hypoglycemics2009-06-17 13:292.4 MB
... ● Control genes involved in glucose and lipid metabolism ● Increase insulin sensitivity in muscle and adipose tissue ● Decrease triglycerides ● Increases HDL PHARMACOKINETICS ● Orally (once daily dose) ● Highly bound to plasma albumins ● Slow onset of activity ● Half life 3-4 h ● Metabolized by CYP4 ...
... ● Control genes involved in glucose and lipid metabolism ● Increase insulin sensitivity in muscle and adipose tissue ● Decrease triglycerides ● Increases HDL PHARMACOKINETICS ● Orally (once daily dose) ● Highly bound to plasma albumins ● Slow onset of activity ● Half life 3-4 h ● Metabolized by CYP4 ...
product monograph - Eli Lilly Canada
... including ZYPREXA and other drugs not essential to therapy; 2) intensive symptomatic treatment and medical monitoring; and 3) treatment of any concomitant serious medical problems for which specific treatments are available. There is no general agreement about specific pharmacological treatment for ...
... including ZYPREXA and other drugs not essential to therapy; 2) intensive symptomatic treatment and medical monitoring; and 3) treatment of any concomitant serious medical problems for which specific treatments are available. There is no general agreement about specific pharmacological treatment for ...
Bipolar disorder: assessment and management
... 1.3 Assessing suspected bipolar disorder in adults in secondary care ....................................................................... 20 1.4 Managing crisis, risk and behaviour that challenges in adults with bipolar disorder in secondary care 21 1.5 Managing mania or hypomania in adults in se ...
... 1.3 Assessing suspected bipolar disorder in adults in secondary care ....................................................................... 20 1.4 Managing crisis, risk and behaviour that challenges in adults with bipolar disorder in secondary care 21 1.5 Managing mania or hypomania in adults in se ...
insulin
... • Langerhans islets B-cells lesion (usually caused by autoimmune disease) → infiltration of islets with Tlymphocytes • Antibodies against islets tissue and insulin ...
... • Langerhans islets B-cells lesion (usually caused by autoimmune disease) → infiltration of islets with Tlymphocytes • Antibodies against islets tissue and insulin ...
Doctor Discussion Guide
... medicine are at an increased risk of death, compared to placebo (sugar pill). GEODON is not approved for treating these patients. GEODON may increase the risk of changes to your heart rhythm. You should not take GEODON if you have certain kinds of heart conditions that change your heart rhythm, a re ...
... medicine are at an increased risk of death, compared to placebo (sugar pill). GEODON is not approved for treating these patients. GEODON may increase the risk of changes to your heart rhythm. You should not take GEODON if you have certain kinds of heart conditions that change your heart rhythm, a re ...
Neurochemical Neutralization of Methamphetamine With High
... The major finding reported here is that indatraline, a reuptake inhibitor with high affinity for NE, DA, and 5-HT transporters (Hyttel and Larsen, 1985), blocks the ability of METH and MDMA to release these neurotransmitters. The results demonstrate that an indatraline, or a similarly acting agent, ...
... The major finding reported here is that indatraline, a reuptake inhibitor with high affinity for NE, DA, and 5-HT transporters (Hyttel and Larsen, 1985), blocks the ability of METH and MDMA to release these neurotransmitters. The results demonstrate that an indatraline, or a similarly acting agent, ...
Serotonin syndrome vs neuroleptic malignant syndrome: A contrast of causes, diagnoses,
... of the logical fallacy that correlation proves causation. The studies indirectly demonstrate that agitated patients were administered significantly higher doses of antipsychotics, thereby increasing the probability of developing NMS. Antipsychotic potency. Although it has been suggested that high-po ...
... of the logical fallacy that correlation proves causation. The studies indirectly demonstrate that agitated patients were administered significantly higher doses of antipsychotics, thereby increasing the probability of developing NMS. Antipsychotic potency. Although it has been suggested that high-po ...
product monograph
... pancreas in male rats and pituitary adenomas in female mice have been noted (see Product Monograph Part II: TOXICOLOGY). These changes have been attributed to elevated prolactin levels and have also been observed with other dopamine receptor antagonists. The physiological differences between rats an ...
... pancreas in male rats and pituitary adenomas in female mice have been noted (see Product Monograph Part II: TOXICOLOGY). These changes have been attributed to elevated prolactin levels and have also been observed with other dopamine receptor antagonists. The physiological differences between rats an ...
Misuse and abuse of quetiapine
... substance abuse, and personality disorders, often in conflict with the law. Therefore, clinicians should be cautious when prescribing quetiapine to such patients. Key words: quetiapine, abuse, addiction. ...
... substance abuse, and personality disorders, often in conflict with the law. Therefore, clinicians should be cautious when prescribing quetiapine to such patients. Key words: quetiapine, abuse, addiction. ...
Drug-induced psychomimetic effects as a model for psychosis
... of both dopaminergic and serotonergic receptors. Administration of mescaline primarily leads to disturbances of perception -predominantly visual hallucinations- and was considered an excellent model for psychosis at the time. When Albert Hofmann discovered the psychomimetic effects of lysergic acid ...
... of both dopaminergic and serotonergic receptors. Administration of mescaline primarily leads to disturbances of perception -predominantly visual hallucinations- and was considered an excellent model for psychosis at the time. When Albert Hofmann discovered the psychomimetic effects of lysergic acid ...
Minoxidil Topical Solution USP 2%
... mg per day, as tolerated, to a recommended dose of 3 mg per day. Although efficacy has been demonstrated in studies of adolescent patients with schizophrenia at doses between 1 mg to 6 mg per day, no additional benefit was observed above 3 mg per day, and higher doses were associated with more adver ...
... mg per day, as tolerated, to a recommended dose of 3 mg per day. Although efficacy has been demonstrated in studies of adolescent patients with schizophrenia at doses between 1 mg to 6 mg per day, no additional benefit was observed above 3 mg per day, and higher doses were associated with more adver ...
PDR - Seroquel Tablets
... (BPRS), a multi-item inventory of general psychopathology traditionally used to evaluate the effects of drug treatment in schizophrenia. The BPRS psychosis cluster (conceptual disorganization, hallucinatory behavior, suspiciousness, and unusual thought content) is considered a particularly useful su ...
... (BPRS), a multi-item inventory of general psychopathology traditionally used to evaluate the effects of drug treatment in schizophrenia. The BPRS psychosis cluster (conceptual disorganization, hallucinatory behavior, suspiciousness, and unusual thought content) is considered a particularly useful su ...
National Adult Clozapine Titration Chart User Guide
... adverse drug events. Research shows that many adverse events reported in Australian hospitals are associated with medications. It also demonstrates that improvements to medication chart design can improve the safety of medication processes in hospitals. The following are general requirements regardi ...
... adverse drug events. Research shows that many adverse events reported in Australian hospitals are associated with medications. It also demonstrates that improvements to medication chart design can improve the safety of medication processes in hospitals. The following are general requirements regardi ...
SYMBYAX®
... Approximately 57% and 30% of the dose was recovered in the urine and feces, respectively. In the plasma, olanzapine accounted for only 12% of the AUC for total radioactivity, indicating significant exposure to metabolites. After multiple dosing, the major circulating metabolites were the 10-N-glucur ...
... Approximately 57% and 30% of the dose was recovered in the urine and feces, respectively. In the plasma, olanzapine accounted for only 12% of the AUC for total radioactivity, indicating significant exposure to metabolites. After multiple dosing, the major circulating metabolites were the 10-N-glucur ...
Nicotine and Schizophrenia
... • High nicotine needed to activate the low affinity a-7 receptor • Schizophrenics may be using nicotine in order to achieve a specific effect on a-7 receptors that is not seen in other groups of smokers. • Schizophrenics have reduced number of nicotinic receptors • Desensitization may have more prof ...
... • High nicotine needed to activate the low affinity a-7 receptor • Schizophrenics may be using nicotine in order to achieve a specific effect on a-7 receptors that is not seen in other groups of smokers. • Schizophrenics have reduced number of nicotinic receptors • Desensitization may have more prof ...
Treatment with leptin
... Glibenclamide may be contraindicated in those with G6PD deficiency, as it may cause acute haemolysis. • Recently published data suggest glibenclamide is associated with ...
... Glibenclamide may be contraindicated in those with G6PD deficiency, as it may cause acute haemolysis. • Recently published data suggest glibenclamide is associated with ...
CYP2D6 - PGXL Laboratories
... CYP2C9 Poor Metabolizer (PM): This patient’s genotype is consistent with significantly reduced CYP2C9 enzymatic activity. Reduced CYP2C9 activity leads to lower dose requirement (e.g., warfarin) due to decreased clearance, increased elimination half-life, and increased time to reach steady-state blo ...
... CYP2C9 Poor Metabolizer (PM): This patient’s genotype is consistent with significantly reduced CYP2C9 enzymatic activity. Reduced CYP2C9 activity leads to lower dose requirement (e.g., warfarin) due to decreased clearance, increased elimination half-life, and increased time to reach steady-state blo ...
MDD - Roger Peele
... patients at risk for arrhythmia if citalopram therapy is considered • A maximum daily dosage of 20 mg for all patients older than 60 • Discontinuing the drug if QTc measurements are consistently greater than 500 ms ...
... patients at risk for arrhythmia if citalopram therapy is considered • A maximum daily dosage of 20 mg for all patients older than 60 • Discontinuing the drug if QTc measurements are consistently greater than 500 ms ...
Intracellular Modulation of NMDA Receptor Function by
... an intraneuronal signal transduction mechanism. This facilitation of NMDA activity is necessary for antipsychotic drugmediated gene expression and may contribute to the therapeutic benefits as well as side effects of antipsychotic drug treatment. ...
... an intraneuronal signal transduction mechanism. This facilitation of NMDA activity is necessary for antipsychotic drugmediated gene expression and may contribute to the therapeutic benefits as well as side effects of antipsychotic drug treatment. ...
Zeldox oral suspension ENG SmPC
... An approximately 3-fold increased risk of cerebrovascular adverse events has been seen in randomised placebo-controlled clinical trials in the dementia population with some atypical antipsychotics. The mechanism for this increased risk is not known. An increased risk cannot be excluded for other ant ...
... An approximately 3-fold increased risk of cerebrovascular adverse events has been seen in randomised placebo-controlled clinical trials in the dementia population with some atypical antipsychotics. The mechanism for this increased risk is not known. An increased risk cannot be excluded for other ant ...
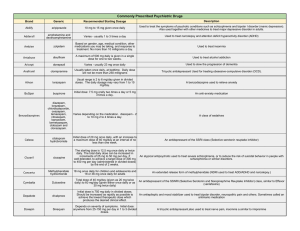
Commonly Prescribed Psychiatric Medications
... Initial dose: 0.5 to 5 mg orally 2 to 3 times a day. A "typical" antipsychotic, one of the oldest, usually given in conjunction with "cogentin", an antiparkinsonic. This is due Dosage may go up to: 1 to 30 mg/day in 2 or 3 to the high occurrence of tardive dyskinesia on patients with prolonged Haldo ...
... Initial dose: 0.5 to 5 mg orally 2 to 3 times a day. A "typical" antipsychotic, one of the oldest, usually given in conjunction with "cogentin", an antiparkinsonic. This is due Dosage may go up to: 1 to 30 mg/day in 2 or 3 to the high occurrence of tardive dyskinesia on patients with prolonged Haldo ...
Treatment of Tics and Tourette Syndrome | SpringerLink
... monotherapy are recommended. First-tier medications, notably the α-adrenergic agonists, are recommended for individuals with milder tics, especially persons with both tics and ADHD. Second-tier medications include various typical and atypical neuroleptics. Their sequence of prescription is often bas ...
... monotherapy are recommended. First-tier medications, notably the α-adrenergic agonists, are recommended for individuals with milder tics, especially persons with both tics and ADHD. Second-tier medications include various typical and atypical neuroleptics. Their sequence of prescription is often bas ...
Zeldox capsule, hard ENG SmPC
... An approximately 3-fold increased risk of cerebrovascular adverse events has been seen in randomised placebo-controlled clinical trials in the dementia population with some atypical antipsychotics. The mechanism for this increased risk is not known. An increased risk cannot be excluded for other ant ...
... An approximately 3-fold increased risk of cerebrovascular adverse events has been seen in randomised placebo-controlled clinical trials in the dementia population with some atypical antipsychotics. The mechanism for this increased risk is not known. An increased risk cannot be excluded for other ant ...
Atypical antipsychotic
The atypical antipsychotics (AAP; also known as second generation antipsychotics (SGAs)) are a group of antipsychotic drugs (antipsychotic drugs in general are also known as major tranquilisers and neuroleptics, although the latter is usually reserved for the typical antipsychotics) used to treat psychiatric conditions. Some atypical antipsychotics have received regulatory approval (e.g. by the FDA of the US, the TGA of Australia, the MHRA of the UK) for schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, autism, and as an adjunct in major depressive disorder.Both generations of medication tend to block receptors in the brain's dopamine pathways. Atypicals are less likely – than the most widely-used typical antipsychotic haloperidol – to cause extrapyramidal motor control disabilities in patients such as unsteady Parkinson's disease-type movements, body rigidity, and involuntary tremors. However, only a few of the atypicals have been demonstrated to be superior to lesser-used, low-potency first-generation antipsychotics in this regard.As experience with these agents has grown, several studies have questioned the utility of broadly characterizing antipsychotic drugs as “atypical/second generation"" as opposed to “first generation,” noting that each agent has its own efficacy and side-effect profile. It has been argued that a more nuanced view in which the needs of individual patients are matched to the properties of individual drugs is more appropriate. Although atypical antipsychotics are thought to be safer than typical antipsychotics, they still have severe side effects, including tardive dyskinesia (a serious movement disorder), neuroleptic malignant syndrome, and increased risk of stroke, sudden cardiac death, blood clots, and diabetes. Significant weight gain may also occur. Critics have argued that ""the time has come to abandon the terms first-generation and second-generation antipsychotics, as they do not merit this distinction.""