psychweek3 - Ms. Bishop`s Classroom
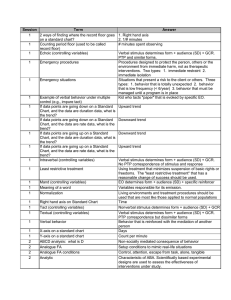
... overweight/normal, male/female, number of bites, number of items ordered, amount of food left, number of chews, amount of time spent eating) 2. How would you measure this? (count and record, tally, stopwatch?) ...
... overweight/normal, male/female, number of bites, number of items ordered, amount of food left, number of chews, amount of time spent eating) 2. How would you measure this? (count and record, tally, stopwatch?) ...
GUIDE10
... the removal of an aversive stimulus. Both positive and negative reinforcement strengthen behavior. Any event that decreases a behavior either by presenting an aversive stimulus or by removing a positive one is called punishment. The effects of punishment are much less predictable than those of rewar ...
... the removal of an aversive stimulus. Both positive and negative reinforcement strengthen behavior. Any event that decreases a behavior either by presenting an aversive stimulus or by removing a positive one is called punishment. The effects of punishment are much less predictable than those of rewar ...
Notes
... – simple associations between stimuli • Today’s researchers – considering how imagined stimuli (e.g., thoughts) can produce a response ...
... – simple associations between stimuli • Today’s researchers – considering how imagined stimuli (e.g., thoughts) can produce a response ...
UNIT VI Notes File
... Perceived control is basic to human functioning – people that lack control are more likely be sick and even have shorter life spans (stress = more cortisol in the body) People differ in how much control they believe they have in their lives – External Locus of Control: the perception that we lack co ...
... Perceived control is basic to human functioning – people that lack control are more likely be sick and even have shorter life spans (stress = more cortisol in the body) People differ in how much control they believe they have in their lives – External Locus of Control: the perception that we lack co ...
i Learning
... Cognition and Operant Conditioning Overjustification Effect the effect of promising a reward for doing what one already likes to do the person may now see the reward, rather than intrinsic interest,, as the motivation for performing the task ...
... Cognition and Operant Conditioning Overjustification Effect the effect of promising a reward for doing what one already likes to do the person may now see the reward, rather than intrinsic interest,, as the motivation for performing the task ...
File
... behavior made him an influential, but controversial figure. Many psychologists criticized Skinner for underestimating the importance of cognitive and biological constraints. ...
... behavior made him an influential, but controversial figure. Many psychologists criticized Skinner for underestimating the importance of cognitive and biological constraints. ...
Session
... Behavior that requires some "opportunity" or specific antecedent to occur. Ex: in order to follow directions, there must first be a direction given. Refers to a change in observed behavior when antecedent stimuli are changed Reinforcing a behavior in the presence of some antecedent and extinguishing ...
... Behavior that requires some "opportunity" or specific antecedent to occur. Ex: in order to follow directions, there must first be a direction given. Refers to a change in observed behavior when antecedent stimuli are changed Reinforcing a behavior in the presence of some antecedent and extinguishing ...
Consequences of Behavior
... influence will depend on how well the individual remembers the model’s action after the model is no longer readily available. OB_UG_2002 GSM ...
... influence will depend on how well the individual remembers the model’s action after the model is no longer readily available. OB_UG_2002 GSM ...
Unit 5
... Primary reinforcer - any reinforcer that is naturally reinforcing by meeting a basic biological need, such as hunger, thirst, or touch. Secondary reinforcer - any reinforcer that becomes reinforcing after being paired with a primary reinforcer, such as praise, tokens, gold stars, or ...
... Primary reinforcer - any reinforcer that is naturally reinforcing by meeting a basic biological need, such as hunger, thirst, or touch. Secondary reinforcer - any reinforcer that becomes reinforcing after being paired with a primary reinforcer, such as praise, tokens, gold stars, or ...
Learning - Villanova University
... - role of classical conditioning: CS (dog), US (dog bite) UR (pain, fear) => CS (dog) – fear response; role of operant conditioning: avoid CS (dog) reduces anxiety => continue avoiding CS - treatment: pair fear stimuli with relaxation (or other pleasurable stimuli) other things: fear of some sti ...
... - role of classical conditioning: CS (dog), US (dog bite) UR (pain, fear) => CS (dog) – fear response; role of operant conditioning: avoid CS (dog) reduces anxiety => continue avoiding CS - treatment: pair fear stimuli with relaxation (or other pleasurable stimuli) other things: fear of some sti ...
Basic Concepts and Principles of Behavior Analysis (PSY 5231-01)
... from the experimental analysis of behavior and how they relate to the profession of applied behavior analysis. The class emphasizes Content Area #3 (Basic principles of Behavior) and Content Area #2 ( Definition & Characteristics of Applied Behavior Analysis) of the Applied Behavior Analysis Task Li ...
... from the experimental analysis of behavior and how they relate to the profession of applied behavior analysis. The class emphasizes Content Area #3 (Basic principles of Behavior) and Content Area #2 ( Definition & Characteristics of Applied Behavior Analysis) of the Applied Behavior Analysis Task Li ...
Advanced - Dick Malott
... Goal: If you master these objectives, you will have an excellent understanding of the most commonly confused issues in the field of behavior analysis, issues about which even many professional behavior analysts seem confused. (Incidentally, the confusion usually takes the form of erroneously classif ...
... Goal: If you master these objectives, you will have an excellent understanding of the most commonly confused issues in the field of behavior analysis, issues about which even many professional behavior analysts seem confused. (Incidentally, the confusion usually takes the form of erroneously classif ...
1st Semester Final Exam "Cliff Notes" Review Sheet (Units 1-7)
... Why aren’t intuition and common sense enough to provide information about people’s thoughts and behaviors? What are hindsight and overconfidence? 4-2 Scientific attitude and critical thinking What are 3 main components of the scientific attitude? Who is James Randi? What is critical thinking? Module ...
... Why aren’t intuition and common sense enough to provide information about people’s thoughts and behaviors? What are hindsight and overconfidence? 4-2 Scientific attitude and critical thinking What are 3 main components of the scientific attitude? Who is James Randi? What is critical thinking? Module ...
Prominent Theorist Research
... environments as well as the original environment. If something that is reinforced differently in different environments then that particular behavior could only exist in one place. Finally, studying behavior should be viewed as studying nature. Even though Skinner’s studies took place in a laborator ...
... environments as well as the original environment. If something that is reinforced differently in different environments then that particular behavior could only exist in one place. Finally, studying behavior should be viewed as studying nature. Even though Skinner’s studies took place in a laborator ...
Abnormal-Psychology-in-a-Changing-World-7th
... Which of the following is NOT one of the three regions of the mind described by Freud? a. the conscious c. the preconscious b. the superconscious d. the unconscious ...
... Which of the following is NOT one of the three regions of the mind described by Freud? a. the conscious c. the preconscious b. the superconscious d. the unconscious ...
Behavior Modification (PSYC B45)
... Instructor’s Goals: At the end of this course you should have a better understanding and appreciation of the multitude of factors that contribute to behavior. You will be able to demonstrate mastery of the fundamental principles and assumptions of operant conditioning; the ability to correctly apply ...
... Instructor’s Goals: At the end of this course you should have a better understanding and appreciation of the multitude of factors that contribute to behavior. You will be able to demonstrate mastery of the fundamental principles and assumptions of operant conditioning; the ability to correctly apply ...
Learning - Ed W. Clark High School
... – A schedule that a rewards a learner only for the first correct response after some defined period of time. – Example: B.F. Skinner put rats in a box with a lever connected to a feeder. It only provided a reinforcement after 60 seconds. The rats quickly learned that it didn’t matter how early or of ...
... – A schedule that a rewards a learner only for the first correct response after some defined period of time. – Example: B.F. Skinner put rats in a box with a lever connected to a feeder. It only provided a reinforcement after 60 seconds. The rats quickly learned that it didn’t matter how early or of ...
Verbal Behavior Glossary Mark L. Sundberg 2/19/04 Audience
... some aspect of a speaker’s own verbal behavior functions as an SD, or an MO, for additional speaker verbal behavior. The autoclitic relation can be thought of as verbal behavior about verbal behavior. Automatic punishment Automatic punishment is a type of conditioned punishment where a response prod ...
... some aspect of a speaker’s own verbal behavior functions as an SD, or an MO, for additional speaker verbal behavior. The autoclitic relation can be thought of as verbal behavior about verbal behavior. Automatic punishment Automatic punishment is a type of conditioned punishment where a response prod ...
CONSUMER LEARNING
... and/experiences all the time; he interprets these, learns from them and stores these in his memory for retrieval. This addition of knowledge to the memory bank may alter/modify existing information (this entire bank is called the Associative Network). The upgraded information provides a basis for fu ...
... and/experiences all the time; he interprets these, learns from them and stores these in his memory for retrieval. This addition of knowledge to the memory bank may alter/modify existing information (this entire bank is called the Associative Network). The upgraded information provides a basis for fu ...
Chapter 5 Learning (Updated)
... • Describe basic classical conditioning phenomena, such as acquisition, extinction, spontaneous recovery, generalization, discrimination, and higher-order learning. • Predict the effects of operant conditioning (e.g., positive reinforcement, negative reinforcement, punishment). • Predict how practic ...
... • Describe basic classical conditioning phenomena, such as acquisition, extinction, spontaneous recovery, generalization, discrimination, and higher-order learning. • Predict the effects of operant conditioning (e.g., positive reinforcement, negative reinforcement, punishment). • Predict how practic ...
Operant Conditioning - Parkway C-2
... from happening again by following it with a negative consequence ...
... from happening again by following it with a negative consequence ...
Chapter 5: Learning
... Punishment Skinner strongly opposed the use of punishment; he advocated the greater use of positive reinforcement to strengthen desirable behaviors. The effectiveness of positive reinforcement can be enhanced in several ways. a. Reinforce an incompatible behavior (alternative behavior) b. Stop reinf ...
... Punishment Skinner strongly opposed the use of punishment; he advocated the greater use of positive reinforcement to strengthen desirable behaviors. The effectiveness of positive reinforcement can be enhanced in several ways. a. Reinforce an incompatible behavior (alternative behavior) b. Stop reinf ...
Learning and Behaviorism
... Sultan, one of Kohler's chimpanzes, learned to use a stick to pull bananas from outside of his cage by putting pieces of stick together. Given two sticks that could be fitted together to make a single pole that was long enough to reach the bananas, aligned the sticks and in a flash of sudden inspira ...
... Sultan, one of Kohler's chimpanzes, learned to use a stick to pull bananas from outside of his cage by putting pieces of stick together. Given two sticks that could be fitted together to make a single pole that was long enough to reach the bananas, aligned the sticks and in a flash of sudden inspira ...