Auditory Aerobics
... patterns of stimulation, to cause desirable and specific changes in the neural connections of the brain, specifically within the auditory processing system. Such stimulation is able to force the brain to create new neural pathways and ...
... patterns of stimulation, to cause desirable and specific changes in the neural connections of the brain, specifically within the auditory processing system. Such stimulation is able to force the brain to create new neural pathways and ...
Special Senses
... 4. Neurons carrying equilibrium travel through the vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII). The information will be sent to vestibular nuclei between the pons and medulla and to the cerebellum. With information about equilibrium, vision and proprioception, appropriate motor outputs to maintain balance can b ...
... 4. Neurons carrying equilibrium travel through the vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII). The information will be sent to vestibular nuclei between the pons and medulla and to the cerebellum. With information about equilibrium, vision and proprioception, appropriate motor outputs to maintain balance can b ...
Neuroembryology
... – How do neurons segregate themselves into functionally distinct, appropriately sized, and appropriately interconnected populations? – What is the relationship between structure & function and how is the match between the two achieved? ...
... – How do neurons segregate themselves into functionally distinct, appropriately sized, and appropriately interconnected populations? – What is the relationship between structure & function and how is the match between the two achieved? ...
Chapter 2 Power Point: The Biological Perspective
... firing a neural impulse. • Action potential - the release of the neural impulse consisting of a reversal of the electrical charge within the axon. • Allows positive sodium ions to enter the cell. ...
... firing a neural impulse. • Action potential - the release of the neural impulse consisting of a reversal of the electrical charge within the axon. • Allows positive sodium ions to enter the cell. ...
a Tool for Relating Neuronal Form to Function
... pair) shows that voltage spreads from the teacher to the student synapse with little attenuation, which would favor voltage-dependent associative interactions. Figure 4B shows a different CAl pyramidal cell in which the apical dendrite bifurcates shortly after arising from the soma. Two teacher syna ...
... pair) shows that voltage spreads from the teacher to the student synapse with little attenuation, which would favor voltage-dependent associative interactions. Figure 4B shows a different CAl pyramidal cell in which the apical dendrite bifurcates shortly after arising from the soma. Two teacher syna ...
Click here to get the file
... (feedback) Extrastriate visual cortical areas V3 – V5. More complex representation of visual stimulus with feedback from other cortical areas (eg. attention). ...
... (feedback) Extrastriate visual cortical areas V3 – V5. More complex representation of visual stimulus with feedback from other cortical areas (eg. attention). ...
Neural Oscillation www.AssignmentPoint.com Neural oscillation is
... and the rhythmic changes in electric potential caused by their action potentials will add up (constructive interference). That is, synchronized firing patterns result in synchronized input into other cortical areas, which gives rise to largeamplitude oscillations of the local field potential. These ...
... and the rhythmic changes in electric potential caused by their action potentials will add up (constructive interference). That is, synchronized firing patterns result in synchronized input into other cortical areas, which gives rise to largeamplitude oscillations of the local field potential. These ...
Sound frequency (pitch, tone) measured in hertz (cycles per sec)
... Many technological innovations (blinking alarms, text-phones) make this possible. Similar adaptations and cultural affiliation are not seen in the blind community. ...
... Many technological innovations (blinking alarms, text-phones) make this possible. Similar adaptations and cultural affiliation are not seen in the blind community. ...
Notes
... different perceptions. This is the broad basis of the physiological approach of studying the perceptual process. Nerves are composed of smaller structures called neurons. Neurons consist of 1. Cell Body: This contains the nucleus and other metabolic structures required to keep the cell alive. 2. Den ...
... different perceptions. This is the broad basis of the physiological approach of studying the perceptual process. Nerves are composed of smaller structures called neurons. Neurons consist of 1. Cell Body: This contains the nucleus and other metabolic structures required to keep the cell alive. 2. Den ...
ben_slides2
... emergence of novel perceptual qualities that were not present in each individual odorant ...
... emergence of novel perceptual qualities that were not present in each individual odorant ...
FIGURE LEGENDS FIGURE 34.1 Somatic and autonomic styles of
... FIGURE 34.2 Details of the organization of the SNS and its sensory inputs. In thoracic and lumbar levels of the spinal cord, preganglionic neuronal somata located in the intermediolateral cell column project through ventral roots to either paravertebral chain ganglia or prevertebral ganglia, as illu ...
... FIGURE 34.2 Details of the organization of the SNS and its sensory inputs. In thoracic and lumbar levels of the spinal cord, preganglionic neuronal somata located in the intermediolateral cell column project through ventral roots to either paravertebral chain ganglia or prevertebral ganglia, as illu ...
The Binding Problem
... Different assemblies are distinguished from one another by the independence of their firing patterns. Thus, multiple, highly salient distributed signals can coexist in the same network of cortical areas at the same time, each providing an independent representation of grouped features. Whenever conj ...
... Different assemblies are distinguished from one another by the independence of their firing patterns. Thus, multiple, highly salient distributed signals can coexist in the same network of cortical areas at the same time, each providing an independent representation of grouped features. Whenever conj ...
Design of Optoelectronic Interface Between Neuron
... imitates axon. The optoelectronic communication channel consists of light emission diode (LED), optical fiber and photodiode. Electronic neuron modulates the intensity of LED emission into the fiber and the photodiode detects the light and converts optical signal into electrical pulses that stimulat ...
... imitates axon. The optoelectronic communication channel consists of light emission diode (LED), optical fiber and photodiode. Electronic neuron modulates the intensity of LED emission into the fiber and the photodiode detects the light and converts optical signal into electrical pulses that stimulat ...
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
... Postganglionic Neurons in the Sympathetic Division • An axon may synapse with postganglionic neurons in the ganglion it first reaches or • Sympathetic chains or • An axon may continue, without synapsing, through the sympathetic trunk ganglion to end at a prevertebral ganglion and synapse with postg ...
... Postganglionic Neurons in the Sympathetic Division • An axon may synapse with postganglionic neurons in the ganglion it first reaches or • Sympathetic chains or • An axon may continue, without synapsing, through the sympathetic trunk ganglion to end at a prevertebral ganglion and synapse with postg ...
OTTO LOEWI
... idea that the transmission should be electrical, just like the propagation wave along the axon. It was actually making sense to imagine electrical synapses. Unfortunately there were three important arguments against such simple picture of the nervous system. The first is the unidirectional flow of i ...
... idea that the transmission should be electrical, just like the propagation wave along the axon. It was actually making sense to imagine electrical synapses. Unfortunately there were three important arguments against such simple picture of the nervous system. The first is the unidirectional flow of i ...
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
... Sympathetic Division • An axon may synapse with postganglionic neurons in the ganglion it first reaches or • Sympathetic chains or • An axon may continue, without synapsing, through the sympathetic trunk ganglion to end at a prevertebral ganglion and synapse with postganglionic neurons there or • An ...
... Sympathetic Division • An axon may synapse with postganglionic neurons in the ganglion it first reaches or • Sympathetic chains or • An axon may continue, without synapsing, through the sympathetic trunk ganglion to end at a prevertebral ganglion and synapse with postganglionic neurons there or • An ...
Vanderbilt neuroscientists identify “oops center” in the brain
... performed with human subjects using electroencephalograms (EEG) and fMRI, a remote sensing technique that measures levels of brain activity. Michael Coles and coworkers at the University of Illinois discovered an EEG signal that occurred when human subjects made errors. They called this the “blunder ...
... performed with human subjects using electroencephalograms (EEG) and fMRI, a remote sensing technique that measures levels of brain activity. Michael Coles and coworkers at the University of Illinois discovered an EEG signal that occurred when human subjects made errors. They called this the “blunder ...
Cortical Neurons and Circuits: A Tutorial
... The neocortex is that part of the brain which makes up the outer 2 to 4 mm of the cerebral hemispheres. It is the ‘gray matter’ of the brain lying atop the cerebral ‘white matter’ composed of myelinated axons that interconnect different regions of the brain. All the higher-level psychophysical funct ...
... The neocortex is that part of the brain which makes up the outer 2 to 4 mm of the cerebral hemispheres. It is the ‘gray matter’ of the brain lying atop the cerebral ‘white matter’ composed of myelinated axons that interconnect different regions of the brain. All the higher-level psychophysical funct ...
DeepNetUnderstand
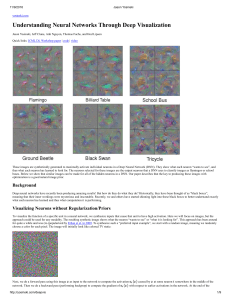
... Instead, these new, synthetic images show that discriminatively trained networks do in fact learn much more than we thought, including much about the global structure of objects. For more discussion on this issue, see the last two paragraphs of our paper. This last observation raises some interestin ...
... Instead, these new, synthetic images show that discriminatively trained networks do in fact learn much more than we thought, including much about the global structure of objects. For more discussion on this issue, see the last two paragraphs of our paper. This last observation raises some interestin ...
ch12Boundarygabor
... Neural processing responsible for vision • photoreceptors • retina – bipolar and horizontal cells – ganglion cells (optic nerve) ...
... Neural processing responsible for vision • photoreceptors • retina – bipolar and horizontal cells – ganglion cells (optic nerve) ...
Cortical Neurons and Circuits: A Tutorial
... The neocortex is that part of the brain which makes up the outer 2 to 4 mm of the cerebral hemispheres. It is the ‘gray matter’ of the brain lying atop the cerebral ‘white matter’ composed of myelinated axons that interconnect different regions of the brain. All the higher-level psychophysical funct ...
... The neocortex is that part of the brain which makes up the outer 2 to 4 mm of the cerebral hemispheres. It is the ‘gray matter’ of the brain lying atop the cerebral ‘white matter’ composed of myelinated axons that interconnect different regions of the brain. All the higher-level psychophysical funct ...
File - JMH Psychiatry Residency
... - Catecholamine hypothesis - Indoleamine hypothesis - Role of dopamine 2. Genetics - Theoretical background - Gene environment interaction - Genome wide association studies 3. Neurohormonal theories - Cortisol, CRF - Neurokinins (substance P) 4. Neuroplasticity, Neural Atrophy and Neurogenesis 5. Ps ...
... - Catecholamine hypothesis - Indoleamine hypothesis - Role of dopamine 2. Genetics - Theoretical background - Gene environment interaction - Genome wide association studies 3. Neurohormonal theories - Cortisol, CRF - Neurokinins (substance P) 4. Neuroplasticity, Neural Atrophy and Neurogenesis 5. Ps ...
Student Worksheets
... Neurons are nerve cells that are composed of three major sections, as shown in Fig. 1: the dendrites, the cell body, and the axon. These nerves cells transmit electrochemical signals to cells such as other neurons, muscles, and endocrine cells. This signal transmission is, for example, how the brain ...
... Neurons are nerve cells that are composed of three major sections, as shown in Fig. 1: the dendrites, the cell body, and the axon. These nerves cells transmit electrochemical signals to cells such as other neurons, muscles, and endocrine cells. This signal transmission is, for example, how the brain ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.