EM_INDUCTION
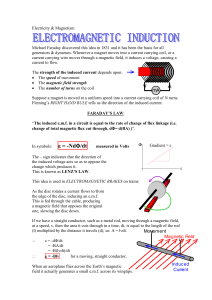
... “The induced e.m.f. in a circuit is equal to the rate of change of flux linkage (i.e. change of total magnetic flux cut through, d= d(BA) )”. ...
... “The induced e.m.f. in a circuit is equal to the rate of change of flux linkage (i.e. change of total magnetic flux cut through, d= d(BA) )”. ...
Interactions between Electricity and Magnetism
... Mag/Elec Interactions Electro-magnets If you coil a wire into a helical form (like wrapping a wire around a cylinder) and run a current through it, each circular coil creates a small mag field. The mag field from each coil “adds up” to create what looks like a magnet with a North and South po ...
... Mag/Elec Interactions Electro-magnets If you coil a wire into a helical form (like wrapping a wire around a cylinder) and run a current through it, each circular coil creates a small mag field. The mag field from each coil “adds up” to create what looks like a magnet with a North and South po ...
Magnetism Challenge
... field. They are a neutron, an electron, a proton, and an alpha particle (+2). Which track is the ...
... field. They are a neutron, an electron, a proton, and an alpha particle (+2). Which track is the ...
Magnetic Fields and Electromagnetic Induction --
... 20. Indicate graphically the direction of B generated by the two currents, respectively, and the direction of the magnetic forces exerted on the currents. ...
... 20. Indicate graphically the direction of B generated by the two currents, respectively, and the direction of the magnetic forces exerted on the currents. ...
SurveyMotors
... perpendicular to the magnetic field and perpendicular to the current. (If the current is in the same direction as the field, there is no force.) ...
... perpendicular to the magnetic field and perpendicular to the current. (If the current is in the same direction as the field, there is no force.) ...
ELECTRIC MOTOR
... This phenomenon is known as electromagnetic induction. The direction of induced current can be found using Fleming’s right-hand rule. Stretch the thumb, forefinger and middle finger of right hand so that they are perpendicular to each other ,if the forefinger indicates the direction of magnetic fiel ...
... This phenomenon is known as electromagnetic induction. The direction of induced current can be found using Fleming’s right-hand rule. Stretch the thumb, forefinger and middle finger of right hand so that they are perpendicular to each other ,if the forefinger indicates the direction of magnetic fiel ...
Week 2: Current and Intro to Circuits
... • How do they work? • What effects do they have on us? ...
... • How do they work? • What effects do they have on us? ...
922
... moment is weak and opposite the applied magnetic field. Paramagnetic substances are those in which the magnetic moment is weak and in the same direction as the applied magnetic field. In ferromagnetic substances, interactions between atoms cause magnetic moments to align and create a strong magnetiz ...
... moment is weak and opposite the applied magnetic field. Paramagnetic substances are those in which the magnetic moment is weak and in the same direction as the applied magnetic field. In ferromagnetic substances, interactions between atoms cause magnetic moments to align and create a strong magnetiz ...
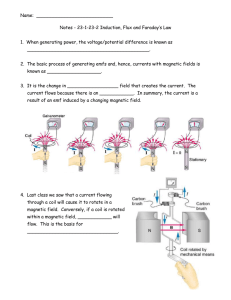
Name: Notes - 23-1-23-2 Induction, Flux and Faraday`s Law 1. When
... 1. When generating power, the voltage/potential difference is known as ___________________________________________. 2. The basic process of generating emfs and, hence, currents with magnetic fields is known as ___________________. 3. It is the change in __________________ field that creates the curr ...
... 1. When generating power, the voltage/potential difference is known as ___________________________________________. 2. The basic process of generating emfs and, hence, currents with magnetic fields is known as ___________________. 3. It is the change in __________________ field that creates the curr ...
Imaging of local magnetic structure by polarized neutron holography
... local arrangement of nuclei around a specific nucleus can be answered but discovering the local spin arrangement around a specific (e.g. impurity) nucleus is still a challenging problem. Neutrons possess magnetic moment and therefore they are candidates for holographic mapping of local magnetic stru ...
... local arrangement of nuclei around a specific nucleus can be answered but discovering the local spin arrangement around a specific (e.g. impurity) nucleus is still a challenging problem. Neutrons possess magnetic moment and therefore they are candidates for holographic mapping of local magnetic stru ...
Features of spin-orbit-induced dynamics in magnetic nanofilms
... The prospects of the creation of new layered magnetic nanostructures possessing by the property of the field and current-govern magnetic dynamics with ultimately small energy consumption as base elements for nanodevices of an information technology with high bit densities and high-frequency radiatio ...
... The prospects of the creation of new layered magnetic nanostructures possessing by the property of the field and current-govern magnetic dynamics with ultimately small energy consumption as base elements for nanodevices of an information technology with high bit densities and high-frequency radiatio ...
Lesson 2 - Electromagnetism
... Straight line conductors When electricity flows through a wire (straight line conductor) an ...
... Straight line conductors When electricity flows through a wire (straight line conductor) an ...
Giant magnetoresistance
Giant magnetoresistance (GMR) is a quantum mechanical magnetoresistance effect observed in thin-film structures composed of alternating ferromagnetic and non-magnetic conductive layers. The 2007 Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to Albert Fert and Peter Grünberg for the discovery of GMR.The effect is observed as a significant change in the electrical resistance depending on whether the magnetization of adjacent ferromagnetic layers are in a parallel or an antiparallel alignment. The overall resistance is relatively low for parallel alignment and relatively high for antiparallel alignment. The magnetization direction can be controlled, for example, by applying an external magnetic field. The effect is based on the dependence of electron scattering on the spin orientation.The main application of GMR is magnetic field sensors, which are used to read data in hard disk drives, biosensors, microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) and other devices. GMR multilayer structures are also used in magnetoresistive random-access memory (MRAM) as cells that store one bit of information.In literature, the term giant magnetoresistance is sometimes confused with colossal magnetoresistance of ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic semiconductors, which is not related to the multilayer structure.