The circuits and magnetism game
... 13. Electric current can best be induced in a wire by A. moving a magnet up and down near the wire. B. rotating the wire. C. stretching the wire. D. setting the wire near a magnet. E. none of the above ...
... 13. Electric current can best be induced in a wire by A. moving a magnet up and down near the wire. B. rotating the wire. C. stretching the wire. D. setting the wire near a magnet. E. none of the above ...
What are Electromagnets
... declination angle or magnetic declination. There are ways to mathematically calculate the declination angle, and when relying on a compos, this difference in direction must be accounted for or else you will not reach your exact destination. The larger your distance from the North Pole, the large you ...
... declination angle or magnetic declination. There are ways to mathematically calculate the declination angle, and when relying on a compos, this difference in direction must be accounted for or else you will not reach your exact destination. The larger your distance from the North Pole, the large you ...
A three-dimensional magnetic field and electromagnetic force
... one of the “ten most significant algorithms” in scientific computation discovered in the 20th century [1, 2]. The method allows the evaluation of the product between a dense matrix (having some particular structure) and a vector in O ( N log N ) operations, whereas direct multiplication requires O N ...
... one of the “ten most significant algorithms” in scientific computation discovered in the 20th century [1, 2]. The method allows the evaluation of the product between a dense matrix (having some particular structure) and a vector in O ( N log N ) operations, whereas direct multiplication requires O N ...
Magnetism Review
... Explanation: A force is exerted on charged particles only when they move at an angle to magnetic field lines. The force is greatest when motion is at right angles to the magnetic field. ...
... Explanation: A force is exerted on charged particles only when they move at an angle to magnetic field lines. The force is greatest when motion is at right angles to the magnetic field. ...
3D Inversion of magnetic total gradient data in the presence of
... independent of magnetization direction. However, it has been demonstrated that the magnitude of the gradient vector (total gradient), often erroneously termed 3D analytic signal, has a minimal dependence on magnetization direction. In particular, if the anomaly is half reduced to the pole, the corre ...
... independent of magnetization direction. However, it has been demonstrated that the magnitude of the gradient vector (total gradient), often erroneously termed 3D analytic signal, has a minimal dependence on magnetization direction. In particular, if the anomaly is half reduced to the pole, the corre ...
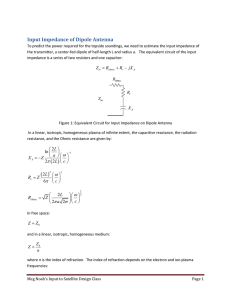
Input Impedance of Dipole Antenna
... field B0, of 0.41G. For these conditions, the electron plasma frequency, fpe, is 1.27 MHz and the electron gyromagnetic frequency, fce, is 1.15 MHz. Therefore, transmission only occurs at operating frequencies above 1.27 MHz, when the plasma parameter X=( fpe/f)2 is less than 1 (Figure 2). Since the ...
... field B0, of 0.41G. For these conditions, the electron plasma frequency, fpe, is 1.27 MHz and the electron gyromagnetic frequency, fce, is 1.15 MHz. Therefore, transmission only occurs at operating frequencies above 1.27 MHz, when the plasma parameter X=( fpe/f)2 is less than 1 (Figure 2). Since the ...
Electromagnetic induction
... as an immobile electric charge does not produce a magnetic field. The movement of a magnet in relation to a conductor results in the flow of current across the conductor, just as the movement of charges in a conductor produces a magnetic field. The phenomenon of electric-current induction by a chang ...
... as an immobile electric charge does not produce a magnetic field. The movement of a magnet in relation to a conductor results in the flow of current across the conductor, just as the movement of charges in a conductor produces a magnetic field. The phenomenon of electric-current induction by a chang ...
Lecture 18 - UConn Physics
... rest (electrostatics) since this would correspond to the potential difference between a point and itself. Consequently, there can be no "potential function" corresponding to these induced E fields. ...
... rest (electrostatics) since this would correspond to the potential difference between a point and itself. Consequently, there can be no "potential function" corresponding to these induced E fields. ...
Giant magnetoresistance
Giant magnetoresistance (GMR) is a quantum mechanical magnetoresistance effect observed in thin-film structures composed of alternating ferromagnetic and non-magnetic conductive layers. The 2007 Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to Albert Fert and Peter Grünberg for the discovery of GMR.The effect is observed as a significant change in the electrical resistance depending on whether the magnetization of adjacent ferromagnetic layers are in a parallel or an antiparallel alignment. The overall resistance is relatively low for parallel alignment and relatively high for antiparallel alignment. The magnetization direction can be controlled, for example, by applying an external magnetic field. The effect is based on the dependence of electron scattering on the spin orientation.The main application of GMR is magnetic field sensors, which are used to read data in hard disk drives, biosensors, microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) and other devices. GMR multilayer structures are also used in magnetoresistive random-access memory (MRAM) as cells that store one bit of information.In literature, the term giant magnetoresistance is sometimes confused with colossal magnetoresistance of ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic semiconductors, which is not related to the multilayer structure.