Learning - Forensic Consultation
... neutral stimulus (NS) becomes a conditioned stimulus (CS) through repeated pairings with a previously conditioned stimulus (CS) ...
... neutral stimulus (NS) becomes a conditioned stimulus (CS) through repeated pairings with a previously conditioned stimulus (CS) ...
Chapter 8: Learning
... – The removal of a stimulus after a particular response to increase the likelihood the response will recur – The stimulus removed is usually unpleasant – Example: Taking an aspirin to get rid of a headache ...
... – The removal of a stimulus after a particular response to increase the likelihood the response will recur – The stimulus removed is usually unpleasant – Example: Taking an aspirin to get rid of a headache ...
classical conditioning - Warren County Public Schools
... BACKWARD CONDITIONING the CS follows the UCS; classical conditioning works most slowly this way (if it even works at all) 2. PREDICTABILITY not enough for the CS and the USC to just occur together; they must reliably occur together before classical cond. occurs; cond. is quicker when the CS always s ...
... BACKWARD CONDITIONING the CS follows the UCS; classical conditioning works most slowly this way (if it even works at all) 2. PREDICTABILITY not enough for the CS and the USC to just occur together; they must reliably occur together before classical cond. occurs; cond. is quicker when the CS always s ...
Relative timing: from behaviour to neurons
... SOA is positive when stimulus A is presented first and negative when stimulus B is presented first. The single-headed arrow (green) corresponds to the point of subjective simultaneity (PSS), the SOA that corresponds to 50% on the ordinate. The double-headed arrow (blue) indicates the just notable di ...
... SOA is positive when stimulus A is presented first and negative when stimulus B is presented first. The single-headed arrow (green) corresponds to the point of subjective simultaneity (PSS), the SOA that corresponds to 50% on the ordinate. The double-headed arrow (blue) indicates the just notable di ...
Crash Course Study Guide for AP Psychology Exam
... a. Negative afterimage: If you stare at one color and then look at white space, you see a color afterimage in the complementary hue of the original stimulus 2. Opponent-process theory (Hering): receptor cells are arranged in pairs: red/green, blue/yellow, and black/white. If one color is stimulated, ...
... a. Negative afterimage: If you stare at one color and then look at white space, you see a color afterimage in the complementary hue of the original stimulus 2. Opponent-process theory (Hering): receptor cells are arranged in pairs: red/green, blue/yellow, and black/white. If one color is stimulated, ...
Chapter Six Learning
... out the can opener, but not when you take out the blender. b) Your nephew squeals excitedly at the sound of any song by the Wiggles. c) You no longer wake up when your alarm clock goes off each morning. d) After being bitten by your neighbor’s dachshund, you are now afraid of every dog that you enco ...
... out the can opener, but not when you take out the blender. b) Your nephew squeals excitedly at the sound of any song by the Wiggles. c) You no longer wake up when your alarm clock goes off each morning. d) After being bitten by your neighbor’s dachshund, you are now afraid of every dog that you enco ...
Modeling working memory and decision making using generic
... Classical experimental paradigm to study working memory and decision making Subject has to compare two stimuli (tactile, visual, auditory etc.) The experiment starts with presentation of the first stimulus Second stimulus is presented after a temporal delay Subject needs to make a binary (yes/no) de ...
... Classical experimental paradigm to study working memory and decision making Subject has to compare two stimuli (tactile, visual, auditory etc.) The experiment starts with presentation of the first stimulus Second stimulus is presented after a temporal delay Subject needs to make a binary (yes/no) de ...
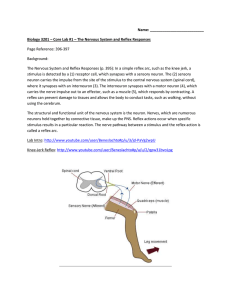
Core Lab #1 - Reflex Responses
... where it synapses with an interneuron (3). The interneuron synapses with a motor neuron (4), which carries the nerve impulse out to an effector, such as a muscle (5), which responds by contracting. A reflex can prevent damage to tissues and allows the body to conduct tasks, such as walking, without ...
... where it synapses with an interneuron (3). The interneuron synapses with a motor neuron (4), which carries the nerve impulse out to an effector, such as a muscle (5), which responds by contracting. A reflex can prevent damage to tissues and allows the body to conduct tasks, such as walking, without ...
Packet #25 Imagine you are working on a research paper about how
... network (e.g., the perception of a dog or an odor) might be sufficient to activate the whole network and hence lead to the experience of fear or anxiety. From this perspective, generalization concerns the question of how stimuli that are related to the original CS are integrated into this associativ ...
... network (e.g., the perception of a dog or an odor) might be sufficient to activate the whole network and hence lead to the experience of fear or anxiety. From this perspective, generalization concerns the question of how stimuli that are related to the original CS are integrated into this associativ ...
Making Sense of Animal Conditioning
... may be learned when a stimulus (e.g., a snake) precedes a frightening event (e.g., someone screams; Watson and Rayner 1920). Classical conditioning may facilitate digestion because stimuli that predict food may help to prepare the body for digestion of that food (Woods and Strubbe 1994). Classical c ...
... may be learned when a stimulus (e.g., a snake) precedes a frightening event (e.g., someone screams; Watson and Rayner 1920). Classical conditioning may facilitate digestion because stimuli that predict food may help to prepare the body for digestion of that food (Woods and Strubbe 1994). Classical c ...
5. Operant Conditioning V2
... In operant conditioning, if responses are not made, the consequence doesn’t happen. In classical conditioning, responses occur regardless of responding. ...
... In operant conditioning, if responses are not made, the consequence doesn’t happen. In classical conditioning, responses occur regardless of responding. ...
Option E - OoCities
... experiment, he removed half of the eggs that a female goose had laid and kept them in an incubator. Lorenz was with the goslings when they hatched out from those eggs, and he remained with them for a few hours. He was therefore the first moving object that they saw. The goslings did not show normal ...
... experiment, he removed half of the eggs that a female goose had laid and kept them in an incubator. Lorenz was with the goslings when they hatched out from those eggs, and he remained with them for a few hours. He was therefore the first moving object that they saw. The goslings did not show normal ...
What is real? How do you define real?
... tion potentials can vary somewhat in duration, amplitude, and shape, image, skin stimulation, sound, odor etc..). they visual are typically treated in neural encoding studies as identical stereotyped If we ignore the briefsequence, duration or of number an action alternatives: describe spike of pote ...
... tion potentials can vary somewhat in duration, amplitude, and shape, image, skin stimulation, sound, odor etc..). they visual are typically treated in neural encoding studies as identical stereotyped If we ignore the briefsequence, duration or of number an action alternatives: describe spike of pote ...
Speed, noise, information and the graded nature of neuronal
... is the binning into R response bins, in which case the correction term to be subtracted depends solely on the number Rs of bins relevant for each stimulus [6]: ...
... is the binning into R response bins, in which case the correction term to be subtracted depends solely on the number Rs of bins relevant for each stimulus [6]: ...
1 Preface Dear Psychology Students, Anyone can
... able to form an image and thus we see. The cornea and the lens have the task to bend the light rays so that they hit the retina. The retina is located at the back of the eyeball and contains the sensory receptors for seeing. In the eye there are two different kinds of receptors, namely rods and cone ...
... able to form an image and thus we see. The cornea and the lens have the task to bend the light rays so that they hit the retina. The retina is located at the back of the eyeball and contains the sensory receptors for seeing. In the eye there are two different kinds of receptors, namely rods and cone ...
AP Psychology_UbD Unit Plan_Unit V_Sensation
... Meaning UNDERSTANDINGS Students will understand that … ...
... Meaning UNDERSTANDINGS Students will understand that … ...
Classical and Operant Conditioning
... – it is sometimes called “reflexive learning” – it is sometimes called respondent conditioning ...
... – it is sometimes called “reflexive learning” – it is sometimes called respondent conditioning ...
Learning - Gordon State College
... response to a stimulus Unconditioned stimulus (UCS): naturally and automatically elicits a response Conditioned response (CR): learned response to a previously neutral stimulus Conditioned stimulus (CS): after repeated pairings with UCS, elicits the same response ...
... response to a stimulus Unconditioned stimulus (UCS): naturally and automatically elicits a response Conditioned response (CR): learned response to a previously neutral stimulus Conditioned stimulus (CS): after repeated pairings with UCS, elicits the same response ...
Protection from extinction
... model of conditioning proposed that the total associative strength of a compound is compared with the strength that a reinforcer can produce in order to compute an error term. That error term is then used to update the associative strengths of all the elements in the compound. The phenomenon of bloc ...
... model of conditioning proposed that the total associative strength of a compound is compared with the strength that a reinforcer can produce in order to compute an error term. That error term is then used to update the associative strengths of all the elements in the compound. The phenomenon of bloc ...
Ch 9 Escape
... Anybody who has lived very long is quite aware of the fact that life is no "bed of roses." Although there are many positive reinforcements which maintain our activities, another class of stimuli called aversive, exerts powerful control over our behavior. Life is full of annoyances, harassments, and ...
... Anybody who has lived very long is quite aware of the fact that life is no "bed of roses." Although there are many positive reinforcements which maintain our activities, another class of stimuli called aversive, exerts powerful control over our behavior. Life is full of annoyances, harassments, and ...
Review of the Pain Pathway
... 1)Acute pain facilitates tissue repair. The pain response is proportional to the injury and generally responds well to most analgesics such as opioids and NSAIDs. 2)Chronic pain is long lasting (in humans it is longer than 3-6 month duration) and often is not proportional to the stimulus. The neuroe ...
... 1)Acute pain facilitates tissue repair. The pain response is proportional to the injury and generally responds well to most analgesics such as opioids and NSAIDs. 2)Chronic pain is long lasting (in humans it is longer than 3-6 month duration) and often is not proportional to the stimulus. The neuroe ...