Molecular Basis for Induction of Ocular Dominance
... 3. One form of homosynaptic LTD is induced by postsynaptic NMDA receptor activation and a second form depends on metabotropic glutamate receptor activation. Under most experimental conditions, induction of homosynaptic LTD in the CA1 region and neocortex is inhibited when NMDA receptors are blocked ...
... 3. One form of homosynaptic LTD is induced by postsynaptic NMDA receptor activation and a second form depends on metabotropic glutamate receptor activation. Under most experimental conditions, induction of homosynaptic LTD in the CA1 region and neocortex is inhibited when NMDA receptors are blocked ...
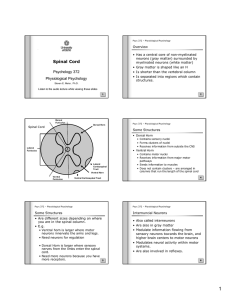
Spinal Cord
... • Ventral horn is larger where motor neurons innervate the arms and legs. • Need neurons for regulation • Dorsal Horn is larger where sensory nerves from the limbs enter the spinal cord. • Need more neurons because you have more receptors. ...
... • Ventral horn is larger where motor neurons innervate the arms and legs. • Need neurons for regulation • Dorsal Horn is larger where sensory nerves from the limbs enter the spinal cord. • Need more neurons because you have more receptors. ...
Development of the central and peripheral nervous system Central
... o basal regions of hemispheres are bulging into the lateral ventricles as the basal ganglia o ependyme and the vascularised mesenchyme forms the choroid plexus of the lateral ventricles o hippocampus is also bulging into the lateral ventricles o hemispheres are growing over the diencephalon, mesence ...
... o basal regions of hemispheres are bulging into the lateral ventricles as the basal ganglia o ependyme and the vascularised mesenchyme forms the choroid plexus of the lateral ventricles o hippocampus is also bulging into the lateral ventricles o hemispheres are growing over the diencephalon, mesence ...
The Neurally Controlled Animat: Biological Brains Acting
... the development of more robust biologically-based artificial animals and control systems, and shed light on the neural codes within these networks. With this information we could create artificial animals as a control system to solve a wide variety of tasks, or map the neural processing power to per ...
... the development of more robust biologically-based artificial animals and control systems, and shed light on the neural codes within these networks. With this information we could create artificial animals as a control system to solve a wide variety of tasks, or map the neural processing power to per ...
Brain-implantable biomimetic electronics as the next era in neural
... communicate with existing, living neural tissue in a bidirectional manner. Given that both electronic and neural systems generate and respond to electrical signals, this is feasible, though the region-specific, nonuniform distribution of neurons within the brain places substantial constraints on the ...
... communicate with existing, living neural tissue in a bidirectional manner. Given that both electronic and neural systems generate and respond to electrical signals, this is feasible, though the region-specific, nonuniform distribution of neurons within the brain places substantial constraints on the ...
THE ELECTRICAL BRAIN
... AMERICAN MIND, June/July]. All the evidence speaks for the involvement of electrical synapses: they are found in a network of neurons that is normally responsible for inhibiting the overlying nervous system in which the attack takes place; scientists have observed epilepsylike discharges by groups o ...
... AMERICAN MIND, June/July]. All the evidence speaks for the involvement of electrical synapses: they are found in a network of neurons that is normally responsible for inhibiting the overlying nervous system in which the attack takes place; scientists have observed epilepsylike discharges by groups o ...
Nervous System Lecture- Part II
... Proprioception Receptors Located throughout body Structurally simple General Senses Sensation – transduction of stimulus energy Perception – conscious awareness of stimulus energy Receptive field – area on body monitored by a single receptor cell Adaptation – reduction in sensitivity in the presence ...
... Proprioception Receptors Located throughout body Structurally simple General Senses Sensation – transduction of stimulus energy Perception – conscious awareness of stimulus energy Receptive field – area on body monitored by a single receptor cell Adaptation – reduction in sensitivity in the presence ...
Document
... • Gender-specific areas appear in both brain and spinal cord, depending on presence or absence of fetal testosterone • Maternal exposure to radiation, drugs (e.g., alcohol and opiates), or infection can harm the developing CNS • Smoking decreases oxygen in the blood, which can lead to neuron death a ...
... • Gender-specific areas appear in both brain and spinal cord, depending on presence or absence of fetal testosterone • Maternal exposure to radiation, drugs (e.g., alcohol and opiates), or infection can harm the developing CNS • Smoking decreases oxygen in the blood, which can lead to neuron death a ...
CHARLES UNIVERSITY
... Aim: The aim of the thesis is to introduce nitric oxide (NO) and its role in physiology and pathophysiolgy of central nervous system (CNS), with the intention of epileptiform activity in the nervous tissue. Our research was realized on rat hippocampal slices in vitro and it compares the experimental ...
... Aim: The aim of the thesis is to introduce nitric oxide (NO) and its role in physiology and pathophysiolgy of central nervous system (CNS), with the intention of epileptiform activity in the nervous tissue. Our research was realized on rat hippocampal slices in vitro and it compares the experimental ...
Transcripts/01_15 11
... ii. Project to widespread areas of cortex (gets info from everyway and sends it everywhere) and the Basal ganglia. iii. They produce general changes in cortical function including arousal, alertness, and cortical tone. This is brain stem reticular formation input. b. Reticular nucleus i. Reticular m ...
... ii. Project to widespread areas of cortex (gets info from everyway and sends it everywhere) and the Basal ganglia. iii. They produce general changes in cortical function including arousal, alertness, and cortical tone. This is brain stem reticular formation input. b. Reticular nucleus i. Reticular m ...
download file
... the normal orderly progression of BFs recorded in the rat A1. Each polygon represents one electrode penetration. The color of each polygon indicates the BF in kilohertz. The polygons (Voronoi tessellations) were generated so that every point on the cortical surface was assumed to have the characteri ...
... the normal orderly progression of BFs recorded in the rat A1. Each polygon represents one electrode penetration. The color of each polygon indicates the BF in kilohertz. The polygons (Voronoi tessellations) were generated so that every point on the cortical surface was assumed to have the characteri ...
36_LectureSlidesAdde..
... • Leptin inhibits NPY/AgRP neurons. This decreases inhibition to the catabolic pathway and decreases excitation to the anabolic pathway. The net result is an increase in catabolic pathway activity relative to the anabolic pathway. • Leptin stimulates POMC otherwise known as aMSH/CART neurons. This i ...
... • Leptin inhibits NPY/AgRP neurons. This decreases inhibition to the catabolic pathway and decreases excitation to the anabolic pathway. The net result is an increase in catabolic pathway activity relative to the anabolic pathway. • Leptin stimulates POMC otherwise known as aMSH/CART neurons. This i ...
Laboratory Exercise 10: Anatomy and Physiology of the Spinal Cord
... The patellar reflex (knee-jerk) and calcaneal reflex (Achilles reflex) are examples. .Polysynaptic Ipsilateral Reflex The withdrawal or flexor reflex has an interneuron between the sensory and motor neuron. Due to the interneuron, it brings the stimulus to the level of consciousness. This reflex has ...
... The patellar reflex (knee-jerk) and calcaneal reflex (Achilles reflex) are examples. .Polysynaptic Ipsilateral Reflex The withdrawal or flexor reflex has an interneuron between the sensory and motor neuron. Due to the interneuron, it brings the stimulus to the level of consciousness. This reflex has ...
The Central Nervous System LBHS Version
... to functional de cits. They also conduct animal studies where they stimulate brain areas and see if there are any behavioral changes. They use a technique called transmagnetic stimulation (TMS) to temporarily deactivate speci c parts of the cortex using strong magnets placed outside the head; and th ...
... to functional de cits. They also conduct animal studies where they stimulate brain areas and see if there are any behavioral changes. They use a technique called transmagnetic stimulation (TMS) to temporarily deactivate speci c parts of the cortex using strong magnets placed outside the head; and th ...
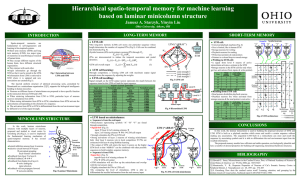
From/To LTM - Ohio University
... Neurons on different layers of minicolumns are proposed to have specific function in the interaction between STM and LTM. When retrieving information from LTM to STM, particular layer of neurons receives stimulation from LTM. When storing information from STM to LTM, stimulations from STM acti ...
... Neurons on different layers of minicolumns are proposed to have specific function in the interaction between STM and LTM. When retrieving information from LTM to STM, particular layer of neurons receives stimulation from LTM. When storing information from STM to LTM, stimulations from STM acti ...
stereological estimates of dopaminergic, gabaergic and
... Key words: VGluT2, GAD, reward, midbrain, basal ganglia. Abstract—Midbrain dopamine neurons in the ventral tegmental area, substantia nigra and retrorubral field play key roles in reward processing, learning and memory, and movement. Within these midbrain regions and admixed with the dopamine neuron ...
... Key words: VGluT2, GAD, reward, midbrain, basal ganglia. Abstract—Midbrain dopamine neurons in the ventral tegmental area, substantia nigra and retrorubral field play key roles in reward processing, learning and memory, and movement. Within these midbrain regions and admixed with the dopamine neuron ...
CaseStudyBrain2016
... Case Studies Directions: Based on the information provided indicate as much as you can about the location of the brain damage experienced by each of the following individuals (Note answers may vary but be sure to explain your proposals). All of the following case studies are based on real patients. ...
... Case Studies Directions: Based on the information provided indicate as much as you can about the location of the brain damage experienced by each of the following individuals (Note answers may vary but be sure to explain your proposals). All of the following case studies are based on real patients. ...
A Critical Review of the Role of the Proposed VMpo Nucleus in Pain
... basis of this limited sample of recordings, the lamina I input to the region of VMpo seems to be thermoreceptive and nociceptive. Dostrovsky and Craig were unable to activate cold-responsive lamina I STT cells antidromically from the ventrobasal complex in 2 monkeys in which a stimulating electrode ...
... basis of this limited sample of recordings, the lamina I input to the region of VMpo seems to be thermoreceptive and nociceptive. Dostrovsky and Craig were unable to activate cold-responsive lamina I STT cells antidromically from the ventrobasal complex in 2 monkeys in which a stimulating electrode ...
48_lecture_presentation - Course
... effect of an EPSP. The summed effect of EPSPs and IPSPs determines whether an axon hillock will reach threshold and generate an action potential. Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
... effect of an EPSP. The summed effect of EPSPs and IPSPs determines whether an axon hillock will reach threshold and generate an action potential. Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
File - cbcpsychology
... Participants are matched according to the variable(s) whose influence should be controlled e.g. intelligence, memory ability, etc. The pairings could also be based on characteristics such as I.Q., age, Controls the effects of the variable(s) on which participants are matched, thus MatchedPairs minim ...
... Participants are matched according to the variable(s) whose influence should be controlled e.g. intelligence, memory ability, etc. The pairings could also be based on characteristics such as I.Q., age, Controls the effects of the variable(s) on which participants are matched, thus MatchedPairs minim ...
Commentary: Saccadic eye movements
... the control of visual fixation and saccadic eye movements. The superficial layers of the SC contain neurons that receive direct retinal inputs as well as inputs from other visual areas (Robinson and McClurkin, 1989). These visual neurons are organized into a visual map of the contralateral visual he ...
... the control of visual fixation and saccadic eye movements. The superficial layers of the SC contain neurons that receive direct retinal inputs as well as inputs from other visual areas (Robinson and McClurkin, 1989). These visual neurons are organized into a visual map of the contralateral visual he ...
the giant serotonergic neuron of aplysia: a multi
... least three silver grains or if the same profile was labeled widest part of the varicosity, with a long axis of 2.5 pm and a short axis of 1 pm, is quite close to one end. The in at least two adjacent sections. Background labeling was essentially negligible as indicated by the absence of length of t ...
... least three silver grains or if the same profile was labeled widest part of the varicosity, with a long axis of 2.5 pm and a short axis of 1 pm, is quite close to one end. The in at least two adjacent sections. Background labeling was essentially negligible as indicated by the absence of length of t ...
Cortical Maps - White Rose Research Online
... one might graph the excitation of one neuron by another against the distance that separates them in the tissue. Or an interaction may be described in terms of the functional relationships between neurons, as one might graph the correspondence between neurons as a function of the similarity of their ...
... one might graph the excitation of one neuron by another against the distance that separates them in the tissue. Or an interaction may be described in terms of the functional relationships between neurons, as one might graph the correspondence between neurons as a function of the similarity of their ...
a)write short notes about the anatomy of optic nerve
... Schwann cells. sincc the optic nerve is comparable to a tract within the central nervous system, The optic nerve leaves the orbital cavity through the optic canal and unites with the optic nerve ol'the opposite side to larm the optic chiasma Optic Chiasma In the chiasma. the libel'S tj'om the nasal ...
... Schwann cells. sincc the optic nerve is comparable to a tract within the central nervous system, The optic nerve leaves the orbital cavity through the optic canal and unites with the optic nerve ol'the opposite side to larm the optic chiasma Optic Chiasma In the chiasma. the libel'S tj'om the nasal ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.