Chemistry 1A – Chapter 11 Objectives Name Hour Indiana State
... C.2.6 Use the periodic table and electron configuration to determine an element's number of valence electrons and its chemical and physical properties. Chapter 11 Objectives 11.2 Electromagnetic Radiation Do p.353 #5,6 ...
... C.2.6 Use the periodic table and electron configuration to determine an element's number of valence electrons and its chemical and physical properties. Chapter 11 Objectives 11.2 Electromagnetic Radiation Do p.353 #5,6 ...
科目名 Course Title Extreme Laser Physics [極限レーザー物理E] 講義
... 授業の目標 Objectives: Interactions between optical field and atomic, molecular, and materials system have been providing interesting issues in physics. This course covers the basics of ultrafast optics and atomic physics, necessary to understand rapidly growing research field in atomic, molecular, and o ...
... 授業の目標 Objectives: Interactions between optical field and atomic, molecular, and materials system have been providing interesting issues in physics. This course covers the basics of ultrafast optics and atomic physics, necessary to understand rapidly growing research field in atomic, molecular, and o ...
Operating Principles
... There are three types of electron transitions, as shown in figure 2. The first type of transition, shown in figure 2 (a), is known as resonant absorption. An electron transits from the stable low energy level, E1, to the higher energy level, E2, by absorbing light. Figure 2 (b) shows spontaneous emi ...
... There are three types of electron transitions, as shown in figure 2. The first type of transition, shown in figure 2 (a), is known as resonant absorption. An electron transits from the stable low energy level, E1, to the higher energy level, E2, by absorbing light. Figure 2 (b) shows spontaneous emi ...
QOLECTURE1
... Suppose that the density of light is made larger and larger The atoms would follow this increase for some time absorbing more and more, but would ultimately reach their maximum capacity when all atoms become excited ...
... Suppose that the density of light is made larger and larger The atoms would follow this increase for some time absorbing more and more, but would ultimately reach their maximum capacity when all atoms become excited ...
Excited State Processes and Application to Lasers The technology
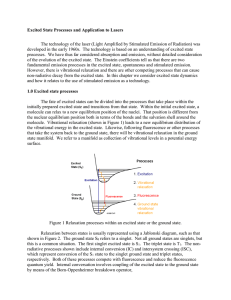
... The technology of the laser (Light Amplified by Stimulated Emission of Radiation) was developed in the early 1960s. The technology is based on an understanding of excited state processes. We have thus far considered absorption and emission, without detailed consideration of the evolution of the exci ...
... The technology of the laser (Light Amplified by Stimulated Emission of Radiation) was developed in the early 1960s. The technology is based on an understanding of excited state processes. We have thus far considered absorption and emission, without detailed consideration of the evolution of the exci ...
Introduction to Atomic Spectroscopy
... irradiated with a monochromatic beam of radiation of enough energy to cause electronic excitation, emission takes place in all directions. The emitted radiation from the first excited electronic level, collected at 90o to the incident beam, is called resonance fluorescence. Photons of the same wavel ...
... irradiated with a monochromatic beam of radiation of enough energy to cause electronic excitation, emission takes place in all directions. The emitted radiation from the first excited electronic level, collected at 90o to the incident beam, is called resonance fluorescence. Photons of the same wavel ...
laser2-broadening
... linear momentum is made with precision p, then the product of the two uncertainties can never be less than h/2 ...
... linear momentum is made with precision p, then the product of the two uncertainties can never be less than h/2 ...










![科目名 Course Title Extreme Laser Physics [極限レーザー物理E] 講義](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003538965_1-4c9ae3641327c1116053c260a01760fe-300x300.png)