File
... diminishing of a CR in classical conditioning, when a UCS does not follow a CS in operant conditioning, when a response is no longer reinforced ...
... diminishing of a CR in classical conditioning, when a UCS does not follow a CS in operant conditioning, when a response is no longer reinforced ...
Here
... Stimulus-response (S-R) theories are central to the principles of conditioning. They are based on the assumption that human behaviour is learned. One of the early contributors to the field, American psychologist Edward L. Thorndike, postulated the Law of Effect, which stated that those behavioral re ...
... Stimulus-response (S-R) theories are central to the principles of conditioning. They are based on the assumption that human behaviour is learned. One of the early contributors to the field, American psychologist Edward L. Thorndike, postulated the Law of Effect, which stated that those behavioral re ...
lecture 2
... type of learning he was studying the physiology of digestion when he noticed a funny thing. digestion starts in the mouth where saliva begins to break down food. Dogs would salivate when he put the food powder in their mouths. But experienced dogs would also salivate when the experimenter walked ...
... type of learning he was studying the physiology of digestion when he noticed a funny thing. digestion starts in the mouth where saliva begins to break down food. Dogs would salivate when he put the food powder in their mouths. But experienced dogs would also salivate when the experimenter walked ...
Classical, Instrumental and Operant Conditioning
... response that occurs after some fixed time has passed since last reward. No matter how many responses have been made during that interval. Variable-interval schedules: they reinforce the first response after some period of time, but the amount of time varies. Average. ...
... response that occurs after some fixed time has passed since last reward. No matter how many responses have been made during that interval. Variable-interval schedules: they reinforce the first response after some period of time, but the amount of time varies. Average. ...
File
... a procedure in which the conditioned stimulus in one conditioning experience is paired with a new neutral stimulus, creating a second (often weaker) conditioned stimulus. (For example, an animal that has learned that a tone predicts food might then learn that a light predicts the tone and begin resp ...
... a procedure in which the conditioned stimulus in one conditioning experience is paired with a new neutral stimulus, creating a second (often weaker) conditioned stimulus. (For example, an animal that has learned that a tone predicts food might then learn that a light predicts the tone and begin resp ...
FREE Sample Here
... which requires him to be at work an hour earlier. To save some time in the morning and sleep in as long as possible, he waits to drink his first cup of coffee until he gets to his office. He notices that he feels much more alert, not only in the morning, but all day long as well. Using one of the be ...
... which requires him to be at work an hour earlier. To save some time in the morning and sleep in as long as possible, he waits to drink his first cup of coffee until he gets to his office. He notices that he feels much more alert, not only in the morning, but all day long as well. Using one of the be ...
Classical Conditioning
... of learning that occurs as a result of the repeated association of two stimuli. One of the two stimuli would normally elicit a reflexive, involuntary or automatic response. This is called the unconditioned stimulus (UCS) since it does not need to be conditioned in order to elicit the involuntary res ...
... of learning that occurs as a result of the repeated association of two stimuli. One of the two stimuli would normally elicit a reflexive, involuntary or automatic response. This is called the unconditioned stimulus (UCS) since it does not need to be conditioned in order to elicit the involuntary res ...
Chapter 6 PSYCH
... The Russian Physiologist Ivan Pavlov came up with the concept of Classical Conditioning This is when a person’s or animals response becomes attached to a new stimulus Classical conditioning is an example of learning Learning- the relatively permanent change in behavior that results from experience W ...
... The Russian Physiologist Ivan Pavlov came up with the concept of Classical Conditioning This is when a person’s or animals response becomes attached to a new stimulus Classical conditioning is an example of learning Learning- the relatively permanent change in behavior that results from experience W ...
Behaviorism and Cogntivism
... Information processing is governed by an internal process — rather than external circumstance as emphasized by behaviorism. The process includes selecting information (attention), translating information (encoding), and recalling that information when appropriate (retrieval). ...
... Information processing is governed by an internal process — rather than external circumstance as emphasized by behaviorism. The process includes selecting information (attention), translating information (encoding), and recalling that information when appropriate (retrieval). ...
MS-PowerPoint
... originally irrelevant stimulus that, after association with an unconditioned stimulus, comes to trigger a conditioned response ...
... originally irrelevant stimulus that, after association with an unconditioned stimulus, comes to trigger a conditioned response ...
practice test mod 19
... 10. Every time Evan took the leash out of the closet Fido would get excited. Apparently Fido had learned to associate the sight of the leash with a walk, and that naturally made him excited. Evan stopped taking Fido for a walk when he took the leash out. Eventually, Fido stopped getting excited at t ...
... 10. Every time Evan took the leash out of the closet Fido would get excited. Apparently Fido had learned to associate the sight of the leash with a walk, and that naturally made him excited. Evan stopped taking Fido for a walk when he took the leash out. Eventually, Fido stopped getting excited at t ...
File
... Most learning is Associative learning – Associative Learning is that certain events occur together. The events may be two stimuli (as in classical conditioning) or a response and its consequence (as in operant conditioning). How many of you have to have popcorn when you go to the movies??? Walk on t ...
... Most learning is Associative learning – Associative Learning is that certain events occur together. The events may be two stimuli (as in classical conditioning) or a response and its consequence (as in operant conditioning). How many of you have to have popcorn when you go to the movies??? Walk on t ...
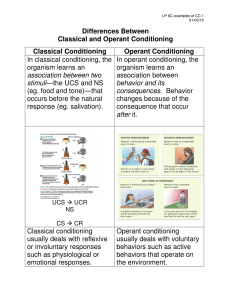
Differences Between Classical and Operant Conditioning Classical
... organism learns an association between two stimuli—the UCS and NS (eg. food and tone)—that occurs before the natural response (eg. salivation). ...
... organism learns an association between two stimuli—the UCS and NS (eg. food and tone)—that occurs before the natural response (eg. salivation). ...
unit 6 — learning - Mayfield City Schools
... The naturally occurring response to the unconditioned stimulus in classical conditioning. A stimulus that unconditionallynaturally and automatically-triggers a response in classical conditioning. In classical conditioning, the learned response to a previously neutral (now conditioned) stimulus (CS). ...
... The naturally occurring response to the unconditioned stimulus in classical conditioning. A stimulus that unconditionallynaturally and automatically-triggers a response in classical conditioning. In classical conditioning, the learned response to a previously neutral (now conditioned) stimulus (CS). ...
Learning Review Game
... An executive in a computer software firm works with his office door closed. At the same time every hour he opens the door to see what his employees are doing. The employees have learned to work especially hard during the five minutes before and while the door is open. Their work pattern is typical o ...
... An executive in a computer software firm works with his office door closed. At the same time every hour he opens the door to see what his employees are doing. The employees have learned to work especially hard during the five minutes before and while the door is open. Their work pattern is typical o ...
Ch. 6: Learning through Conditioning compiled by Cetin I. Learning
... originally evoked by another stimulus A. Also called Pavlovian Conditioning B. Discovered by Ivan Pavlov, a Russian psychologist who studied digestion, around 1900 i. Studied what he called “psychic reflexes” which is the learned association between a stimulus and response ii. The response was saliv ...
... originally evoked by another stimulus A. Also called Pavlovian Conditioning B. Discovered by Ivan Pavlov, a Russian psychologist who studied digestion, around 1900 i. Studied what he called “psychic reflexes” which is the learned association between a stimulus and response ii. The response was saliv ...
Operant Conditioning
... strengthened if followed by reinforcement or diminished if followed by punishment. ...
... strengthened if followed by reinforcement or diminished if followed by punishment. ...
Ch 8 Jeopardy Answers
... Automatic response to a particular natural stimulus. Which produce higher or faster response rates: ratio or interval schedules of reinforcement? An example of a secondary reinforcer. This is designed to weaken our tendency to do something. ...
... Automatic response to a particular natural stimulus. Which produce higher or faster response rates: ratio or interval schedules of reinforcement? An example of a secondary reinforcer. This is designed to weaken our tendency to do something. ...
Psychology - Bristol Public Schools
... Observational Learning • Learning by watching what others do and what happens to them for doing it ...
... Observational Learning • Learning by watching what others do and what happens to them for doing it ...
Habitual Behaviour
... Stimulus generalization can occur in both classical conditioning and operant conditioning. However, a subject can be taught to discriminate between similar stimuli and to only respond to a specific stimulus. For example, imagine that a dog has been trained to run to his owner when he hears a whistle ...
... Stimulus generalization can occur in both classical conditioning and operant conditioning. However, a subject can be taught to discriminate between similar stimuli and to only respond to a specific stimulus. For example, imagine that a dog has been trained to run to his owner when he hears a whistle ...
OTHER THEORIES OF PERSONALITY BEHAVIORISM AND
... Classical Conditioning A innocuous or neutral stimulus pared with an unconditioned stimulus can become a conditioned stimulus Operant Conditioning and Intermittent Reinforcement Social Learning theory Albert Bandura All people have an inherent tendency to construe the events of their experience and ...
... Classical Conditioning A innocuous or neutral stimulus pared with an unconditioned stimulus can become a conditioned stimulus Operant Conditioning and Intermittent Reinforcement Social Learning theory Albert Bandura All people have an inherent tendency to construe the events of their experience and ...
Classical conditioning

Classical conditioning (also known as Pavlovian or respondent conditioning) is a learning process in which an innate response to a potent stimulus comes to be elicited in response to a previously neutral stimulus; this is achieved by repeated pairings of the neutral stimulus with the potent stimulus. The basic facts about classical conditioning were discovered by Ivan Pavlov through his famous experiments with dogs. Together with operant conditioning, classical conditioning became the foundation of Behaviorism, a school of psychology that dominated psychology in the mid-20th century and is still an important influence on the practice of psychological therapy and the study of animal behaviour (ethology). Classical conditioning is now the best understood of the basic learning processes, and its neural substrates are beginning to be understood.