Prokaryote Gene Expression Section 1 Overview of RNA
... They are translated from the 5’ to the 3’ end Generally mRNAs are linear (although some prokaryotic RNA viruses are circular and act as mRNAs) ...
... They are translated from the 5’ to the 3’ end Generally mRNAs are linear (although some prokaryotic RNA viruses are circular and act as mRNAs) ...
Notes
... 2) Chargaff’s Rules, and 3) X-Ray evidence. DNA is a nucleic acid polymer made of 4 different monomers called nucleotides. ...
... 2) Chargaff’s Rules, and 3) X-Ray evidence. DNA is a nucleic acid polymer made of 4 different monomers called nucleotides. ...
II - Humble ISD
... change in the total _number_____ of chromosomes. Does not alter individual _genes____. These errors generally occur during _meiosis___ or _mitosis_____. B. Types of Chromosomal Mutations ...
... change in the total _number_____ of chromosomes. Does not alter individual _genes____. These errors generally occur during _meiosis___ or _mitosis_____. B. Types of Chromosomal Mutations ...
I. TRANSCRIPTION
... Expression of the b-globin gene is a typical process. This gene contains two introns and three exons. Interestingly, the codon of the 30th amino acid, AGG, is separated by an intron. As a result, the first two nucleotides AG are in one exon and the third nucleotide G is in another exon. ...
... Expression of the b-globin gene is a typical process. This gene contains two introns and three exons. Interestingly, the codon of the 30th amino acid, AGG, is separated by an intron. As a result, the first two nucleotides AG are in one exon and the third nucleotide G is in another exon. ...
Protein Synthesis Activity
... 2. Cut out your nucleotides from the cutouts sheet. 3. Glue the sequence of nucleotides you transcribed to the back of your answer sheet and draw in the covalent bonds to complete the “backbone” of your mRNA molecule. 4. Please answer the questions in the Transcription section on your answer sheet. ...
... 2. Cut out your nucleotides from the cutouts sheet. 3. Glue the sequence of nucleotides you transcribed to the back of your answer sheet and draw in the covalent bonds to complete the “backbone” of your mRNA molecule. 4. Please answer the questions in the Transcription section on your answer sheet. ...
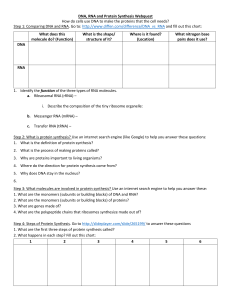
DNA, RNA and Protein Synthesis Webquest
... 1. What are the monomers (subunits or building blocks) of DNA and RNA? 2. What are the monomers (subunits or building blocks) of proteins? 3. What are genes made of? 4. What are the polypeptide chains that ribosomes synthesize made out of? Step 4: Steps of Protein Synthesis. Go to http://slideplayer ...
... 1. What are the monomers (subunits or building blocks) of DNA and RNA? 2. What are the monomers (subunits or building blocks) of proteins? 3. What are genes made of? 4. What are the polypeptide chains that ribosomes synthesize made out of? Step 4: Steps of Protein Synthesis. Go to http://slideplayer ...
Modelling Protein Synthesis - Jannali
... • Translation is the process where the information now on the RNA molecule is used to make a new polypeptide chain. • mRNA strand binds to a ribosome at the end with the start codon. (Ribosome's act as site for polypeptide synthesis ) •A tRNA carrying the amino acid methionine and anticodon (UAC) bi ...
... • Translation is the process where the information now on the RNA molecule is used to make a new polypeptide chain. • mRNA strand binds to a ribosome at the end with the start codon. (Ribosome's act as site for polypeptide synthesis ) •A tRNA carrying the amino acid methionine and anticodon (UAC) bi ...
Slide 1
... • Disulfide bonds can form between two cysteine side chains in proteins. • The 5’end of RNA is capped by the addition of 7-methylguanosine . • Nucleotides are joined together by phosphodiester linkage between 5’and 3’ carbon atoms to form nucleic acids. ...
... • Disulfide bonds can form between two cysteine side chains in proteins. • The 5’end of RNA is capped by the addition of 7-methylguanosine . • Nucleotides are joined together by phosphodiester linkage between 5’and 3’ carbon atoms to form nucleic acids. ...
bio12_sm_07_2
... Both DNA transcription - produces 2 semi-create new -produces a conserved double complementary nucleic single strand of stranded DNA molecules acid strands mRNA -uses DNA polymerase -read DNA code -use RNA polymerase 7. Answers may vary. Sample answer: The organism could produce more proteins than i ...
... Both DNA transcription - produces 2 semi-create new -produces a conserved double complementary nucleic single strand of stranded DNA molecules acid strands mRNA -uses DNA polymerase -read DNA code -use RNA polymerase 7. Answers may vary. Sample answer: The organism could produce more proteins than i ...
Protein Synthesis part 2
... releases the protein from the last tRNA molecule (which is sitting in the P site). ...
... releases the protein from the last tRNA molecule (which is sitting in the P site). ...
DNA/RNA/Protein Questions
... What does Translation mean? What organelle makes proteins? What role does tRNA play in making proteins? What is an "anticodon"? What structure is it on? How is mRNA used to make proteins. Why are proteins so important to life? Given a strand of mRNA, be able to make an amino acid chain. (You will be ...
... What does Translation mean? What organelle makes proteins? What role does tRNA play in making proteins? What is an "anticodon"? What structure is it on? How is mRNA used to make proteins. Why are proteins so important to life? Given a strand of mRNA, be able to make an amino acid chain. (You will be ...
Chapter 9 Slide PDF
... Splicing defects cause several human genetic disorders One hemoglobin disorder, b-thalassemia, is due to mutations at the exon/intron region that results in lower splicing efficiency and lower b-globin protein ...
... Splicing defects cause several human genetic disorders One hemoglobin disorder, b-thalassemia, is due to mutations at the exon/intron region that results in lower splicing efficiency and lower b-globin protein ...
DNA and RNA
... • Is the genetic code universal? (Do all organisms use the same codon/amino acid genetic code?) • How does the above question relate to the linked history of the life on Earth? ...
... • Is the genetic code universal? (Do all organisms use the same codon/amino acid genetic code?) • How does the above question relate to the linked history of the life on Earth? ...
File
... is part of the Ribosomes which work with the other forms of RNA to construct proteins. tRNA carries amino acids which are the smallest building blocks in the process of making proteins. The Ribosomes connect the tRNA to the mRNA so that the code mimics the original DNA. The amino acids that the tRNA ...
... is part of the Ribosomes which work with the other forms of RNA to construct proteins. tRNA carries amino acids which are the smallest building blocks in the process of making proteins. The Ribosomes connect the tRNA to the mRNA so that the code mimics the original DNA. The amino acids that the tRNA ...
Biology 212 General Genetics
... an inherited change in a gene often affects the sequence of the protein mutant result of a mutation can refer to a mutant gene or mutant organism Some examples of mutations in the PAH (phenylalanine hydroxylase) gene that can lead to PKU (see Fig. 1.18 and 1.19): R408W mutant One of four m ...
... an inherited change in a gene often affects the sequence of the protein mutant result of a mutation can refer to a mutant gene or mutant organism Some examples of mutations in the PAH (phenylalanine hydroxylase) gene that can lead to PKU (see Fig. 1.18 and 1.19): R408W mutant One of four m ...
Recombinant DNA Technology
... – Many species store mRNAs in the cytoplasm of the egg. These mRNAs are inactive due to masking by proteins. Fertilization of the egg initiates unmasking and translation of these mRNAs. • Availability of specific tRNAs – In the embryonic development of a hornworm, an mRNA is present from day 1 but a ...
... – Many species store mRNAs in the cytoplasm of the egg. These mRNAs are inactive due to masking by proteins. Fertilization of the egg initiates unmasking and translation of these mRNAs. • Availability of specific tRNAs – In the embryonic development of a hornworm, an mRNA is present from day 1 but a ...
1. I can tell the difference between mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA
... RNA polymerase is the enzyme responsible for transcription. It then unwinds and separates the DNA and then adds complementary RNA nucleotides using the DNA as a pattern. Once the gene is fully transcribed into RNA, the mRNA is edited. ...
... RNA polymerase is the enzyme responsible for transcription. It then unwinds and separates the DNA and then adds complementary RNA nucleotides using the DNA as a pattern. Once the gene is fully transcribed into RNA, the mRNA is edited. ...
RNA - Universitas Esa Unggul
... the ribosomes, the protein synthesis factories in the cell. It is coded so that every three nucleotides (a codon) correspond to one amino acid. In eukaryotic cells, once precursor mRNA (pre-mRNA) has been transcribed from DNA, it is processed to mature mRNA. This removes its introns—non-coding secti ...
... the ribosomes, the protein synthesis factories in the cell. It is coded so that every three nucleotides (a codon) correspond to one amino acid. In eukaryotic cells, once precursor mRNA (pre-mRNA) has been transcribed from DNA, it is processed to mature mRNA. This removes its introns—non-coding secti ...
Document
... transfer RNA Small, ~80 nucleotides long. tRNA exists as a single-stranded molecule. However, regions of double helix can form where there is some base pair complementation (U and A , G and C), resulting in hairpin loops. The RNA molecule with its hairpin loops is said to have a secondary structure ...
... transfer RNA Small, ~80 nucleotides long. tRNA exists as a single-stranded molecule. However, regions of double helix can form where there is some base pair complementation (U and A , G and C), resulting in hairpin loops. The RNA molecule with its hairpin loops is said to have a secondary structure ...