Microbial Ecology: Where are we now?
... complex microbial communities as well as their shift over time (Muyzer and Smalla 1998). Community profiling by DGGE is recommended as an important clinical tool that depends on the differences between the genetic sequences of various bacterial communities, thereby generating different banding patte ...
... complex microbial communities as well as their shift over time (Muyzer and Smalla 1998). Community profiling by DGGE is recommended as an important clinical tool that depends on the differences between the genetic sequences of various bacterial communities, thereby generating different banding patte ...
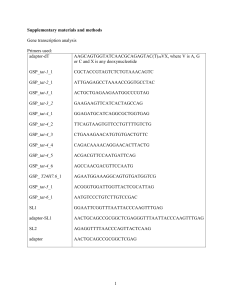
Supplementary Table 1: WormBase IDs and given
... following order with the DNA solution, 50μl of 2.5M CaCl2 and 20μl of 0.1M spermidine and then vigorously vortexed for 3 more minutes. The coated particles were pelleted to remove the supernatant, washed once with alcohol (as above) and re-suspended by vigorous vortexing in 100μl of alcohol. The su ...
... following order with the DNA solution, 50μl of 2.5M CaCl2 and 20μl of 0.1M spermidine and then vigorously vortexed for 3 more minutes. The coated particles were pelleted to remove the supernatant, washed once with alcohol (as above) and re-suspended by vigorous vortexing in 100μl of alcohol. The su ...
Finishing the Human Genome
... Doug Brutlag Professor Emeritus of Biochemistry & Medicine Stanford University School of Medicine Doug Brutlag 2011 ...
... Doug Brutlag Professor Emeritus of Biochemistry & Medicine Stanford University School of Medicine Doug Brutlag 2011 ...
Molecular insights into mitochondrial transcription and its
... triphosphate (ATP), through the process of oxidative phosphorylation. The mitochondrion contains its own genome, a small circular DNA molecule (mtDNA), encoding essential subunits of the oxidative phosphorylation system. Initiation of mitochondrial transcription involves three proteins, the mitochon ...
... triphosphate (ATP), through the process of oxidative phosphorylation. The mitochondrion contains its own genome, a small circular DNA molecule (mtDNA), encoding essential subunits of the oxidative phosphorylation system. Initiation of mitochondrial transcription involves three proteins, the mitochon ...
video slide - Dublin City Schools Home
... A Closer Look: Obtaining the Gene of Interest • How can a researcher obtain DNA that encodes a particular gene of interest? • The “shotgun” approach is one way to synthesize a gene of interest. – Millions of recombinant plasmids containing different segments of foreign DNA are produced. – This coll ...
... A Closer Look: Obtaining the Gene of Interest • How can a researcher obtain DNA that encodes a particular gene of interest? • The “shotgun” approach is one way to synthesize a gene of interest. – Millions of recombinant plasmids containing different segments of foreign DNA are produced. – This coll ...
Cloning and Polymorphisms of Yak Lactate Dehydrogenase b Gene
... and ldhb-M or ldhb-S and ldhb-M, exhibiting only one broad band for LDH1 (also LDH2, and LDH3) on the gel as shown in Figure 1. However, the PCR-RFLP protocol can accurately determine the genotypes of ldhb at position 896, which specify LDH1-F and LDH1-M/LDH-S phenotypes (Table 4). The reason for th ...
... and ldhb-M or ldhb-S and ldhb-M, exhibiting only one broad band for LDH1 (also LDH2, and LDH3) on the gel as shown in Figure 1. However, the PCR-RFLP protocol can accurately determine the genotypes of ldhb at position 896, which specify LDH1-F and LDH1-M/LDH-S phenotypes (Table 4). The reason for th ...
background of the invention
... With reference to FIG. 2 for a schematic view showing the layout of a field-effect transistor chip of a field-effect transistor type biosensor in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention, a field-effect transistor chip is fabrication by an n-well complementary metal oxide semiconductor ...
... With reference to FIG. 2 for a schematic view showing the layout of a field-effect transistor chip of a field-effect transistor type biosensor in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention, a field-effect transistor chip is fabrication by an n-well complementary metal oxide semiconductor ...
Microplate-Based Pathlength Correction Method for Photometric
... Summary of the characteristic DNA assay performance values is shown in Table I. The limit of detection is around 0.3–0.5 µg/ml of DNA with a 384-well plate, and between 0.5–0.9 µg/ml with a 96-well plate. This is the lowest concentration that can be reliably separated from the blank level in order t ...
... Summary of the characteristic DNA assay performance values is shown in Table I. The limit of detection is around 0.3–0.5 µg/ml of DNA with a 384-well plate, and between 0.5–0.9 µg/ml with a 96-well plate. This is the lowest concentration that can be reliably separated from the blank level in order t ...
GENtle, a free multi-purpose molecular biology tool
... 2 Abstract A result of modern techniques in molecular biology, especially DNA sequencing, is the exponentially growing amount of available data. Besides giant, specialized databases, which are accessible over the Internet, all work groups in the field of molecular biology today need to handle, modif ...
... 2 Abstract A result of modern techniques in molecular biology, especially DNA sequencing, is the exponentially growing amount of available data. Besides giant, specialized databases, which are accessible over the Internet, all work groups in the field of molecular biology today need to handle, modif ...
Document
... Mendel’s Law of Segregation A. Law of Segregation states that a pair of factors (alleles) is segregated, or separated, during the formation of gametes (reproductive cells) (1) When two gametes combine during fertilization, the offspring have two factors controlling a specific trait (Gg) ...
... Mendel’s Law of Segregation A. Law of Segregation states that a pair of factors (alleles) is segregated, or separated, during the formation of gametes (reproductive cells) (1) When two gametes combine during fertilization, the offspring have two factors controlling a specific trait (Gg) ...
Fulltext PDF - Indian Academy of Sciences
... Origin and roles of DNA methylation patterns mutations and various types of extended addition–deletion mutations). Sites of cytosine methylations are themselves hotspots for occurrence of mutations. The cytosine methylation and histone modification marks amplify the genetic variation manifold epigen ...
... Origin and roles of DNA methylation patterns mutations and various types of extended addition–deletion mutations). Sites of cytosine methylations are themselves hotspots for occurrence of mutations. The cytosine methylation and histone modification marks amplify the genetic variation manifold epigen ...
Supplementary Materials and methods (doc 154K)
... on LB agar containing the appropriate antibiotics (neomycin 50 mg/L, kanamycin 1200 mg/L, gentamycin 128 mg/L and chloramphenicol 50 mg/L), donors were selected on LB agar with neomycin (50 mg/L) and kanamycin (1200 mg/L). ...
... on LB agar containing the appropriate antibiotics (neomycin 50 mg/L, kanamycin 1200 mg/L, gentamycin 128 mg/L and chloramphenicol 50 mg/L), donors were selected on LB agar with neomycin (50 mg/L) and kanamycin (1200 mg/L). ...
Gene regulation in three dimensions
... taking the time to answer my questions. Last, but not least I would like to thank Julie my fiancé who has supported me and been there for me when I needed it the most. K.T.W ...
... taking the time to answer my questions. Last, but not least I would like to thank Julie my fiancé who has supported me and been there for me when I needed it the most. K.T.W ...
NUCLEIC ACID ECONOMY IN BACTERIA INFECTED WITH
... medium, and transferred to peptone broth not containing P~. Time was measured from the moment at which the infected cells were returned to nutrient medium. From the infected culture, phage yields and distributions of preassimilated P~ were measured at intervals as already described. In addition, tot ...
... medium, and transferred to peptone broth not containing P~. Time was measured from the moment at which the infected cells were returned to nutrient medium. From the infected culture, phage yields and distributions of preassimilated P~ were measured at intervals as already described. In addition, tot ...
OLSON LAB PROTOCOL: Working with RNA
... the pH and the resulting A260/A280 ratio can vary greatly. Lower pH results in a lower A260/A280 ratio and reduced sensitivity to protein contamination.* For accurate values, we recommend measuring absorbance in 10 mM Tris·Cl, pH 7.5. Pure RNA has an A260/A280 ratio of 1.9–2.1† in 10 mM Tris·Cl, pH ...
... the pH and the resulting A260/A280 ratio can vary greatly. Lower pH results in a lower A260/A280 ratio and reduced sensitivity to protein contamination.* For accurate values, we recommend measuring absorbance in 10 mM Tris·Cl, pH 7.5. Pure RNA has an A260/A280 ratio of 1.9–2.1† in 10 mM Tris·Cl, pH ...
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids

Nucleic acid electrophoresis is an analytical technique used to separate DNA or RNA fragments by size and reactivity. Nucleic acid molecules which are to be analyzed are set upon a viscous medium, the gel, where an electric field induces the nucleic acids to migrate toward the anode, due to the net negative charge of the sugar-phosphate backbone of the nucleic acid chain. The separation of these fragments is accomplished by exploiting the mobilities with which different sized molecules are able to pass through the gel. Longer molecules migrate more slowly because they experience more resistance within the gel. Because the size of the molecule affects its mobility, smaller fragments end up nearer to the anode than longer ones in a given period. After some time, the voltage is removed and the fragmentation gradient is analyzed. For larger separations between similar sized fragments, either the voltage or run time can be increased. Extended runs across a low voltage gel yield the most accurate resolution. Voltage is, however, not the sole factor in determining electrophoresis of nucleic acids.The nucleic acid to be separated can be prepared in several ways before separation by electrophoresis. In the case of large DNA molecules, the DNA is frequently cut into smaller fragments using a DNA restriction endonuclease (or restriction enzyme). In other instances, such as PCR amplified samples, enzymes present in the sample that might affect the separation of the molecules are removed through various means before analysis. Once the nucleic acid is properly prepared, the samples of the nucleic acid solution are placed in the wells of the gel and a voltage is applied across the gel for a specified amount of time.The DNA fragments of different lengths are visualized using a fluorescent dye specific for DNA, such as ethidium bromide. The gel shows bands corresponding to different nucleic acid molecules populations with different molecular weight. Fragment size is usually reported in ""nucleotides"", ""base pairs"" or ""kb"" (for thousands of base pairs) depending upon whether single- or double-stranded nucleic acid has been separated. Fragment size determination is typically done by comparison to commercially available DNA markers containing linear DNA fragments of known length.The types of gel most commonly used for nucleic acid electrophoresis are agarose (for relatively long DNA molecules) and polyacrylamide (for high resolution of short DNA molecules, for example in DNA sequencing). Gels have conventionally been run in a ""slab"" format such as that shown in the figure, but capillary electrophoresis has become important for applications such as high-throughput DNA sequencing. Electrophoresis techniques used in the assessment of DNA damage include alkaline gel electrophoresis and pulsed field gel electrophoresis.For short DNA segments such as 20 to 60 bp double stranded DNA, running them in Polyacrylamide gel (PAGE) will give better resolution(native condition). Similarly, RNA and single stranded DNA can be run and visualised by PAGE gels containing denaturing agents such as Urea. PAGE gels are widely used in techniques such as DNA foot printing, EMSA and other DNA-protein interaction techniques.The measurement and analysis are mostly done with a specialized gel analysis software. Capillary electrophoresis results are typically displayed in a trace view called an electropherogram.