Composition of splicing complex in chloroplasts identified
... green fluorescent protein, the chloroplasts fluoresce red. integrated into their cells. Chloroplasts therefore have their own genetic material - a relic from the Credit: General and Molecular Botany, RUB cyanobacterial genome. However, the chloroplasts are dependent on the communication with the cel ...
... green fluorescent protein, the chloroplasts fluoresce red. integrated into their cells. Chloroplasts therefore have their own genetic material - a relic from the Credit: General and Molecular Botany, RUB cyanobacterial genome. However, the chloroplasts are dependent on the communication with the cel ...
12-Transcription-The Relationship Between Genes and Proteins
... For short primary transcripts with few introns, polyadenylation, cleavage, and splicing usually follows termination, as shown. For large genes with multiple introns, introns often are spliced out of the nascent RNA before transcription of the gene is complete. Note that the 5′ cap is retained in mat ...
... For short primary transcripts with few introns, polyadenylation, cleavage, and splicing usually follows termination, as shown. For large genes with multiple introns, introns often are spliced out of the nascent RNA before transcription of the gene is complete. Note that the 5′ cap is retained in mat ...
1. How many main types of RNA are there?(B4.2g) a.1 b.3 c
... 15. Chromosome number is reduced by meiosis because between meiosis I and meiosis II A. crossing-over occurs. B. metaphase occurs. C. replication occurs twice. D. replication does not occur. ...
... 15. Chromosome number is reduced by meiosis because between meiosis I and meiosis II A. crossing-over occurs. B. metaphase occurs. C. replication occurs twice. D. replication does not occur. ...
Bio07_TR__U04_CH12.QXD
... ribosome reaches a stop codon, it falls away from the protein chain and the messenger RNA molecule. Transcription has ended. ...
... ribosome reaches a stop codon, it falls away from the protein chain and the messenger RNA molecule. Transcription has ended. ...
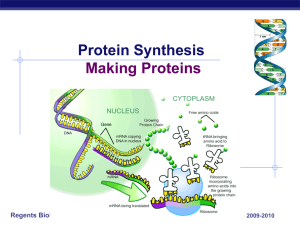
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... several initiation factors, and this complex in turn binds to mRNA (step 1). In bacteria, this binding involves a sequence of up to six ribonucleotides (AGGAGG, not shown), which precedes the initial AUG start codon of mRNA. This sequence (containing only purines and called the Shine-Dalgarno sequen ...
... several initiation factors, and this complex in turn binds to mRNA (step 1). In bacteria, this binding involves a sequence of up to six ribonucleotides (AGGAGG, not shown), which precedes the initial AUG start codon of mRNA. This sequence (containing only purines and called the Shine-Dalgarno sequen ...
Exam 2
... a. methanogenesis; lithotroph. b. respiration; heterotroph. c. fermentation; organotroph. d. carbon fixation; phototroph. e. none of the above. 25. Glycolytic reactions with a near-zero ∆Go’ can particpate in the over all pathway of gluconeogenesis because they are: a. reversible. b. irreversible. c ...
... a. methanogenesis; lithotroph. b. respiration; heterotroph. c. fermentation; organotroph. d. carbon fixation; phototroph. e. none of the above. 25. Glycolytic reactions with a near-zero ∆Go’ can particpate in the over all pathway of gluconeogenesis because they are: a. reversible. b. irreversible. c ...
Text S4.
... To estimate c1/rwt, we utilized the fact that a fitness cost of 3.2% was observed for a misfolded protein expressed at 0.1% of the proteome of the yeast cell [6]. In other words, ...
... To estimate c1/rwt, we utilized the fact that a fitness cost of 3.2% was observed for a misfolded protein expressed at 0.1% of the proteome of the yeast cell [6]. In other words, ...
Lecture Notes - Course Notes
... as post-transcriptional processing, involving cleavages of some sequences and additions of others. The fully processed, mature mRNA, is then transported to the cytoplasm, where translation takes place. It is the 3’ to 5’ strand of the DNA that is usually transcribed, but the 5’ to 3’ sequence of the ...
... as post-transcriptional processing, involving cleavages of some sequences and additions of others. The fully processed, mature mRNA, is then transported to the cytoplasm, where translation takes place. It is the 3’ to 5’ strand of the DNA that is usually transcribed, but the 5’ to 3’ sequence of the ...
EXAM Banswers2 - HonorsBiologyWiki
... 15. Chromosome number is reduced by meiosis because between meiosis I and meiosis II A. crossing-over occurs. B. metaphase occurs. C. replication occurs twice. D. replication does not occur. ...
... 15. Chromosome number is reduced by meiosis because between meiosis I and meiosis II A. crossing-over occurs. B. metaphase occurs. C. replication occurs twice. D. replication does not occur. ...
DNA Replication - :: FAPERTA UGM
... experimental conditions, at essentially all developmental stages, or in virtually all cells. ...
... experimental conditions, at essentially all developmental stages, or in virtually all cells. ...
Biology-Chapter8 (Biology
... A. DNA, mRNA, mRNA, polypeptide, enzyme B. DNA, mRNA, tRNA, polypeptide, enzyme C. enzyme, polypeptide, mRNA, mRNA, DNA D. mRNA, DNA, mRNA, enzyme, polypeptide 9. Proteins are built up or synthesized by the code stored in the DNA molecules. Which concept about protein synthesis in an organism is NOT ...
... A. DNA, mRNA, mRNA, polypeptide, enzyme B. DNA, mRNA, tRNA, polypeptide, enzyme C. enzyme, polypeptide, mRNA, mRNA, DNA D. mRNA, DNA, mRNA, enzyme, polypeptide 9. Proteins are built up or synthesized by the code stored in the DNA molecules. Which concept about protein synthesis in an organism is NOT ...
IN VITRO TRANSCRIPTION . TRANSLATION - UTH e
... transcripts. Typically, eukaryotic mRNAs are characterized by two post-transcriptional modifications: a 5'-7 methyl-GTP cap and a 3' poly(A) tail. Both modifications contribute to the stability of the mRNA by preventing degradation. Additionally, the 5' cap structure enhances the translation of mRNA ...
... transcripts. Typically, eukaryotic mRNAs are characterized by two post-transcriptional modifications: a 5'-7 methyl-GTP cap and a 3' poly(A) tail. Both modifications contribute to the stability of the mRNA by preventing degradation. Additionally, the 5' cap structure enhances the translation of mRNA ...
Genomics
... Translation • mRNA migrates out of the nucleus to the ribosome • Protein synthesis takes place based on the genetic code • A three base codon codes for an amino acid ...
... Translation • mRNA migrates out of the nucleus to the ribosome • Protein synthesis takes place based on the genetic code • A three base codon codes for an amino acid ...
No Slide Title
... Generate hypotheses about the mechanisms underlying observed phenotypes (disease) Ability to uncover unanticipated connections ...
... Generate hypotheses about the mechanisms underlying observed phenotypes (disease) Ability to uncover unanticipated connections ...
Pre-post test questions
... bioinformatics and translation and the difficult concept of where translation starts. 15. Individuals with the diseases -thalassemia and sickle cell anemia both have mutations in the gene for hemoglobin. How could mutations in the same gene cause two different disease phenotypes? The different mut ...
... bioinformatics and translation and the difficult concept of where translation starts. 15. Individuals with the diseases -thalassemia and sickle cell anemia both have mutations in the gene for hemoglobin. How could mutations in the same gene cause two different disease phenotypes? The different mut ...
Gene Section YPEL3 (yippee-like 3 (Drosophila)) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... colonies compared to uninduced cells. YPEL3 expressing U2OS and MCF7 cells also showed an increase in cellular senescence as shown by increases β-galactosidase activity and the appearance of foci within the nuclei of senescent cells (SAHF) (Kelley et al., 2010). ...
... colonies compared to uninduced cells. YPEL3 expressing U2OS and MCF7 cells also showed an increase in cellular senescence as shown by increases β-galactosidase activity and the appearance of foci within the nuclei of senescent cells (SAHF) (Kelley et al., 2010). ...
Slide 1
... be highly diagnostic of a particular organism or group of related organisms. Signature sequences can be used to generate specific phylogenetic probes, useful for FISH or microbial community analyses. ...
... be highly diagnostic of a particular organism or group of related organisms. Signature sequences can be used to generate specific phylogenetic probes, useful for FISH or microbial community analyses. ...
Mahoney Abstract for Pathway to Independence Grant
... subfamily of RGS proteins, uniquely identifies smooth muscle cells (SMCs) from arteries relative to veins. The RGS family of proteins functions to control the duration of cellular signals mediated through G-Protein Coupled Receptors (GPCRs). RGS proteins act as GTPase Activating Proteins (GAPs) for ...
... subfamily of RGS proteins, uniquely identifies smooth muscle cells (SMCs) from arteries relative to veins. The RGS family of proteins functions to control the duration of cellular signals mediated through G-Protein Coupled Receptors (GPCRs). RGS proteins act as GTPase Activating Proteins (GAPs) for ...
origin of genes, the genetic code, and genomes
... A pocket at the center of the GlmS ribozyme specifically binds a molecule of glucosamine-6phosphate close to the scissile phosphate; the glucosamine-6-phosphate plays a key role in GlmS acid-base catalysis. Similar recruitment of amino acids as cofactors might have been the first step from an RNA wo ...
... A pocket at the center of the GlmS ribozyme specifically binds a molecule of glucosamine-6phosphate close to the scissile phosphate; the glucosamine-6-phosphate plays a key role in GlmS acid-base catalysis. Similar recruitment of amino acids as cofactors might have been the first step from an RNA wo ...
Protein Synthesis powerpoint
... Eukaryotic cells modify RNA after transcription • Enzymes in the eukaryotic nucleus modify premRNA before the genetic messages are dispatched to the cytoplasm. • At the 5’ end of the pre-mRNA molecule, a modified form of guanine is added, the 5’ cap. • This helps protect mRNA from hydrolytic enzyme ...
... Eukaryotic cells modify RNA after transcription • Enzymes in the eukaryotic nucleus modify premRNA before the genetic messages are dispatched to the cytoplasm. • At the 5’ end of the pre-mRNA molecule, a modified form of guanine is added, the 5’ cap. • This helps protect mRNA from hydrolytic enzyme ...
Macromolecules
... 3) What are two monomers of lipids 4) Name 2 polymers of lipids. 5) What are phospholipids for? Is the tail hydrophobic or hydrophilic? Is the head hydrophobic or hydrophilic? ...
... 3) What are two monomers of lipids 4) Name 2 polymers of lipids. 5) What are phospholipids for? Is the tail hydrophobic or hydrophilic? Is the head hydrophobic or hydrophilic? ...