Assumptions of Behaviorism
... A prompt of cue that comes before a behavior that results in the correct behavior being elicited. ...
... A prompt of cue that comes before a behavior that results in the correct behavior being elicited. ...
Chapter_2 - Forensic Consultation
... Correlational study: attempt to find positive/negative relationship between variables. Correlations are reported as numbers from –1.0 (perfect negative correlation) to +1.0 (perfect positive correlation) ...
... Correlational study: attempt to find positive/negative relationship between variables. Correlations are reported as numbers from –1.0 (perfect negative correlation) to +1.0 (perfect positive correlation) ...
Chapter15
... For example, “ate because hungry” “ate because good price, 6 hours since last meal, etc.” Free Will vs. Determinism: -Free Will: We are free and spontaneous. We are responsible for what we did. -Determinism: Our behaviors are determined by Environmental control. For example, you bought a computer ...
... For example, “ate because hungry” “ate because good price, 6 hours since last meal, etc.” Free Will vs. Determinism: -Free Will: We are free and spontaneous. We are responsible for what we did. -Determinism: Our behaviors are determined by Environmental control. For example, you bought a computer ...
Abnormal Behavior in Historical Context
... community has done a remarkable job of opening the doors of college to more and more students, we have not seen equal strides in the number of students who actually complete four-year degrees. (Education Trust, 2004) ...
... community has done a remarkable job of opening the doors of college to more and more students, we have not seen equal strides in the number of students who actually complete four-year degrees. (Education Trust, 2004) ...
MAET 2009 Year 2 - MSU EdTech Sandbox
... Skinner’s Influence • Find software on the web that uses behaviorist principles to teach • http://viking.coe.uh.edu/~ichen/ebook/etit/behavior.htm ...
... Skinner’s Influence • Find software on the web that uses behaviorist principles to teach • http://viking.coe.uh.edu/~ichen/ebook/etit/behavior.htm ...
Psychology - Elyria Catholic High School
... (yuch – mind) (logos – study) • The Study of Human Thought and Behavior. ...
... (yuch – mind) (logos – study) • The Study of Human Thought and Behavior. ...
File
... etc.), with the goal of reaching one’s full potential once basic needs are met. • Developed by Abraham Maslow and Carl Rogers – behavior reflects innate ‘actualization’ – focus on conscious forces and self perception – more positive view of basic forces than Freud’s ...
... etc.), with the goal of reaching one’s full potential once basic needs are met. • Developed by Abraham Maslow and Carl Rogers – behavior reflects innate ‘actualization’ – focus on conscious forces and self perception – more positive view of basic forces than Freud’s ...
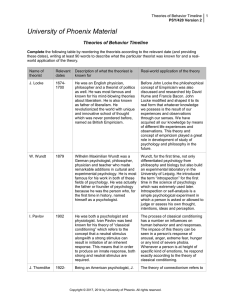
psy420r2_theories_of_behavior_timeline_1
... physiologist. Ivan Pavlov was best known for his theory of “classical conditioning” which refers to the concept that a neutral stimulus alongwith a strong stimulus can result in initiation of an inherent response. This means that in order to produce an innate response, both strong and neutral stimul ...
... physiologist. Ivan Pavlov was best known for his theory of “classical conditioning” which refers to the concept that a neutral stimulus alongwith a strong stimulus can result in initiation of an inherent response. This means that in order to produce an innate response, both strong and neutral stimul ...
Educ2130 chapter 1 B
... * Behaviors and actions, rather than thoughts or emotions, are worthy of study. * Behaviorists believe that all behavior is learned and can also be unlearned and replaced by new behaviors. * A key element to this theory of learning is the rewarded response. The desired response must be rewarded in o ...
... * Behaviors and actions, rather than thoughts or emotions, are worthy of study. * Behaviorists believe that all behavior is learned and can also be unlearned and replaced by new behaviors. * A key element to this theory of learning is the rewarded response. The desired response must be rewarded in o ...
Chapter 1 ppt - s3.amazonaws.com
... Founded the school of psychoanalysis Focused on unconscious motives and internal conflicts. Freud primarily worked with patients directly not by testing things in a lab. Really focused on unconscious activities primarily those that were sexual and aggressive in nature. Psychodynamic: most of what ex ...
... Founded the school of psychoanalysis Focused on unconscious motives and internal conflicts. Freud primarily worked with patients directly not by testing things in a lab. Really focused on unconscious activities primarily those that were sexual and aggressive in nature. Psychodynamic: most of what ex ...
Four
... Make It Quick and Strong Enough Punish the Act, Not the Person It Should Be Consistent Across Time and People • It Should Have Informational Value • It Is More Effective in a Warm and Supportive Relationship ...
... Make It Quick and Strong Enough Punish the Act, Not the Person It Should Be Consistent Across Time and People • It Should Have Informational Value • It Is More Effective in a Warm and Supportive Relationship ...
Chapter 9: Behavior Therapy
... Based on the principles and procedures of the scientific method Learning new behaviors is the core of the therapy Interventions tailored to fit individual needs Therapy deals with client’s current problems and the factors influencing them Does not deal with historical determinants Treatment goals ar ...
... Based on the principles and procedures of the scientific method Learning new behaviors is the core of the therapy Interventions tailored to fit individual needs Therapy deals with client’s current problems and the factors influencing them Does not deal with historical determinants Treatment goals ar ...
LECTURE 11 THE MEANING OF CRIME: SOCIAL PROCESS
... implicitly use one or more social learning variables. Loss of privileges (visits, temporary absences) or loss of remission are negative punishments… taking away or withholding positively valued stimuli. ...
... implicitly use one or more social learning variables. Loss of privileges (visits, temporary absences) or loss of remission are negative punishments… taking away or withholding positively valued stimuli. ...
1. Introduction and Chapter 1 What is Applied Behavior
... o What events determine activity patterns? o What events determine verbal reports? o Freudian schema entirely fictional: Show me the superego o How to measure bipolar personality (or manipulate it) independent of verbal report? ...
... o What events determine activity patterns? o What events determine verbal reports? o Freudian schema entirely fictional: Show me the superego o How to measure bipolar personality (or manipulate it) independent of verbal report? ...
Behavior - Catawba County Schools
... organism reacts to changes in its internal condition or external environment. On a sheet of paper, make a list of as many behaviors as possible. You will have two minutes. 2. After you have finished this section, revisit your list. Write the letter “I” next to any words that describe innate, or unle ...
... organism reacts to changes in its internal condition or external environment. On a sheet of paper, make a list of as many behaviors as possible. You will have two minutes. 2. After you have finished this section, revisit your list. Write the letter “I” next to any words that describe innate, or unle ...
Document
... • Peter has some emotional problems and is acting out in school. His teacher notices that – while bright- he lacks self-esteem. He is left alone at home and is not eating properly. She found out recently that he is also homeless. She believes that with time and help, he can reach his full potential. ...
... • Peter has some emotional problems and is acting out in school. His teacher notices that – while bright- he lacks self-esteem. He is left alone at home and is not eating properly. She found out recently that he is also homeless. She believes that with time and help, he can reach his full potential. ...
Chapter 1 What is Psychology? Philosophical Developments
... The science of behavior and mental processes Behavior—observable actions of a person or animal Mind—thoughts, feelings, sensations, perceptions, memories, dreams, motives and other subjective experiences Science—an objective way to answer questions based on observable facts/data and well-described m ...
... The science of behavior and mental processes Behavior—observable actions of a person or animal Mind—thoughts, feelings, sensations, perceptions, memories, dreams, motives and other subjective experiences Science—an objective way to answer questions based on observable facts/data and well-described m ...
Chapter 1
... The science of behavior and mental processes Behavior—observable actions of a person or animal Mind—thoughts, feelings, sensations, perceptions, memories, dreams, motives and other subjective experiences Science—an objective way to answer questions based on observable facts/data and well-described m ...
... The science of behavior and mental processes Behavior—observable actions of a person or animal Mind—thoughts, feelings, sensations, perceptions, memories, dreams, motives and other subjective experiences Science—an objective way to answer questions based on observable facts/data and well-described m ...
Matching - University of Phoenix
... Match the definitions to the correct theoretical model. 1. _____ Experiences as a child affect life. Child is influenced by caretaker but also has a part in development. 2. _____ 2–3 years of age and the body wants to retain and eliminate. 3. _____ When a stimulus elicits a specific response 4. ____ ...
... Match the definitions to the correct theoretical model. 1. _____ Experiences as a child affect life. Child is influenced by caretaker but also has a part in development. 2. _____ 2–3 years of age and the body wants to retain and eliminate. 3. _____ When a stimulus elicits a specific response 4. ____ ...
A Short History of Psychology
... – Structuralism-study the basic elements that make up human mental experiences – Introspection • Looking inward- analyzing immediate sensations and how they related to one another. ...
... – Structuralism-study the basic elements that make up human mental experiences – Introspection • Looking inward- analyzing immediate sensations and how they related to one another. ...
- OoCities
... Social learning is the theory that we can learn through both observation and direct experience. Social learning theory is an extension of operant conditioning; it assumes that behavior is a function of consequences ∙ it also acknowledges the existence of observational learning and the importance of ...
... Social learning is the theory that we can learn through both observation and direct experience. Social learning theory is an extension of operant conditioning; it assumes that behavior is a function of consequences ∙ it also acknowledges the existence of observational learning and the importance of ...
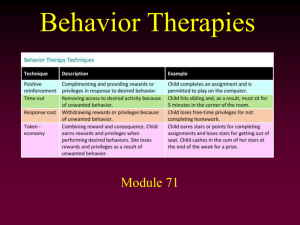
Module 71 - Behavioral Therapy
... • A type of counterconditioning that associates an unpleasant state (such as nausea) with an unwanted behavior • The person is replacing a positive (relaxing) but harmful response with a negative/aversive response • Example with alcoholism: Lace a drink with a drug that makes the person becomes sick ...
... • A type of counterconditioning that associates an unpleasant state (such as nausea) with an unwanted behavior • The person is replacing a positive (relaxing) but harmful response with a negative/aversive response • Example with alcoholism: Lace a drink with a drug that makes the person becomes sick ...
Operant Conditioning
... your teeth, riding a bike, walking to school and so on. Behavior chains are very important to all of us; as is the procedure for building chains, which is called chaining. Instinctive Drift - Although humans, animals, etc., can learn to perform different behaviors, there are times when they stop per ...
... your teeth, riding a bike, walking to school and so on. Behavior chains are very important to all of us; as is the procedure for building chains, which is called chaining. Instinctive Drift - Although humans, animals, etc., can learn to perform different behaviors, there are times when they stop per ...
Theory of planned behavior

In psychology, the theory of planned behavior (abbreviated TPB) is a theory that links beliefs and behavior. The concept was proposed by Icek Ajzen to improve on the predictive power of the theory of reasoned action by including perceived behavioural control. It is one of the most predictive persuasion theories. It has been applied to studies of the relations among beliefs, attitudes, behavioral intentions and behaviors in various fields such as advertising, public relations, advertising campaigns and healthcare.The theory states that attitude toward behavior, subjective norms, and perceived behavioral control, together shape an individual's behavioral intentions and behaviors.