Chapter 2
... Glial Cells • Glial cells - grey fatty cells that: • Provide support for the neurons to grow • Deliver nutrients to neurons • Produce myelin to coat axons ...
... Glial Cells • Glial cells - grey fatty cells that: • Provide support for the neurons to grow • Deliver nutrients to neurons • Produce myelin to coat axons ...
Network Self-Organization Explains the Statistics and
... strengths of local excitatory connections in cortex and hippocampus is long-tailed, exhibiting a small number of synaptic connections of very large efficacy. At the same time, new synaptic connections are constantly being created and individual synaptic connection strengths show substantial fluctuat ...
... strengths of local excitatory connections in cortex and hippocampus is long-tailed, exhibiting a small number of synaptic connections of very large efficacy. At the same time, new synaptic connections are constantly being created and individual synaptic connection strengths show substantial fluctuat ...
Learning - Dot Point 2.
... • The hippocampus plays a central role in the mechanism of learning. – Learning new information which will become declarative memory typically involves an interaction between the hippocampus and relevant areas of the cerebral cortex which specialise in storing declarative-type information, such as t ...
... • The hippocampus plays a central role in the mechanism of learning. – Learning new information which will become declarative memory typically involves an interaction between the hippocampus and relevant areas of the cerebral cortex which specialise in storing declarative-type information, such as t ...
How the prefrontal executive got its stripes
... to the frontal cortex. All cortical areas project to the input nuclei of the basal ganglia (caudate and putamen) but only frontal cortices (motor, premotor and prefrontal) receive the output of the basal ganglia via the thalamus. The simplified diagram shows only the ‘direct’ pathway through the bas ...
... to the frontal cortex. All cortical areas project to the input nuclei of the basal ganglia (caudate and putamen) but only frontal cortices (motor, premotor and prefrontal) receive the output of the basal ganglia via the thalamus. The simplified diagram shows only the ‘direct’ pathway through the bas ...
9.14 Lecture 16: Descending Pathways and Evolution Notes
... • Present in frogs, – with input from striatum and cerebellum. – Striatal inputs tend to end mainly in pre-rubral field of the ventral thalamus ...
... • Present in frogs, – with input from striatum and cerebellum. – Striatal inputs tend to end mainly in pre-rubral field of the ventral thalamus ...
Rising blood glucose level - Grosse Pointe Public School System
... Signal reaches synaptic terminal causing vesicles containing neurotransmitters to be released into synapse Neurotransmitters diffuse across the synapse and bind to receptors on receiving cell ...
... Signal reaches synaptic terminal causing vesicles containing neurotransmitters to be released into synapse Neurotransmitters diffuse across the synapse and bind to receptors on receiving cell ...
Chapter 4
... of the parietal lobe was removed from half the monkeys and part of the temporal lobe was removed from the other half. – Retesting the monkeys showed that: • Removal of temporal lobe tissue resulted in problems with the object discrimination task - Where pathway • Removal of parietal lobe tissue resu ...
... of the parietal lobe was removed from half the monkeys and part of the temporal lobe was removed from the other half. – Retesting the monkeys showed that: • Removal of temporal lobe tissue resulted in problems with the object discrimination task - Where pathway • Removal of parietal lobe tissue resu ...
Ch04
... of the parietal lobe was removed from half the monkeys and part of the temporal lobe was removed from the other half. – Retesting the monkeys showed that: • Removal of temporal lobe tissue resulted in problems with the object discrimination task - Where pathway • Removal of parietal lobe tissue resu ...
... of the parietal lobe was removed from half the monkeys and part of the temporal lobe was removed from the other half. – Retesting the monkeys showed that: • Removal of temporal lobe tissue resulted in problems with the object discrimination task - Where pathway • Removal of parietal lobe tissue resu ...
DOI: 10.1515/aucts-2015-0011 ACTA UIVERSITATIS CIBINIENSIS
... In recent decades, advances in neuroscience have been spectacular, particularly those related to the properties of neurons and complex molecules that affect neuronal response (Dziac, 2008). Thus, the discovery of brain nature and principles which govern the activity, we may be able to understand th ...
... In recent decades, advances in neuroscience have been spectacular, particularly those related to the properties of neurons and complex molecules that affect neuronal response (Dziac, 2008). Thus, the discovery of brain nature and principles which govern the activity, we may be able to understand th ...
ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY Measuring Action potential
... One goal of the lab sessions is to teach you a common way in which these potentials are observed and measured – using an oscilloscope. Time The voltages we are recording are not constant (that would not be very interesting!). Indeed, they can change very rapidly. We often refer to the voltage measur ...
... One goal of the lab sessions is to teach you a common way in which these potentials are observed and measured – using an oscilloscope. Time The voltages we are recording are not constant (that would not be very interesting!). Indeed, they can change very rapidly. We often refer to the voltage measur ...
File - Wk 1-2
... Cells in this layer are squamous, have an external basal lamina on both surfaces, are contractile (contain actin filaments), and have tight junctions. o Epineurium: the dense irregular connective tissue that surrounds and binds nerve ...
... Cells in this layer are squamous, have an external basal lamina on both surfaces, are contractile (contain actin filaments), and have tight junctions. o Epineurium: the dense irregular connective tissue that surrounds and binds nerve ...
The Basal Ganglia
... shown by PD patients (e.g. Wisconsin Card Sorting Test). [“Impairment of cognitive processes involved in deciding what to do on the basis of prior concepts in a sequence – one concept of mental action should lead to the next, within an overall cognitive plan.” Similar to the basal ganglia’s motor fu ...
... shown by PD patients (e.g. Wisconsin Card Sorting Test). [“Impairment of cognitive processes involved in deciding what to do on the basis of prior concepts in a sequence – one concept of mental action should lead to the next, within an overall cognitive plan.” Similar to the basal ganglia’s motor fu ...
Control of Wake and Sleep States
... Initial Components: Glutamatergic neurons of parabrachial nucleus (PB), Noradrenergic neurons from Locus Coeruleus (LC), Serotonergic neurons from dorsal and medial raphe (DR), and Dopaminergic periaqueductal gray (PAG) neurons. Intermediate Connections: Glutamatergic, Histaminergic, and Orexinergic ...
... Initial Components: Glutamatergic neurons of parabrachial nucleus (PB), Noradrenergic neurons from Locus Coeruleus (LC), Serotonergic neurons from dorsal and medial raphe (DR), and Dopaminergic periaqueductal gray (PAG) neurons. Intermediate Connections: Glutamatergic, Histaminergic, and Orexinergic ...
Sense and Control
... Sensory neurons, have specialised endings sensitive only to stimuli such as heat and light. These form part of the body’s larger sense organs (eyes, ears etc.), which function by collecting different energy forms. The sensory neuron then converts this energy into an electrical impulse. ...
... Sensory neurons, have specialised endings sensitive only to stimuli such as heat and light. These form part of the body’s larger sense organs (eyes, ears etc.), which function by collecting different energy forms. The sensory neuron then converts this energy into an electrical impulse. ...
Neuroscience 7a – Neuromuscular, spinal cord
... 3. Stretch reflex and its descending control. 4. Flexion (withdrawal) and crossed extension reflexes. Synapses Synapses are found throughout the nervous system and allow contact between neurones and themselves or muscles. The contact ratio (i.e. the number of neurones that are in contact with others ...
... 3. Stretch reflex and its descending control. 4. Flexion (withdrawal) and crossed extension reflexes. Synapses Synapses are found throughout the nervous system and allow contact between neurones and themselves or muscles. The contact ratio (i.e. the number of neurones that are in contact with others ...
A temporal trace and SOM-based model of complex cell development
... visual stimuli that are seen close together in time are likely generated by the same object. For example, if we are looking at a book at time = 0 s, it is quite likely that the object we see at time = 30 ms is that same book. The trace rule models this by slowing down the response time of the neuron ...
... visual stimuli that are seen close together in time are likely generated by the same object. For example, if we are looking at a book at time = 0 s, it is quite likely that the object we see at time = 30 ms is that same book. The trace rule models this by slowing down the response time of the neuron ...
Neural Network
... ● Training data say, x1 = 0 and x2 = 0, output is 0. ● Compute y = Step(w1*x1 + w2*x2) = 0. Output is correct so weights are not changed. ● For training data x1=0 and x2 = 1, output is 1 ● Compute y = Step(w1*x1 + w2*x2) = 0.4 = 1. Output is correct so weights are not changed. ● Next training data x ...
... ● Training data say, x1 = 0 and x2 = 0, output is 0. ● Compute y = Step(w1*x1 + w2*x2) = 0. Output is correct so weights are not changed. ● For training data x1=0 and x2 = 1, output is 1 ● Compute y = Step(w1*x1 + w2*x2) = 0.4 = 1. Output is correct so weights are not changed. ● Next training data x ...
Cholinergic Basal Forebrain Neurons Burst with Theta during
... screw was placed in the frontal bone between the frontal lobes and olfactory bulbs to serve as a reference. After recovery from surgery (2 d), the animals were habituated to the head fixation (6 –9 d). While lying in a Plexiglas box, they were prevented from twisting their bodies but otherwise able ...
... screw was placed in the frontal bone between the frontal lobes and olfactory bulbs to serve as a reference. After recovery from surgery (2 d), the animals were habituated to the head fixation (6 –9 d). While lying in a Plexiglas box, they were prevented from twisting their bodies but otherwise able ...
Understanding-Psychology-8th-Edition-Morris-Test-Bank
... A teacher grading papers opens the door of the room in which she has been working and becomes aware of loud rock music coming from her son's radio. When she asks him to turn it off, he asks why she is just noticing it now when he's had it on for over 20 minutes. Which of the following psychological ...
... A teacher grading papers opens the door of the room in which she has been working and becomes aware of loud rock music coming from her son's radio. When she asks him to turn it off, he asks why she is just noticing it now when he's had it on for over 20 minutes. Which of the following psychological ...
Slide ()
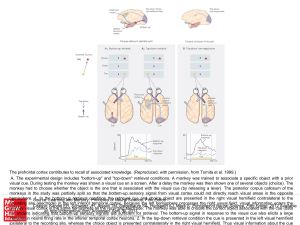
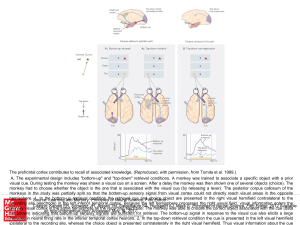
... Citation: Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S. Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon; 2012 Available primary visual cortex in the same hemisphere as the recording electrode. The monkey was able to choose the correct object associated with the cue (data at: htt ...
... Citation: Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S. Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon; 2012 Available primary visual cortex in the same hemisphere as the recording electrode. The monkey was able to choose the correct object associated with the cue (data at: htt ...
Slide ()
... Citation: Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S. Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon; 2012 Available primary visual cortex in the same hemisphere as the recording electrode. The monkey was able to choose the correct object associated with the cue (data at: htt ...
... Citation: Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S. Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon; 2012 Available primary visual cortex in the same hemisphere as the recording electrode. The monkey was able to choose the correct object associated with the cue (data at: htt ...
Multiple Systems in Decision Making: A
... intergrated basal ganglia weights (Frank & Claus, 2006). Supporting this account, a third gene coding for prefrontal function was found to predict participants’ sensitivity to the most recent reinforcement experiences without affecting probabilistic choice (Frank et al., 2007). Because the represent ...
... intergrated basal ganglia weights (Frank & Claus, 2006). Supporting this account, a third gene coding for prefrontal function was found to predict participants’ sensitivity to the most recent reinforcement experiences without affecting probabilistic choice (Frank et al., 2007). Because the represent ...
23. Parasympathetic nervous system
... Visceral sensory and autonomic neurons participate in visceral reflex arcs • Many are spinal reflexes such as defecation and micturition reflexes • Some only involve peripheral neurons: spinal cord not involved (not shown)* *e.g. “enteric” nervous system: 3 neuron reflex arcs entirely within the wa ...
... Visceral sensory and autonomic neurons participate in visceral reflex arcs • Many are spinal reflexes such as defecation and micturition reflexes • Some only involve peripheral neurons: spinal cord not involved (not shown)* *e.g. “enteric” nervous system: 3 neuron reflex arcs entirely within the wa ...
Human brainstem preganglionic parasympathetic
... 1980) and monkey (Perwaiz and Karim, 1982). The preganglionic neurons do not form discrete cell groups, so that it is difficult to identify them on Nissl appearance alone; nor is there a clear rostrocaudal distinction between neurons with axons exiting the brainstem in VII and those exiting in IX, s ...
... 1980) and monkey (Perwaiz and Karim, 1982). The preganglionic neurons do not form discrete cell groups, so that it is difficult to identify them on Nissl appearance alone; nor is there a clear rostrocaudal distinction between neurons with axons exiting the brainstem in VII and those exiting in IX, s ...
21-1
... • Cold receptors in the stratum basale respond to temperatures between 50-105 degrees F • Warm receptors in the dermis respond to temperatures between 90-118 degrees F • Both adapt rapidly at first, but continue to generate impulses at a low frequency • Pain is produced below 50 and over 118 ...
... • Cold receptors in the stratum basale respond to temperatures between 50-105 degrees F • Warm receptors in the dermis respond to temperatures between 90-118 degrees F • Both adapt rapidly at first, but continue to generate impulses at a low frequency • Pain is produced below 50 and over 118 ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.