Molecular cloning and biochemical characterization of a
... converted to volatile aldehydes, alcohols and ketones through the action of other enzymes of the lipoxygenase pathway, e.g. hydroperoxide lyases and isomerases [1]. Some of these volatile compounds are thought to induce the synthesis of molecules, such as systemin, that are important in intercellula ...
... converted to volatile aldehydes, alcohols and ketones through the action of other enzymes of the lipoxygenase pathway, e.g. hydroperoxide lyases and isomerases [1]. Some of these volatile compounds are thought to induce the synthesis of molecules, such as systemin, that are important in intercellula ...
Chapter 17
... • A cell translates an mRNA message into protein with the help of transfer RNA (tRNA) • Molecules of tRNA are not identical: – Each carries a specific amino acid on one end – Each has an anticodon on the other end; the anticodon base-pairs with a complementary codon on mRNA ...
... • A cell translates an mRNA message into protein with the help of transfer RNA (tRNA) • Molecules of tRNA are not identical: – Each carries a specific amino acid on one end – Each has an anticodon on the other end; the anticodon base-pairs with a complementary codon on mRNA ...
Large-Scale Variation Among Human and Great Ape Genomes
... Large-scale genomic rearrangements are a major force of evolutionary change and the ascertainment of such events between the human and great ape genomes is fundamental to a complete understanding of the genetic history and evolution of our species. Here, we present the results of an evolutionary ana ...
... Large-scale genomic rearrangements are a major force of evolutionary change and the ascertainment of such events between the human and great ape genomes is fundamental to a complete understanding of the genetic history and evolution of our species. Here, we present the results of an evolutionary ana ...
an integrated microsystem for allele
... The microsystem has a second PCR chamber (PCR2) for performing an allele-specific amplification. By design of the allele-specific primers, PCR amplification only occurs if a SNP is present [7]. To further illustrate the operational concept, allele-specific PCR is conducted in a commercially availab ...
... The microsystem has a second PCR chamber (PCR2) for performing an allele-specific amplification. By design of the allele-specific primers, PCR amplification only occurs if a SNP is present [7]. To further illustrate the operational concept, allele-specific PCR is conducted in a commercially availab ...
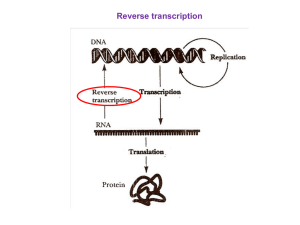
Reverse transcriptase
... • Smaller ribosomal subunits (30S and 50S) • Prokaryotic translation occurs co-transcriptionally and often there are several open reading frames in a single mRNA i.e. polycistronic mRNAs • During initiation the ribosome directly interacts with the mRNA via the Shine Delgarno sequence (directly upst ...
... • Smaller ribosomal subunits (30S and 50S) • Prokaryotic translation occurs co-transcriptionally and often there are several open reading frames in a single mRNA i.e. polycistronic mRNAs • During initiation the ribosome directly interacts with the mRNA via the Shine Delgarno sequence (directly upst ...
Powerpoint Presentation
... •The concentration of X-gal is constant at 0.5M within the cell at all times. •The concentration of X-gal is sufficiently large to have the rate of change of indigo be equal to Vmax. •Vmax is equal to Kcat multiplied by the concentration of β-galactosidase. •The concentration of β-galactosidase is e ...
... •The concentration of X-gal is constant at 0.5M within the cell at all times. •The concentration of X-gal is sufficiently large to have the rate of change of indigo be equal to Vmax. •Vmax is equal to Kcat multiplied by the concentration of β-galactosidase. •The concentration of β-galactosidase is e ...
IGEM_presentation
... bi is the binding constant of component I to its activator, ei is the inverse rate of breakdown of component i. L relates to LexA, R to RecA, R* to RecA* and S to ssDNA Ki is the binding constant of component i to the LexA gene. Cs is the concentration of single stranded DNA ...
... bi is the binding constant of component I to its activator, ei is the inverse rate of breakdown of component i. L relates to LexA, R to RecA, R* to RecA* and S to ssDNA Ki is the binding constant of component i to the LexA gene. Cs is the concentration of single stranded DNA ...
Supplementary Materials and methods (doc 154K)
... 50% PAO1-GFP. Competitions starting at 50% of each strain maximize the ability to detect small differences in fitness. The exact initial proportions were confirmed via flow cytometry (see conditions below). Mixtures were diluted 200-fold in fresh LB and competed for 16 hours at 37°C with no agitatio ...
... 50% PAO1-GFP. Competitions starting at 50% of each strain maximize the ability to detect small differences in fitness. The exact initial proportions were confirmed via flow cytometry (see conditions below). Mixtures were diluted 200-fold in fresh LB and competed for 16 hours at 37°C with no agitatio ...
bsaa animal biotechnology worksheet
... foreign gene into its cells. This animal can pass to its offspring this transgene, or altered gene. All of the cells within the transgenic animal contain this transgene. Some common transgenic methods are: 1. Microinjection—This is the most common method used. InjectingDNAinto a cell using a fine di ...
... foreign gene into its cells. This animal can pass to its offspring this transgene, or altered gene. All of the cells within the transgenic animal contain this transgene. Some common transgenic methods are: 1. Microinjection—This is the most common method used. InjectingDNAinto a cell using a fine di ...
QTL analysis in Mouse Crosses
... Suppose that we have 3 markers M1 , M2 and M3 in that order. How do we calculate the log likelihood of the associated 3-locus marker data from our intercross? Recalling the discussion preceding the Punnett square of the last lecture, the parental haplotypes here are a1a2a3 and b1b2b3 while are would ...
... Suppose that we have 3 markers M1 , M2 and M3 in that order. How do we calculate the log likelihood of the associated 3-locus marker data from our intercross? Recalling the discussion preceding the Punnett square of the last lecture, the parental haplotypes here are a1a2a3 and b1b2b3 while are would ...
Insertion (sufB) in the anticodon loop or base substitution (sufC) in
... mutation contradicts this. These apparently conflicting results further urged us to establish the identity of the dominant sufBl and suJB2 mutations. We note, however, that recessive tRNA mutations have been characterized (see e.g. ref. 1). 1-methylguanosine is present on the 3' side of the anticodo ...
... mutation contradicts this. These apparently conflicting results further urged us to establish the identity of the dominant sufBl and suJB2 mutations. We note, however, that recessive tRNA mutations have been characterized (see e.g. ref. 1). 1-methylguanosine is present on the 3' side of the anticodo ...
Generative Power and Closure Properties of Watson
... is double-stranded chain of nucleotides, which differ by their chemical bases that are adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T), and they are paired as A-T, C-G according to the Watson-Crick complementary as it is illustrated in Figure 1 [1]. The massive parallelism, another fundament ...
... is double-stranded chain of nucleotides, which differ by their chemical bases that are adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T), and they are paired as A-T, C-G according to the Watson-Crick complementary as it is illustrated in Figure 1 [1]. The massive parallelism, another fundament ...
Dosyayı İndir
... of human deaths worldwide. Their impact on health is a major reason for studying them. Like eukaryotes, bacteria often possess allelic differences that affect their cellular traits ...
... of human deaths worldwide. Their impact on health is a major reason for studying them. Like eukaryotes, bacteria often possess allelic differences that affect their cellular traits ...
Q112
... Try to avoid repetitive freeze-thaw cycles of the product to keep the activity of enzyme from decreasing. If only a small amount is used each time, it is recommended to divide it into smaller batches. Invert the tube upside down for several times to mix thoroughly before use. Do not vortex for fear ...
... Try to avoid repetitive freeze-thaw cycles of the product to keep the activity of enzyme from decreasing. If only a small amount is used each time, it is recommended to divide it into smaller batches. Invert the tube upside down for several times to mix thoroughly before use. Do not vortex for fear ...
Did Not Attend (DNA) - Staffordshire and Stoke-On
... targets whereby patients must be offered an appointment and seen within a set number of weeks. Contractual penalties can be imposed should the Partnership Trust fail to meet these targets. The Partnership Trust will seek to ensure that all patients/service users are seen as early as possible during ...
... targets whereby patients must be offered an appointment and seen within a set number of weeks. Contractual penalties can be imposed should the Partnership Trust fail to meet these targets. The Partnership Trust will seek to ensure that all patients/service users are seen as early as possible during ...
Biology 9/5/12 - Scio School District Page
... Checkpoint question: Characteristics of Life (example: fish)(5 min) Video: Viruses and Bacteria…10 minutes -discuss differences between viruses and bacteria Cool down question : (5 min) Viruses / Work on assignment (7 min) -students write answer…due by end of the period Assignment: Describe at least ...
... Checkpoint question: Characteristics of Life (example: fish)(5 min) Video: Viruses and Bacteria…10 minutes -discuss differences between viruses and bacteria Cool down question : (5 min) Viruses / Work on assignment (7 min) -students write answer…due by end of the period Assignment: Describe at least ...
Understanding Our Environment
... Raven - Johnson - Biology: 6th Ed. - All Rights Reserved - McGraw Hill Companies ...
... Raven - Johnson - Biology: 6th Ed. - All Rights Reserved - McGraw Hill Companies ...
Chapter 9 From DNA to Protein
... How is RNA Assembled? (cont’d.) • Transcription begins when an RNA polymerase and regulatory proteins attach to a DNA site called a promoter – RNA polymerase moves over a gene region and unwinds the double helix a bit so it can “read” the base sequence of the DNA strand – The polymerase joins free ...
... How is RNA Assembled? (cont’d.) • Transcription begins when an RNA polymerase and regulatory proteins attach to a DNA site called a promoter – RNA polymerase moves over a gene region and unwinds the double helix a bit so it can “read” the base sequence of the DNA strand – The polymerase joins free ...
1 - Pearson Schools and FE Colleges
... the bases C, G, A and T join together to form DNA. Chains of nucleotides containing C, G, A and U make RNA. Knowledge of how these units join together, and the three-dimensional (3-D) structures in DNA in particular, is the basis of our understanding of molecular genetics. ...
... the bases C, G, A and T join together to form DNA. Chains of nucleotides containing C, G, A and U make RNA. Knowledge of how these units join together, and the three-dimensional (3-D) structures in DNA in particular, is the basis of our understanding of molecular genetics. ...
Io mo0 - Journal of Medical Genetics
... of homologous recombination and mouse embryonic stem cell manipulation have resulted in the generation of transgenic CF mice carrying the AF508 CFTR mutation, the most frequent CF associated mutation.5 Nevertheless, CF mice models have limitations and there is still a need for a natural animal model ...
... of homologous recombination and mouse embryonic stem cell manipulation have resulted in the generation of transgenic CF mice carrying the AF508 CFTR mutation, the most frequent CF associated mutation.5 Nevertheless, CF mice models have limitations and there is still a need for a natural animal model ...
Cre-Lox recombination

In the field of genetics, Cre-Lox recombination is known as a site-specific recombinase technology, and is widely used to carry out deletions, insertions, translocations and inversions at specific sites in the DNA of cells. It allows the DNA modification to be targeted to a specific cell type or be triggered by a specific external stimulus. It is implemented both in eukaryotic and prokaryotic systems.The system consists of a single enzyme, Cre recombinase, that recombines a pair of short target sequences called the Lox sequences. This system can be implemented without inserting any extra supporting proteins or sequences. The Cre enzyme and the original Lox site called the LoxP sequence are derived from bacteriophage P1.Placing Lox sequences appropriately allows genes to be activated, repressed, or exchanged for other genes. At a DNA level many types of manipulations can be carried out. The activity of the Cre enzyme can be controlled so that it is expressed in a particular cell type or triggered by an external stimulus like a chemical signal or a heat shock. These targeted DNA changes are useful in cell lineage tracing and when mutants are lethal if expressed globally.The Cre-Lox system is very similar in action and in usage to the FLP-FRT recombination system.