Von Neumann`s Quintessential Message: Genotype C Ribotype D
... multicellular entity, to reproduce, and nally to die. This information is transcribed from DNA—by enzymes—to generate another class of molecules called ribonucleic acids (RNA). From there, it is translated to generate specic proteins, which are the molecules that underlie the cell’s daily activiti ...
... multicellular entity, to reproduce, and nally to die. This information is transcribed from DNA—by enzymes—to generate another class of molecules called ribonucleic acids (RNA). From there, it is translated to generate specic proteins, which are the molecules that underlie the cell’s daily activiti ...
Document
... accuracy, errors do occur (< 1 error per billion bases copied) – mutations. • If cell survives the mutation, it will be copied every time DNA is replicated • Mutations cause diversity within species • Some mutations have no effect, some are lethal and in very rare occasions mutations are useful – ba ...
... accuracy, errors do occur (< 1 error per billion bases copied) – mutations. • If cell survives the mutation, it will be copied every time DNA is replicated • Mutations cause diversity within species • Some mutations have no effect, some are lethal and in very rare occasions mutations are useful – ba ...
Exam 2 Full v4A Bio200 Sum12
... Cancer is a complex and extremely diverse system of related diseases. We know that these diseases are the result of multiple mutations in cells causing an array of intracellular changes. No single mutation is cancer. Somehow, the combinations of multiple changes lead to malignant unregulated cell gr ...
... Cancer is a complex and extremely diverse system of related diseases. We know that these diseases are the result of multiple mutations in cells causing an array of intracellular changes. No single mutation is cancer. Somehow, the combinations of multiple changes lead to malignant unregulated cell gr ...
Nilgun-Replication05..
... 1) Viruses with dsRNA genomes are complex, contain several segments, and an RNA-dependentRNA-Polymerase. 2) Particles enter cells via endocytosis. 3) Proteolytic digestion results in subviral particles. 4) Core particle moves into the cytoplasm & begin synthesis of early viral mRNAs from the dsRNA g ...
... 1) Viruses with dsRNA genomes are complex, contain several segments, and an RNA-dependentRNA-Polymerase. 2) Particles enter cells via endocytosis. 3) Proteolytic digestion results in subviral particles. 4) Core particle moves into the cytoplasm & begin synthesis of early viral mRNAs from the dsRNA g ...
Personalized medicine - Pitt Department of Biomedical Informatics
... efforts that can be disseminated to a variety of stakeholders, including biomedical scientists, clinicians, and patients.” • Translational = benchside to bedside Atul Butte, JAMIA 2008;15:709-714 doi:10.1197 ...
... efforts that can be disseminated to a variety of stakeholders, including biomedical scientists, clinicians, and patients.” • Translational = benchside to bedside Atul Butte, JAMIA 2008;15:709-714 doi:10.1197 ...
The Discovery, Structure, and Function of DNA
... Transcription: RNA polymerase then goes to work at the promoter site, and moves along the DNA strand, producing a complementary strand of messenger RNA (mRNA), except that U matches with A. When the process reaches a certain termination sequence, the process halts and the mRNA is passes out of the n ...
... Transcription: RNA polymerase then goes to work at the promoter site, and moves along the DNA strand, producing a complementary strand of messenger RNA (mRNA), except that U matches with A. When the process reaches a certain termination sequence, the process halts and the mRNA is passes out of the n ...
Gene Section JARID1A (jumonji, AT rich interactive domain 1A (RBBP2-like))
... From centromere to telomere, yielding mRNA of 6,5 kb. ...
... From centromere to telomere, yielding mRNA of 6,5 kb. ...
OPMD (Occulopharyngeal Muscular Dystrophy)
... Abnormal expansion of a (GCG)6 trinucleotide repeat at the 5’end (exon 1) of the coding region of the poly(A)-binding protein nuclear 1 gene (PABPN1) The (GCG)6 codes for the first 6 alanines in a homopolymeric stretch of 10 alanines. In most patients [8], the (GCG)6 repeat is expanded to (GCG)8-13 ...
... Abnormal expansion of a (GCG)6 trinucleotide repeat at the 5’end (exon 1) of the coding region of the poly(A)-binding protein nuclear 1 gene (PABPN1) The (GCG)6 codes for the first 6 alanines in a homopolymeric stretch of 10 alanines. In most patients [8], the (GCG)6 repeat is expanded to (GCG)8-13 ...
Topic 2 Review
... codon in the A site with the anticodon of an incoming molecule of tRNA with its amino acid. Peptide bond formation: component of large ribosomal subunit catalyzes the formation of a peptide bond between the amino acid extending from the P site and the newly arrived amino acid in the A site. The poly ...
... codon in the A site with the anticodon of an incoming molecule of tRNA with its amino acid. Peptide bond formation: component of large ribosomal subunit catalyzes the formation of a peptide bond between the amino acid extending from the P site and the newly arrived amino acid in the A site. The poly ...
Zebrafish Jeopardy
... There are 250 primary spermatocytes present. This is the number of mature sperm resulting from those spermatocytes. ...
... There are 250 primary spermatocytes present. This is the number of mature sperm resulting from those spermatocytes. ...
Identification of the factors that interact with NCBP, an 80 kDa
... EGY48 was used some shifted bands were observed due to yeast endogenous proteins, however none of them were strictly dependent on the cap structure of the probe (lanes 1-3). We could not detect any additional band with extracts from yeast cells expressing only NCBP or NIP1 (lanes 7-12). It is worth ...
... EGY48 was used some shifted bands were observed due to yeast endogenous proteins, however none of them were strictly dependent on the cap structure of the probe (lanes 1-3). We could not detect any additional band with extracts from yeast cells expressing only NCBP or NIP1 (lanes 7-12). It is worth ...
File
... Process is called RNA splicing (processing) Exons Coding region of DNA and mRNA that will be translated (Expressed) VERY important part of mRNA…it is carrying the message from DNA (def can’t cut this out) ...
... Process is called RNA splicing (processing) Exons Coding region of DNA and mRNA that will be translated (Expressed) VERY important part of mRNA…it is carrying the message from DNA (def can’t cut this out) ...
GZMB- Kolloquium - Georg-August
... How does a major fungal pathogen adapt to its human host? - combining experimentation and modelling to understand stress and nutrient adaptation in Candida albicans. ...
... How does a major fungal pathogen adapt to its human host? - combining experimentation and modelling to understand stress and nutrient adaptation in Candida albicans. ...
Protein Synthesis Project 1516
... however, are not directly recognized by the corresponding amino acids. Another type of RNA called transfer RNA (tRNA) is needed to bring the mRNA and amino acids together. As the code carried by m ...
... however, are not directly recognized by the corresponding amino acids. Another type of RNA called transfer RNA (tRNA) is needed to bring the mRNA and amino acids together. As the code carried by m ...
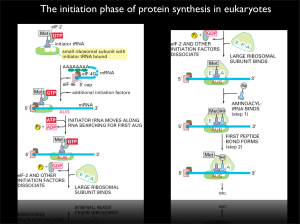
The initiation phase of protein synthesis in eukaryotes
... Figure 7 The binding of the 4E-BPs to eIF4E is regulated by phosphorylation. The 4E-BPs and eIF4Gs compete for a common binding site on eIF4E. Various stimuli increase the phosphorylation of the 4E-BPs. Hyperphosphorylated 4E-BPs have a relatively low affinity for eIF4E. Conversely, a decrease in 4E ...
... Figure 7 The binding of the 4E-BPs to eIF4E is regulated by phosphorylation. The 4E-BPs and eIF4Gs compete for a common binding site on eIF4E. Various stimuli increase the phosphorylation of the 4E-BPs. Hyperphosphorylated 4E-BPs have a relatively low affinity for eIF4E. Conversely, a decrease in 4E ...
Study Guide – Unit 4: Genetics
... a. Cells with mutations will always make normal proteins. b. Some mutations occur when one nitrogen base is substituted for another. c. Some mutations occur when chromosomes don’t separate correctly during meiosis. d. Mutations that occur in a body cell can be passed to an offspring. 18. T F All mut ...
... a. Cells with mutations will always make normal proteins. b. Some mutations occur when one nitrogen base is substituted for another. c. Some mutations occur when chromosomes don’t separate correctly during meiosis. d. Mutations that occur in a body cell can be passed to an offspring. 18. T F All mut ...
Alternative Splicing A very short introduction (in plants)
... Genome-wide analyses of alternative splicing in plants: Opportunities and challenges Genome Res. 2008. 18:1381-1392 ...
... Genome-wide analyses of alternative splicing in plants: Opportunities and challenges Genome Res. 2008. 18:1381-1392 ...
Life
... • The link between nitrogeneous base and amino acid is a molecule called tRNA (transfer RNA) ...
... • The link between nitrogeneous base and amino acid is a molecule called tRNA (transfer RNA) ...
9/19/14 Notes on Macromolecules (powerpoint)
... • Polysaccharides are chains of 3 or more monosaccharides such as starch, which is an example of a macromolecule (a large molecule made up of smaller molecules). • In organisms, polysaccharides function as store houses of energy. ...
... • Polysaccharides are chains of 3 or more monosaccharides such as starch, which is an example of a macromolecule (a large molecule made up of smaller molecules). • In organisms, polysaccharides function as store houses of energy. ...
Genetic regulation in eukaryotes 0. Introduction
... anchored a receptor inducing a strictly regulated cascade of biochemical events (this is far the most frequent situation), called signal transduction. Alternatively, signal molecules can enter the cell and exert their effects in the cytoplasm or in the nucleus. There are three basic types of them. T ...
... anchored a receptor inducing a strictly regulated cascade of biochemical events (this is far the most frequent situation), called signal transduction. Alternatively, signal molecules can enter the cell and exert their effects in the cytoplasm or in the nucleus. There are three basic types of them. T ...
RNA
... the affected RNA editing site is in the ndhD transcript. What are some explanations for these observations? [from Kotera et al. Nature 433:326] ...
... the affected RNA editing site is in the ndhD transcript. What are some explanations for these observations? [from Kotera et al. Nature 433:326] ...
Exam II Notes DNA
... so the two strands can be separated. Then the RNA bases are matched to the DNA strand (they are complementary) to complete transcription. C. After the gene is transcribed into mRNA, it travels outside the nucleus to the ribosome where translation to a protein can occur. IX. Translation A. Once an mR ...
... so the two strands can be separated. Then the RNA bases are matched to the DNA strand (they are complementary) to complete transcription. C. After the gene is transcribed into mRNA, it travels outside the nucleus to the ribosome where translation to a protein can occur. IX. Translation A. Once an mR ...
divergent transcription
... segments, termed exons (expressed sequences), are ligated to form a functional RNA. This process involves a large complex of proteins and auxiliary RNAs called small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs), which interact to form a spliceosome. The function of the five snRNAs (U1, U2, U4, U5, U6) in the spliceosome i ...
... segments, termed exons (expressed sequences), are ligated to form a functional RNA. This process involves a large complex of proteins and auxiliary RNAs called small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs), which interact to form a spliceosome. The function of the five snRNAs (U1, U2, U4, U5, U6) in the spliceosome i ...
Mapping the Body.indd
... b) Help the bacteria to not be eaten by immune system cells. c) Help the bacteria to reproduce. d) Help the bacteria to find food. e) both a and b f) both c and d 64) True or False? Gram negative bacteria are pathogens, while Gram positives are beneficial and many live in our gut. 65) True or False? ...
... b) Help the bacteria to not be eaten by immune system cells. c) Help the bacteria to reproduce. d) Help the bacteria to find food. e) both a and b f) both c and d 64) True or False? Gram negative bacteria are pathogens, while Gram positives are beneficial and many live in our gut. 65) True or False? ...