Molecular Spectroscopy
... There are two important types of light sources used in spectroscopy: polychromatic and monochromatic sources. The polychromatic sources span a wide range of frequencies. For instance, many commercial spectrometers use light sources which emit radiation similar to black-body radiation from hot materi ...
... There are two important types of light sources used in spectroscopy: polychromatic and monochromatic sources. The polychromatic sources span a wide range of frequencies. For instance, many commercial spectrometers use light sources which emit radiation similar to black-body radiation from hot materi ...
Chapter 6 Experiment 4: Wave Interference
... wave that caused standing waves in the sound tube leads to the effects that we will observe today using light waves. ...
... wave that caused standing waves in the sound tube leads to the effects that we will observe today using light waves. ...
Slide 1 - Southwest High School
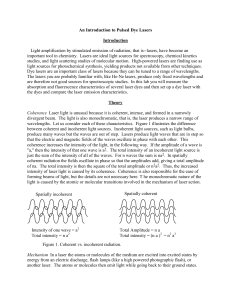
... photons have the same phase. Since one incoming photon produces two outgoing photons, the light intensity is amplified. This process will not sustain itself unless there is a continuing supply of atoms in excited states. This is ensured by exciting electrons into metastable states – excited states t ...
... photons have the same phase. Since one incoming photon produces two outgoing photons, the light intensity is amplified. This process will not sustain itself unless there is a continuing supply of atoms in excited states. This is ensured by exciting electrons into metastable states – excited states t ...
Solid-state quantum computing using spectral holes M. S. Shahriar, P. R. Hemmer,
... minimum of decoherence. This method is analogous to a scheme proposed by Pellizzari et al. 关4兴 which uses adiabatic transfer to move quantum information coherently from one particle to another, then performs quantum logic by inducing single-particle Raman transitions. Consider a situation where each ...
... minimum of decoherence. This method is analogous to a scheme proposed by Pellizzari et al. 关4兴 which uses adiabatic transfer to move quantum information coherently from one particle to another, then performs quantum logic by inducing single-particle Raman transitions. Consider a situation where each ...
Little big photon - Research Laboratory of Electronics
... graininess of matter, or equivalently, the fact that one atom can only absorb one photon at a time. Two photons then interact with one another because the first photon modifies the atom’s state, and hence the atom’s response to the second photon. What, then, is the limit to the interaction of one ph ...
... graininess of matter, or equivalently, the fact that one atom can only absorb one photon at a time. Two photons then interact with one another because the first photon modifies the atom’s state, and hence the atom’s response to the second photon. What, then, is the limit to the interaction of one ph ...
G1033-035
... All Versions of this laser are Class 1M laser product, tested according to IEC 60825-1:2007/EN 60825-1:2007 Single-mode fiber pigtail with SC/APC connectors (standard). Wavelength = 1.5 m. Maximum power = 30 mW. Because of size constraints, laser safety labeling (including an FDA class 1M label) is ...
... All Versions of this laser are Class 1M laser product, tested according to IEC 60825-1:2007/EN 60825-1:2007 Single-mode fiber pigtail with SC/APC connectors (standard). Wavelength = 1.5 m. Maximum power = 30 mW. Because of size constraints, laser safety labeling (including an FDA class 1M label) is ...
For n
... ¾ Photon absorption: When a photon of energy hν12 impinges on the system, an electron in ground state E1 can absorb the photon energy and be excited to state E2. ¾ Spontaneous emission : The electron in state E2 falls down to state E1 by itself quite spontaneously, and emits a photon of energy hν12 ...
... ¾ Photon absorption: When a photon of energy hν12 impinges on the system, an electron in ground state E1 can absorb the photon energy and be excited to state E2. ¾ Spontaneous emission : The electron in state E2 falls down to state E1 by itself quite spontaneously, and emits a photon of energy hν12 ...
Document
... Max Planck (1900) solved the paradox of the blackbody radiation. Classical Physics assumed that atoms and molecules could emit (or absorb) any arbitrary amount of radiant energy. He proposed that this energy could be emitted or absorbed only in discrete quantities. He gave the name of quantum to th ...
... Max Planck (1900) solved the paradox of the blackbody radiation. Classical Physics assumed that atoms and molecules could emit (or absorb) any arbitrary amount of radiant energy. He proposed that this energy could be emitted or absorbed only in discrete quantities. He gave the name of quantum to th ...
Experimental Test of Local Hidden-Variable Theories
... state is populated) there are essentially no rapidly decaying states other than the cascade states. Therefore there is a one-to-one correspondence between all 4358-A and 2537-A photons. As a result comparatively high data accumulation rates were obtained, The experimental arrangement is shown in Fig ...
... state is populated) there are essentially no rapidly decaying states other than the cascade states. Therefore there is a one-to-one correspondence between all 4358-A and 2537-A photons. As a result comparatively high data accumulation rates were obtained, The experimental arrangement is shown in Fig ...
Sections 3 - Columbia Physics
... right. A beam of neutral, spin-1/2 atoms enters from the left (region A) moving with velocity v. This beam is separated into two parallel beams according to the atom’s value of Sz by a region of inhomogeneous magnet field. These two separated beams propagate to the right in region B and are then rec ...
... right. A beam of neutral, spin-1/2 atoms enters from the left (region A) moving with velocity v. This beam is separated into two parallel beams according to the atom’s value of Sz by a region of inhomogeneous magnet field. These two separated beams propagate to the right in region B and are then rec ...