engineering physics ii magnetic materials
... 3.3 CLASSIFICATION OF MAGNETIC MATERIALS ON THE BASIS OF MAGNETIC MOMENT Magnetic materials are classified according to the presence or absence of the permanent magnetic dipoles. Generally, every two electrons in an energy state of an atom will form a pair with opposite spins. Thus the resultant spi ...
... 3.3 CLASSIFICATION OF MAGNETIC MATERIALS ON THE BASIS OF MAGNETIC MOMENT Magnetic materials are classified according to the presence or absence of the permanent magnetic dipoles. Generally, every two electrons in an energy state of an atom will form a pair with opposite spins. Thus the resultant spi ...
engineering physics ii magnetic materials
... 3.3 CLASSIFICATION OF MAGNETIC MATERIALS ON THE BASIS OF MAGNETIC MOMENT Magnetic materials are classified according to the presence or absence of the permanent magnetic dipoles. Generally, every two electrons in an energy state of an atom will form a pair with opposite spins. Thus the resultant spi ...
... 3.3 CLASSIFICATION OF MAGNETIC MATERIALS ON THE BASIS OF MAGNETIC MOMENT Magnetic materials are classified according to the presence or absence of the permanent magnetic dipoles. Generally, every two electrons in an energy state of an atom will form a pair with opposite spins. Thus the resultant spi ...
Magnetism - WordPress.com
... Magnetism was discovered more than 3000 years ago Certain rocks (magnetite) attracted bits of iron Magnetite formed from the slow hardening of the ...
... Magnetism was discovered more than 3000 years ago Certain rocks (magnetite) attracted bits of iron Magnetite formed from the slow hardening of the ...
Abstract Submitted for the Graduate Seminar Meeting of
... Anomalous Magnetic Moment of Muon and g-2 Experiment JAEHYUNG CHOI, SUNY at Stony Brook, NY — The magnetic moment of a particle is one of the physical quantities which can be measured by the experiment and be testified by the theory. Especially, the magnetic moment of electron is precisely measured ...
... Anomalous Magnetic Moment of Muon and g-2 Experiment JAEHYUNG CHOI, SUNY at Stony Brook, NY — The magnetic moment of a particle is one of the physical quantities which can be measured by the experiment and be testified by the theory. Especially, the magnetic moment of electron is precisely measured ...
The Two Characteristics of Superconductivity
... They are bosons. BCS theory presently fails to explain superconductivity of high temperature super conductors Summary of Superconductor Properties: They behave as (no DC resistors) They behave as a perfect dimagnet and experience “Meissner” effect A band gap was implied by the very fact that ...
... They are bosons. BCS theory presently fails to explain superconductivity of high temperature super conductors Summary of Superconductor Properties: They behave as (no DC resistors) They behave as a perfect dimagnet and experience “Meissner” effect A band gap was implied by the very fact that ...
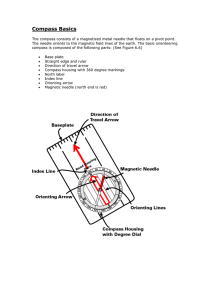
Compass Basics - NSW Public Schools
... True North: (also known as Geographic North or Map North - marked as H on a topographic map - see Figure 6.8) is the geographic north pole where all longitude lines meet. All maps are laid out with true north directly at the top. Unfortunately for the wilderness traveler, true north is not at the sa ...
... True North: (also known as Geographic North or Map North - marked as H on a topographic map - see Figure 6.8) is the geographic north pole where all longitude lines meet. All maps are laid out with true north directly at the top. Unfortunately for the wilderness traveler, true north is not at the sa ...
The role of the helical kink instability in solar coronal ejections
... are powered by the Sun's magnetic field. They are formed as magnetic flux ropes, i.e. magnetic fields twisted about each other. CMEs are the most important drivers of space weather effects on Earth. In particular, the structure of the internal magnetic field of the CME determines the severeness of t ...
... are powered by the Sun's magnetic field. They are formed as magnetic flux ropes, i.e. magnetic fields twisted about each other. CMEs are the most important drivers of space weather effects on Earth. In particular, the structure of the internal magnetic field of the CME determines the severeness of t ...
Plate Tectonics - University of Hawaii at Hilo
... What causes the magnetic field of the earth? How is paleomagnetism useful for determining age of rocks. Magnetic field reversals. What is magnetic inclination? What are the main types of crust-What are the main differences between them? Plate boundary types For each main type, know the types of asso ...
... What causes the magnetic field of the earth? How is paleomagnetism useful for determining age of rocks. Magnetic field reversals. What is magnetic inclination? What are the main types of crust-What are the main differences between them? Plate boundary types For each main type, know the types of asso ...
Magnetic Field Lines
... When many of these orbits are aligned, so are the micro-magnetic fields, creating a larger overall magnetic field around the entire substance. Some substances are temporary magnets because the electron structure of its atoms is not protected from disturbances and the orbits are eventually randomly o ...
... When many of these orbits are aligned, so are the micro-magnetic fields, creating a larger overall magnetic field around the entire substance. Some substances are temporary magnets because the electron structure of its atoms is not protected from disturbances and the orbits are eventually randomly o ...
Giant magnetoresistance
Giant magnetoresistance (GMR) is a quantum mechanical magnetoresistance effect observed in thin-film structures composed of alternating ferromagnetic and non-magnetic conductive layers. The 2007 Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to Albert Fert and Peter Grünberg for the discovery of GMR.The effect is observed as a significant change in the electrical resistance depending on whether the magnetization of adjacent ferromagnetic layers are in a parallel or an antiparallel alignment. The overall resistance is relatively low for parallel alignment and relatively high for antiparallel alignment. The magnetization direction can be controlled, for example, by applying an external magnetic field. The effect is based on the dependence of electron scattering on the spin orientation.The main application of GMR is magnetic field sensors, which are used to read data in hard disk drives, biosensors, microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) and other devices. GMR multilayer structures are also used in magnetoresistive random-access memory (MRAM) as cells that store one bit of information.In literature, the term giant magnetoresistance is sometimes confused with colossal magnetoresistance of ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic semiconductors, which is not related to the multilayer structure.