A general mechanism for perceptual decision
... and connect the percept with the appropriate action, so that you will either be waving frantically, greeting respectfully or taking another sip of coffee. During a rainstorm, however, the sensory input is noisier, and thus you have to look longer to gather more sensory data to make a decision about ...
... and connect the percept with the appropriate action, so that you will either be waving frantically, greeting respectfully or taking another sip of coffee. During a rainstorm, however, the sensory input is noisier, and thus you have to look longer to gather more sensory data to make a decision about ...
Nervous System - Neurons
... functions, and where are they located Where are the cell bodies are located for motor and sensory nerve cells ...
... functions, and where are they located Where are the cell bodies are located for motor and sensory nerve cells ...
Nervous System - Neurons
... functions, and where are they located Where are the cell bodies are located for motor and sensory nerve cells ...
... functions, and where are they located Where are the cell bodies are located for motor and sensory nerve cells ...
Nervous System
... 3. presence of reverberating neuronal circuits 4. duration depends upon the number of neurons in circuit. b. LONG TERM 1. permanent or persistent retention 2. not via reverberating circuits since they will cause neuronal fatigue. 4 some short term signal can be converted to long term if reverberated ...
... 3. presence of reverberating neuronal circuits 4. duration depends upon the number of neurons in circuit. b. LONG TERM 1. permanent or persistent retention 2. not via reverberating circuits since they will cause neuronal fatigue. 4 some short term signal can be converted to long term if reverberated ...
Nervous System - Aurora City Schools
... • Olfactory bulbs - two projections just under the front of the brain that receive information from the receptors in the nose located just below. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. ...
... • Olfactory bulbs - two projections just under the front of the brain that receive information from the receptors in the nose located just below. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. ...
The Nervous System - Division of Social Sciences
... ◦ A neuron with one process attached to its soma; the process divides, with one branch receiving sensory information and the other sending the information into the central nervous system. ...
... ◦ A neuron with one process attached to its soma; the process divides, with one branch receiving sensory information and the other sending the information into the central nervous system. ...
Cortico–basal ganglia circuit mechanism for a decision threshold in
... model for the superior colliculus burst cells, and we tested the hypothesis that these burst cells are suitable for reading out threshold crossing in upstream neurons. Furthermore, the superior colliculus is known to be under the control of the basal ganglia, which have a critical role in voluntary ...
... model for the superior colliculus burst cells, and we tested the hypothesis that these burst cells are suitable for reading out threshold crossing in upstream neurons. Furthermore, the superior colliculus is known to be under the control of the basal ganglia, which have a critical role in voluntary ...
Nervous System - Aurora City Schools
... • Olfactory bulbs - two projections just under the front of the brain that receive information from the receptors in the nose located just below. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. ...
... • Olfactory bulbs - two projections just under the front of the brain that receive information from the receptors in the nose located just below. Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. ...
File
... The Cerebral Cortex: Brain Reorganization Plasticity the brain’s capacity for modification, as evident in brain reorganization following damage (especially in children) and in experiments on the effects of experience on brain development Children have a surplus of neurons When one area is d ...
... The Cerebral Cortex: Brain Reorganization Plasticity the brain’s capacity for modification, as evident in brain reorganization following damage (especially in children) and in experiments on the effects of experience on brain development Children have a surplus of neurons When one area is d ...
Text S1.
... be integrated across the parallel sensors within a given layer using Bayes’s theorem. However, we would like to know the distribution of potential voltages conditional only on the conductance of the channel and knowledge of the rules that govern it, but without certain knowledge of the current confi ...
... be integrated across the parallel sensors within a given layer using Bayes’s theorem. However, we would like to know the distribution of potential voltages conditional only on the conductance of the channel and knowledge of the rules that govern it, but without certain knowledge of the current confi ...
and Third-Order Neurons of Cockroach Ocelli
... responses are essentially linear. Second-order neurons o f a variety of visual systems also generate essentially linear responses. This is the case in vertebrate retinas (Naka et al., 1979; Tranchina et al., 1983; Chappell et al., 1985), in Limulus lateral eyes (Knight et al., 1970), in insect compo ...
... responses are essentially linear. Second-order neurons o f a variety of visual systems also generate essentially linear responses. This is the case in vertebrate retinas (Naka et al., 1979; Tranchina et al., 1983; Chappell et al., 1985), in Limulus lateral eyes (Knight et al., 1970), in insect compo ...
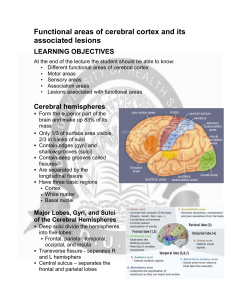
Functional areas of cerebral cortex and its associated lesions
... Left hemisphere – more control over: language, math, and logic Right hemisphere – more involved with: Visual-spatial skills ...
... Left hemisphere – more control over: language, math, and logic Right hemisphere – more involved with: Visual-spatial skills ...
Neurodevelopment and degeneration
... the signaling mechanisms for cell specification, differential ...
... the signaling mechanisms for cell specification, differential ...
Hippocampus – Why is it studied so frequently?
... (CRF), and neuropeptide Y 13, which all are involved in local inhibitory or excitatory circuits 49–52. Enkephalin and glutamate containing hippocampal afferent fibers arise from the adjacent entorhinal cortex 53. The gyrus dentatus granular neurons also may produce enkephalins and dynorphins 54. On ...
... (CRF), and neuropeptide Y 13, which all are involved in local inhibitory or excitatory circuits 49–52. Enkephalin and glutamate containing hippocampal afferent fibers arise from the adjacent entorhinal cortex 53. The gyrus dentatus granular neurons also may produce enkephalins and dynorphins 54. On ...
Slide 1
... Consists of three paired structures – thalamus, hypothalamus, and epithalamus Collectively, these gray matter areas enclose the third ventricle ...
... Consists of three paired structures – thalamus, hypothalamus, and epithalamus Collectively, these gray matter areas enclose the third ventricle ...
A lineage-related reciprocal inhibition circuitry for sensory
... functions as salience detector using competitive inhibition to amplify, maintain or switch between activity states. The resultant gating mechanism translates facilitation, inhibition and disinhibition of behavioural activity as R neuron functions into selection of motor actions and their organisatio ...
... functions as salience detector using competitive inhibition to amplify, maintain or switch between activity states. The resultant gating mechanism translates facilitation, inhibition and disinhibition of behavioural activity as R neuron functions into selection of motor actions and their organisatio ...
Unit 6 Powerpoint
... Characterized by slurred speech, loss of or blurred vision, dizziness, weakness, paralysis of a limb or hemiplegia, coma, and death Ischemic CVA - due to lack of blood supply to a particular area of the brain Hemorrhagic CVA - due to the rupture of a blood vessel in the brain ...
... Characterized by slurred speech, loss of or blurred vision, dizziness, weakness, paralysis of a limb or hemiplegia, coma, and death Ischemic CVA - due to lack of blood supply to a particular area of the brain Hemorrhagic CVA - due to the rupture of a blood vessel in the brain ...
Document
... Sensory ganglionic cells are the primary neurons. Their dendrites innervate receptors of many kinds of discriminative sensations (limb position and movement, pressure, vibration, precise touch) and convey impulses running in spinal nerve towards the spinal ganglion. In spinal ganglion the somata of ...
... Sensory ganglionic cells are the primary neurons. Their dendrites innervate receptors of many kinds of discriminative sensations (limb position and movement, pressure, vibration, precise touch) and convey impulses running in spinal nerve towards the spinal ganglion. In spinal ganglion the somata of ...
Unit 7 PowerPoint (PDF file)
... Characterized by slurred speech, loss of or blurred vision, dizziness, weakness, paralysis of a limb or hemiplegia, coma, and death Ischemic CVA - due to lack of blood supply to a particular area of the brain Hemorrhagic CVA - due to the rupture of a blood vessel in the brain ...
... Characterized by slurred speech, loss of or blurred vision, dizziness, weakness, paralysis of a limb or hemiplegia, coma, and death Ischemic CVA - due to lack of blood supply to a particular area of the brain Hemorrhagic CVA - due to the rupture of a blood vessel in the brain ...
1. A unicellular protest may use a contractile vacuole to expel
... 7. Which of the following sections of the mammalian nephron is incorrectly paired with its function? a. Bowman’s capsule & glomerulus – blood filtration. b. Proximal tubule – secretion of ammonia and H+ into ...
... 7. Which of the following sections of the mammalian nephron is incorrectly paired with its function? a. Bowman’s capsule & glomerulus – blood filtration. b. Proximal tubule – secretion of ammonia and H+ into ...
OL Chapter 2
... • Communication takes place at the synapse, the junction between the axon of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell of the receiving neuron ...
... • Communication takes place at the synapse, the junction between the axon of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell of the receiving neuron ...
The Bio-Psychology Dictionary - Windsor C
... (brain cavities and tunnels). CSF cushions the brain and spinal cord from jolts. This fluid circulates through the brain and the spinal canal. cerebrum - the largest and most complex portion of the brain. It controls thought, learning, and many other complex activities. It is divided into the left a ...
... (brain cavities and tunnels). CSF cushions the brain and spinal cord from jolts. This fluid circulates through the brain and the spinal canal. cerebrum - the largest and most complex portion of the brain. It controls thought, learning, and many other complex activities. It is divided into the left a ...
PDF here
... The SOD1 mutant mouse is the most widely used model of human amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). To determine where and when the pathological changes of motor neuron disease begins, we performed a comprehensive spatiotemporal analysis of disease progression in SOD1G93A mice. Quantitative pathologic ...
... The SOD1 mutant mouse is the most widely used model of human amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). To determine where and when the pathological changes of motor neuron disease begins, we performed a comprehensive spatiotemporal analysis of disease progression in SOD1G93A mice. Quantitative pathologic ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.