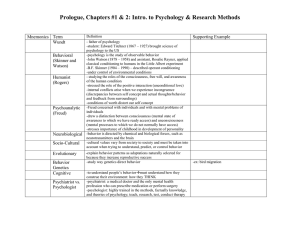
Psychology as a Science
... • A perspective that focuses on the study of conscious experience, the individual’s freedom to choose, and the capacity for personal growth • Stressed the study of conscious experience and an individual’s free will • Healthy individuals should strive to reach their full potential. • Rejected idea th ...
... • A perspective that focuses on the study of conscious experience, the individual’s freedom to choose, and the capacity for personal growth • Stressed the study of conscious experience and an individual’s free will • Healthy individuals should strive to reach their full potential. • Rejected idea th ...
Human Behavioural Science Course 303
... a- anything that reduces an organism drive is negatively reinforcing b- anything that reduces an physical drive is positively reinforcing c- behaviors learned through reinforcement d- anything that produces the unconditioned response e- anything that reduces an organism drive is positively reinforci ...
... a- anything that reduces an organism drive is negatively reinforcing b- anything that reduces an physical drive is positively reinforcing c- behaviors learned through reinforcement d- anything that produces the unconditioned response e- anything that reduces an organism drive is positively reinforci ...
Operant Conditioning
... Operant Conditioning • Operant conditioning investigates the influence of consequences on subsequent behavior. • Operant conditioning investigates the learning of voluntary responses. • It was the dominant school in American psychology from the 1930s through the 1950s. ...
... Operant Conditioning • Operant conditioning investigates the influence of consequences on subsequent behavior. • Operant conditioning investigates the learning of voluntary responses. • It was the dominant school in American psychology from the 1930s through the 1950s. ...
Chapter and Topic of this Review Guide: Chapter 7
... Basic of What Was Done Important Study Albert Bandura Kids watched adults with aggression, then were put into a room with toys and chose to hit a large doll “Bobo Doll” Pavlov Dog salivates when it hears a bell because the bell is associated with food to become a conditioned stimuli Skinner Rat in b ...
... Basic of What Was Done Important Study Albert Bandura Kids watched adults with aggression, then were put into a room with toys and chose to hit a large doll “Bobo Doll” Pavlov Dog salivates when it hears a bell because the bell is associated with food to become a conditioned stimuli Skinner Rat in b ...
mkt348ch1 - Brand Luxury Index
... A revision of the traditional marketing concept that suggests that marketers adhere to principles of social responsibility in the marketing of their goods and services; that is, they must endeavor to satisfy the needs and wants of their target markets in ways that preserve and enhance the well-being ...
... A revision of the traditional marketing concept that suggests that marketers adhere to principles of social responsibility in the marketing of their goods and services; that is, they must endeavor to satisfy the needs and wants of their target markets in ways that preserve and enhance the well-being ...
Behavior
... An INVOLUNTARY behavior is determined by what PRECEDES it Pavlov’s experiments with dogs Pavlov paired a neutral stimulus (a bell) with a meat powder (which made the dog salivate). After continued pairings the dog has become conditioned Eventually, dog salivates to bell alone ...
... An INVOLUNTARY behavior is determined by what PRECEDES it Pavlov’s experiments with dogs Pavlov paired a neutral stimulus (a bell) with a meat powder (which made the dog salivate). After continued pairings the dog has become conditioned Eventually, dog salivates to bell alone ...
Chapter 1
... 7. Which of the following best summarizes Skinner’s ideas about operant conditioning? a. a stimulus paired with a response will, on recurrence, tend to elicit that response again b. learning results from the gradual construction of cognitive maps c. behaviors producing positive consequences tend to ...
... 7. Which of the following best summarizes Skinner’s ideas about operant conditioning? a. a stimulus paired with a response will, on recurrence, tend to elicit that response again b. learning results from the gradual construction of cognitive maps c. behaviors producing positive consequences tend to ...
Study Questions
... for example by switching the correct lever to press to obtain a reward to the previously incorrect lever. The rationale for this strategy is that the action system would facilitate learning changes in the outcome but the habit system would interfere because it is slow to change. 9. Explain the conce ...
... for example by switching the correct lever to press to obtain a reward to the previously incorrect lever. The rationale for this strategy is that the action system would facilitate learning changes in the outcome but the habit system would interfere because it is slow to change. 9. Explain the conce ...
Psychology: the scientific study of behavior and mental processes
... o Believed that the repressed urges caused nervous disorders in his patients o Personality formed in the 6 years so if problems then mean it was early on o Freudian psychoanalysis: the theory and therapy based on freud’s ideas Basis of psychotherapy – a process in which a trained professional help ...
... o Believed that the repressed urges caused nervous disorders in his patients o Personality formed in the 6 years so if problems then mean it was early on o Freudian psychoanalysis: the theory and therapy based on freud’s ideas Basis of psychotherapy – a process in which a trained professional help ...
Chapter 1
... Adaptation to the Environment • Learning—any process through which experience at one time can alter an individual’s behavior at a future time ...
... Adaptation to the Environment • Learning—any process through which experience at one time can alter an individual’s behavior at a future time ...
Down and Dirty study sheet for the AP Psy Exam Source: Mr. B`s
... a. Foot in the door techniqueif a small request is made first a larger request will be easier to fill later b. Door in the face techniquemaking a larger request first then making a smaller one which will seem more reasonable c. Low ballinggetting agreement first, then adding specifics later 5. ...
... a. Foot in the door techniqueif a small request is made first a larger request will be easier to fill later b. Door in the face techniquemaking a larger request first then making a smaller one which will seem more reasonable c. Low ballinggetting agreement first, then adding specifics later 5. ...
Operant Conditioning (BF Skinner)
... If, when an organism emits a behaviour (does something), the consequences of that behaviour are reinforcing, it is more likely to emit (do) it again. What counts as reinforcement, of course, is based on the evidence of the repeated behaviour, which makes the whole argument rather circular. Learning ...
... If, when an organism emits a behaviour (does something), the consequences of that behaviour are reinforcing, it is more likely to emit (do) it again. What counts as reinforcement, of course, is based on the evidence of the repeated behaviour, which makes the whole argument rather circular. Learning ...
Theories of Behavior Change
... How can this theory inform your practice? • Intention has been shown to be the most important variable in predicting behavior change, suggesting that behaviors are often linked with one’s personal motivation.8 This suggests that it may be important to present information to help shape positive atti ...
... How can this theory inform your practice? • Intention has been shown to be the most important variable in predicting behavior change, suggesting that behaviors are often linked with one’s personal motivation.8 This suggests that it may be important to present information to help shape positive atti ...
CHAPTER 3: Causal Factors and Viewpoints
... and hormonal imbalances, temperament, and brain dysfunction and neural plasticity. Investigations in this area show much promise for advancing our knowledge of how the mind and the body interact to produce maladaptive behavior. The oldest psychological viewpoint on abnormal behavior is Freudian psyc ...
... and hormonal imbalances, temperament, and brain dysfunction and neural plasticity. Investigations in this area show much promise for advancing our knowledge of how the mind and the body interact to produce maladaptive behavior. The oldest psychological viewpoint on abnormal behavior is Freudian psyc ...
Lecture3
... Cognitive learning comprises of, “learning a relationship between two stimuli and thus is also called S-S learning. Types of cognitive learning include latent learning and the formation of insights”. Cognitive learning is the result of listening, watching, touching or experiencing. Cognitive learnin ...
... Cognitive learning comprises of, “learning a relationship between two stimuli and thus is also called S-S learning. Types of cognitive learning include latent learning and the formation of insights”. Cognitive learning is the result of listening, watching, touching or experiencing. Cognitive learnin ...
- Employees
... Continuous reinforcement – each correct response is reinforced Extinction - Withholding or removal of positive reinforcement for a previously reinforced behavior. Extinction can also refer to the loss of the association between a conditioned and unconditioned stimulus (tone no longer predicts shock, ...
... Continuous reinforcement – each correct response is reinforced Extinction - Withholding or removal of positive reinforcement for a previously reinforced behavior. Extinction can also refer to the loss of the association between a conditioned and unconditioned stimulus (tone no longer predicts shock, ...
I Have a Dream: My Hopeful Future for Behavior Analysis
... about heredity and environment based largely on rational argument and correlational analyses. The former lacked empirical evidence; the latter lacked experimental control. ...
... about heredity and environment based largely on rational argument and correlational analyses. The former lacked empirical evidence; the latter lacked experimental control. ...
Units 5-6 Guide
... This section of the course introduces students to differences between learned and unlearned behavior. The primary focus is exploration of different kinds of learning, including classical conditioning, operant conditioning, and observational learning. The biological bases of behavior illustrate predi ...
... This section of the course introduces students to differences between learned and unlearned behavior. The primary focus is exploration of different kinds of learning, including classical conditioning, operant conditioning, and observational learning. The biological bases of behavior illustrate predi ...
Criminological Theories
... There are, of course, other ways to arrive at these same conclusions. We can draw inferences out of the Approach and Perspective the theory is located under. Since approaches contain assumptions about human nature, models of society, and so forth, we can use this valuable information to rule out ot ...
... There are, of course, other ways to arrive at these same conclusions. We can draw inferences out of the Approach and Perspective the theory is located under. Since approaches contain assumptions about human nature, models of society, and so forth, we can use this valuable information to rule out ot ...
Notes_1_bcsd Intro to Psych research design
... -conditions of worth distort our self concept -Freud concerned with individuals and with mental problems of individuals -drew a distinction between consciousness (mental state of awareness to which we have ready access) and unconsciousness (mental processes to which we do not normally have access) - ...
... -conditions of worth distort our self concept -Freud concerned with individuals and with mental problems of individuals -drew a distinction between consciousness (mental state of awareness to which we have ready access) and unconsciousness (mental processes to which we do not normally have access) - ...
Learning: The Cognitive Process Classical Conditioning
... What is the meaning of a reward? Difference between reward and positive reinforcement? What is the meaning of a punishment? Differences between punishment and negative reinforcement? Which of the 7 reasons of punishment not being a good method do you agree with the most? Explain why? ...
... What is the meaning of a reward? Difference between reward and positive reinforcement? What is the meaning of a punishment? Differences between punishment and negative reinforcement? Which of the 7 reasons of punishment not being a good method do you agree with the most? Explain why? ...
explain your answer
... A) continuous reinforcement leads to behaviors that will persist longer than behavior learned through partial or intermittent reinforcement B) both continuous reinforcement and partial or intermittent reinforcement lead to behaviors that persist for equally long periods of time C) neither partial no ...
... A) continuous reinforcement leads to behaviors that will persist longer than behavior learned through partial or intermittent reinforcement B) both continuous reinforcement and partial or intermittent reinforcement lead to behaviors that persist for equally long periods of time C) neither partial no ...
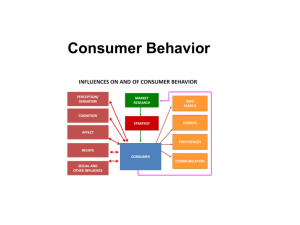
CB Lecture
... Consumer behavior: consists of the actions a person takes in purchasing and using products and services, including the mental and social processes that come before and after these actions. ...
... Consumer behavior: consists of the actions a person takes in purchasing and using products and services, including the mental and social processes that come before and after these actions. ...
Behaviorism
... The Elimination of Metaphysics Example: In a religion where God is beyond human experience, the positivists would say that “God exists” is neither true nor false but meaningless, since no experience could verify it. Kant, Hegel, and Heidegger were also big targets for the positivists. Example Hegel ...
... The Elimination of Metaphysics Example: In a religion where God is beyond human experience, the positivists would say that “God exists” is neither true nor false but meaningless, since no experience could verify it. Kant, Hegel, and Heidegger were also big targets for the positivists. Example Hegel ...
The Behavioral Approach
... Alice leaves her clothes and toys all over her room. It seems that the only time she cleans up her room is when her mother yells at her. When she yells at her, Alice picks up her clothes and put away ...
... Alice leaves her clothes and toys all over her room. It seems that the only time she cleans up her room is when her mother yells at her. When she yells at her, Alice picks up her clothes and put away ...