Magnetic Storms Video Note Skeleton
... The earth’s magnetic field is what makes our compasses point north. Recently, scientists have detected a dramatic change in the earth’s magnetic field. It seems the earth’s magnetic field is rapidly fading. The earth itself is a gigantic magnet. The magnetic field is created deep in the earths core. ...
... The earth’s magnetic field is what makes our compasses point north. Recently, scientists have detected a dramatic change in the earth’s magnetic field. It seems the earth’s magnetic field is rapidly fading. The earth itself is a gigantic magnet. The magnetic field is created deep in the earths core. ...
Document
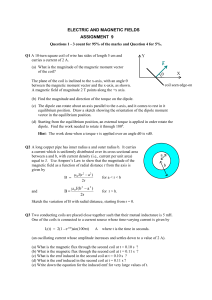
... surrounding space. • The magnetic field exerts a ______ on any other moving charge or current that is in the field. ...
... surrounding space. • The magnetic field exerts a ______ on any other moving charge or current that is in the field. ...
Simulation(s) - Faraday`s Law
... Click the tab for pickup coil 11. Slowly move the north end of the magnet towards the coil, what happens to the electrons in the wire as the field from the north pole of the magnet increases in strength? ________________________________________________________________________________________________ ...
... Click the tab for pickup coil 11. Slowly move the north end of the magnet towards the coil, what happens to the electrons in the wire as the field from the north pole of the magnet increases in strength? ________________________________________________________________________________________________ ...
NAME: Block - The Oakwood School
... 8. When there is no voltage applied the electrons are still moving randomly. Since the number of electrons moving one direction is balanced by electrons moving the opposite direction then there is no net magnetic field. There is no magnetic field because there is no net flow of electrons. Predict w ...
... 8. When there is no voltage applied the electrons are still moving randomly. Since the number of electrons moving one direction is balanced by electrons moving the opposite direction then there is no net magnetic field. There is no magnetic field because there is no net flow of electrons. Predict w ...
Ionic charge transport in an external magnetic field via molecular
... Molecular dynamics simulations of ionic charge transport in condensed phase systems subject to an external magnetic field are relatively uncommon. This is due to two main difficulties. First, the non-canonical form of the Hamiltonian breaks time reversal invariance and key statistical relations do n ...
... Molecular dynamics simulations of ionic charge transport in condensed phase systems subject to an external magnetic field are relatively uncommon. This is due to two main difficulties. First, the non-canonical form of the Hamiltonian breaks time reversal invariance and key statistical relations do n ...
l - Evergreen
... Ex.5.4: (a) A current I is uniformly distributed over a wire of circular cross section with radius a. Find J. ...
... Ex.5.4: (a) A current I is uniformly distributed over a wire of circular cross section with radius a. Find J. ...
Electromagnetic Forces
... or toward each other. The ability to move an object over a distance is called energy The energy associated with electric currents is called electrical energy. The energy an object has due to its movement or position is called mechanical ...
... or toward each other. The ability to move an object over a distance is called energy The energy associated with electric currents is called electrical energy. The energy an object has due to its movement or position is called mechanical ...
Magnets Notes
... What happens when you break a magnet? Draw it after breaking the magnet in half twice. ...
... What happens when you break a magnet? Draw it after breaking the magnet in half twice. ...
Basic Physical Principles of MRI
... • Moving (spinning) charged particle generates its own little magnetic field – Such particles will tend to line up with external magnetic field lines (think of iron filings around a magnet) ...
... • Moving (spinning) charged particle generates its own little magnetic field – Such particles will tend to line up with external magnetic field lines (think of iron filings around a magnet) ...
Pre AP Physics – Circuits and Magnetism Review Sheet
... c. What is the current through each branch of the parallel circuit? [0.1 A, 0.2 A, 0.3 A] 3. A wire 115 m long is at right angles to a uniform magnetic field. The field has a magnetic field strength of 5.0 x 10 -5 T. The current through the wire is 400 A. Find the magnitude of the force. [2.3 N] 4. ...
... c. What is the current through each branch of the parallel circuit? [0.1 A, 0.2 A, 0.3 A] 3. A wire 115 m long is at right angles to a uniform magnetic field. The field has a magnetic field strength of 5.0 x 10 -5 T. The current through the wire is 400 A. Find the magnitude of the force. [2.3 N] 4. ...
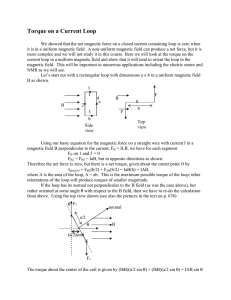
Torque on a Current Loop
... for the energy of a magnetic dipole in a B field, U = − µ ⋅ B , so that the difference between a spin up and down nucleus has an energy ∆U = 2µ B B . The RF signal must match this energy difference to be absorbed – a condition known as a resonance (hence the R in NMR). A spin flip to a higher energy ...
... for the energy of a magnetic dipole in a B field, U = − µ ⋅ B , so that the difference between a spin up and down nucleus has an energy ∆U = 2µ B B . The RF signal must match this energy difference to be absorbed – a condition known as a resonance (hence the R in NMR). A spin flip to a higher energy ...
Right Hand Rule Study Sheet
... A solenoid creates a magnetic field down its center. If a piece of iron is slipped into the solenoid it becomes a stronger electromagnet. This Right Hand Rule can be used to determine the polarity of an electromagnet. Right Hand Rule #3 A current-carrying wire experiences forces when placed in a mag ...
... A solenoid creates a magnetic field down its center. If a piece of iron is slipped into the solenoid it becomes a stronger electromagnet. This Right Hand Rule can be used to determine the polarity of an electromagnet. Right Hand Rule #3 A current-carrying wire experiences forces when placed in a mag ...
LECTURE 11: MAGNETIC SURVEYS Magnetic surveys use
... Flux-gate magnetometer (1nT, vector magnetometer). Two coils are wrapped around 2 ferromagnetic strips. AC current is applied through a primary coil wrapped oppositely around the two strips. If a magnetic field is present, a secondary coil senses the induced field. ...
... Flux-gate magnetometer (1nT, vector magnetometer). Two coils are wrapped around 2 ferromagnetic strips. AC current is applied through a primary coil wrapped oppositely around the two strips. If a magnetic field is present, a secondary coil senses the induced field. ...
Giant magnetoresistance
Giant magnetoresistance (GMR) is a quantum mechanical magnetoresistance effect observed in thin-film structures composed of alternating ferromagnetic and non-magnetic conductive layers. The 2007 Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to Albert Fert and Peter Grünberg for the discovery of GMR.The effect is observed as a significant change in the electrical resistance depending on whether the magnetization of adjacent ferromagnetic layers are in a parallel or an antiparallel alignment. The overall resistance is relatively low for parallel alignment and relatively high for antiparallel alignment. The magnetization direction can be controlled, for example, by applying an external magnetic field. The effect is based on the dependence of electron scattering on the spin orientation.The main application of GMR is magnetic field sensors, which are used to read data in hard disk drives, biosensors, microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) and other devices. GMR multilayer structures are also used in magnetoresistive random-access memory (MRAM) as cells that store one bit of information.In literature, the term giant magnetoresistance is sometimes confused with colossal magnetoresistance of ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic semiconductors, which is not related to the multilayer structure.