b. grey matter c. dorsal root ganglion d. nerve fibers e. interneuron f. synapse g. sensory neuron h. motor neuron ...
... Label the following parts of a spinal cord on the cross-section diagram. a. white matter b. grey matter c. dorsal root ganglion d. nerve fibers e. interneuron f. synapse g. sensory neuron h. motor neuron ...
Specific and Nonspecific Plasticity of the Primary
... • The BF shift was generally based on a decrease in response (inhibition) at the BF of the cortical neuron in the control condition and an increase in response (facilitation) at the BF of the stimulated thalamic neuron. Such a BF shift is also elicited by auditory fear conditioning, and has been kn ...
... • The BF shift was generally based on a decrease in response (inhibition) at the BF of the cortical neuron in the control condition and an increase in response (facilitation) at the BF of the stimulated thalamic neuron. Such a BF shift is also elicited by auditory fear conditioning, and has been kn ...
Chapter 13
... neuron produces a change in membrane potential such that the potential becomes more negative than the resting membrane, this is referred to as ________________ ...
... neuron produces a change in membrane potential such that the potential becomes more negative than the resting membrane, this is referred to as ________________ ...
neural spike
... A neuronal network inspired by the anatomy of the cerebral cortex was simulated to study the self-organization of spiking neurons into neuronal groups. The network consisted of 100 000 reentrantly interconnected neurons exhibiting known types of cortical firing patterns, receptor kinetics, short-ter ...
... A neuronal network inspired by the anatomy of the cerebral cortex was simulated to study the self-organization of spiking neurons into neuronal groups. The network consisted of 100 000 reentrantly interconnected neurons exhibiting known types of cortical firing patterns, receptor kinetics, short-ter ...
Nervous System I - Laurel County Schools
... Unipolor- Cell body with a single process that divides into two branches and functions as an axon.(cell body in ganglion outside the brain or spinal cord) Multipolar- Cell body with many processes, one of which is an axon, the rest dendrites.( Most common type of neuron in the brain and spinal c ...
... Unipolor- Cell body with a single process that divides into two branches and functions as an axon.(cell body in ganglion outside the brain or spinal cord) Multipolar- Cell body with many processes, one of which is an axon, the rest dendrites.( Most common type of neuron in the brain and spinal c ...
Nervous System I - Laurel County Schools
... Unipolor- Cell body with a single process that divides into two branches and functions as an axon.(cell body in ganglion outside the brain or spinal cord) Multipolar- Cell body with many processes, one of which is an axon, the rest dendrites.( Most common type of neuron in the brain and spinal c ...
... Unipolor- Cell body with a single process that divides into two branches and functions as an axon.(cell body in ganglion outside the brain or spinal cord) Multipolar- Cell body with many processes, one of which is an axon, the rest dendrites.( Most common type of neuron in the brain and spinal c ...
The Nervous System
... the nerves which are strings of long, thin cells called NEURONS O Neurons can fire over and over again, hundreds of times a minute O The neuron “fires” on an all-or-nothing principle – must be completely stimulated in order to send messages ...
... the nerves which are strings of long, thin cells called NEURONS O Neurons can fire over and over again, hundreds of times a minute O The neuron “fires” on an all-or-nothing principle – must be completely stimulated in order to send messages ...
Stochastic fluctuations of the synaptic function
... The response of single excitatory synapses in hippocampal neurons to a quantal release of neurotransmitters shows a large variability. In a recent paper, Liu et al., 1999, reported that the stimulation of putative single synaptic boutons of hippocampal neurons at excitatory synapses produced quantal ...
... The response of single excitatory synapses in hippocampal neurons to a quantal release of neurotransmitters shows a large variability. In a recent paper, Liu et al., 1999, reported that the stimulation of putative single synaptic boutons of hippocampal neurons at excitatory synapses produced quantal ...
1. Receptor cells
... against which incoming data are compared and interpreted. - General knowledge of the world in the form of schemas also shape our expectations and hence our knowledge. - Example: How quickly people process the information in photos with a real world scenes as a city street or a kitchen. When people v ...
... against which incoming data are compared and interpreted. - General knowledge of the world in the form of schemas also shape our expectations and hence our knowledge. - Example: How quickly people process the information in photos with a real world scenes as a city street or a kitchen. When people v ...
The Biology of Mind take
... ones, so when gates or “channels” on the neuron’s membrane open positive ions rush in. •This electrochemical process is called “depolarization.” •When a wave of depolarization moves down the axon, it is called an “action potential.” •Myelin is an insulating sheath that covers the axon and speeds up ...
... ones, so when gates or “channels” on the neuron’s membrane open positive ions rush in. •This electrochemical process is called “depolarization.” •When a wave of depolarization moves down the axon, it is called an “action potential.” •Myelin is an insulating sheath that covers the axon and speeds up ...
The Biology of Mind take 2
... ones, so when gates or “channels” on the neuron’s membrane open positive ions rush in. •This electrochemical process is called “depolarization.” •When a wave of depolarization moves down the axon, it is called an “action potential.” •Myelin is an insulating sheath that covers the axon and speeds up ...
... ones, so when gates or “channels” on the neuron’s membrane open positive ions rush in. •This electrochemical process is called “depolarization.” •When a wave of depolarization moves down the axon, it is called an “action potential.” •Myelin is an insulating sheath that covers the axon and speeds up ...
Primary visual cortex
... (a) Shows selective adaptation to a frequency of 7 cycles/degree. There is a dip in the contrast sensitivity function at that spatial frequency ...
... (a) Shows selective adaptation to a frequency of 7 cycles/degree. There is a dip in the contrast sensitivity function at that spatial frequency ...
Nerve Flash Cards
... signals for muscle contraction, etc. What characteristics do all neurons share? They all share certain characteristics. They have longevity (can last a lifetime), they have a high metabolic rate, they cannot divide to reproduce, and they cannot survive without oxygen. ...
... signals for muscle contraction, etc. What characteristics do all neurons share? They all share certain characteristics. They have longevity (can last a lifetime), they have a high metabolic rate, they cannot divide to reproduce, and they cannot survive without oxygen. ...
JARINGAN SYARAF TIRUAN
... series of brief electrical pulses (i.e. spikes or action potentials). 2. The neuron’s cell body (soma) processes the incoming activations and converts them into output activations. 3. The neuron’s nucleus contains the genetic material in the form of DNA. This exists in most types of cells, not just ...
... series of brief electrical pulses (i.e. spikes or action potentials). 2. The neuron’s cell body (soma) processes the incoming activations and converts them into output activations. 3. The neuron’s nucleus contains the genetic material in the form of DNA. This exists in most types of cells, not just ...
Biology and Behavior note frame
... a. The “_______________ _______________” during which a neuron, after firing, cannot _______________ another _______________ _______________ b. Once the refractory period is complete the neuron can _______________ _______________ 3. Resting Potential a. The state of a neuron when it is at _________ ...
... a. The “_______________ _______________” during which a neuron, after firing, cannot _______________ another _______________ _______________ b. Once the refractory period is complete the neuron can _______________ _______________ 3. Resting Potential a. The state of a neuron when it is at _________ ...
Clinical Day
... • Changes in substantia nigra and basal ganglia • Too little dopamine produced (neurotransmitter) • Too much acetylcholine produced ...
... • Changes in substantia nigra and basal ganglia • Too little dopamine produced (neurotransmitter) • Too much acetylcholine produced ...
Circuits, Circuits
... On-Center -vs- Off-Center Retinal Ganglion Cells • The primary visual receptors (rods & cones) actually turn OFF when hit by photons (light) and are ON when they detect dark spots (Hubel, Eye, Brain and Vision, 1988, pg. 54) On-Center (Off-Surround) ...
... On-Center -vs- Off-Center Retinal Ganglion Cells • The primary visual receptors (rods & cones) actually turn OFF when hit by photons (light) and are ON when they detect dark spots (Hubel, Eye, Brain and Vision, 1988, pg. 54) On-Center (Off-Surround) ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.