13Johnson
... in different ways by using different combinations of the same exons, different proteins can be created this is termed alternative splicing the 25,000 genes of the human genome appear to encode as many as 120,000 different mRNAs ...
... in different ways by using different combinations of the same exons, different proteins can be created this is termed alternative splicing the 25,000 genes of the human genome appear to encode as many as 120,000 different mRNAs ...
10-Genes
... B. RNAs are processed to remove introns and splice together exons. C. RNA carries the information that directs protein synthesis. D. proteins assume a specific three dimensional shape to become functional 3. Transcription and DNA replication are similar in all the following ways, EXCEPT; A. The new ...
... B. RNAs are processed to remove introns and splice together exons. C. RNA carries the information that directs protein synthesis. D. proteins assume a specific three dimensional shape to become functional 3. Transcription and DNA replication are similar in all the following ways, EXCEPT; A. The new ...
mol medicine 1
... Haplotype: combination of alleles at multiple, tightly-linked loci that are transmitted together over many generations Anonymous locus : position on genome with no known function DNA marker: polymorphic locus useful for mapping studies RFLP Variation in the length of a restriction fragment detected ...
... Haplotype: combination of alleles at multiple, tightly-linked loci that are transmitted together over many generations Anonymous locus : position on genome with no known function DNA marker: polymorphic locus useful for mapping studies RFLP Variation in the length of a restriction fragment detected ...
genetic engineering
... DNA at a specific section of nucleotides. The fragments are then separated and analyzed using gel electrophoresis (used to compare genomes of different organisms) this way scientists can locate & identify single genes out of millions in a genome. ...
... DNA at a specific section of nucleotides. The fragments are then separated and analyzed using gel electrophoresis (used to compare genomes of different organisms) this way scientists can locate & identify single genes out of millions in a genome. ...
Bacteria Evolving: - American Museum of Natural History
... Like all organisms, bacteria can acquire new traits through muta- ...
... Like all organisms, bacteria can acquire new traits through muta- ...
Microevolution Notes
... Every individual in a population is different in structure and behavior. Ex-pattern, speed, agility, etc ...
... Every individual in a population is different in structure and behavior. Ex-pattern, speed, agility, etc ...
DNA and Gene Expression
... – Assembly of amino acids into peptide chains on basis of information encoded in mRNA – Occurs in ribosomes – mRNA and tRNA ...
... – Assembly of amino acids into peptide chains on basis of information encoded in mRNA – Occurs in ribosomes – mRNA and tRNA ...
Genetics and Protein Synthesis
... The initiator tRNA/mRNA/small ribosomal unit is called the initiation complex. ...
... The initiator tRNA/mRNA/small ribosomal unit is called the initiation complex. ...
Sc9 - a 4.2 (teacher notes)
... with oral antibiotics but more serious infections usually involve hospitalisation for treatment with intravenous antibiotics. Hormone drugs to stimulate ovulation are used for donor insemination, and may also be used to increase the chance of conception for AI using the male partner's sperm. This so ...
... with oral antibiotics but more serious infections usually involve hospitalisation for treatment with intravenous antibiotics. Hormone drugs to stimulate ovulation are used for donor insemination, and may also be used to increase the chance of conception for AI using the male partner's sperm. This so ...
Evolution of Whales: From Land to Water
... Thewissen, J. G. M., Hussain, S. T., and Arif, M. 1994. Fossil evidence for the origin of aquatic locomotion in Archalocete whales. Science. 263(5144): 210-212. Thewissen, J. G. M, Williams, E. M., Roe, L. J., and Hussain, S. T. 2001. Skeletons of terrestrial cetaceans and the relationship of wh ...
... Thewissen, J. G. M., Hussain, S. T., and Arif, M. 1994. Fossil evidence for the origin of aquatic locomotion in Archalocete whales. Science. 263(5144): 210-212. Thewissen, J. G. M, Williams, E. M., Roe, L. J., and Hussain, S. T. 2001. Skeletons of terrestrial cetaceans and the relationship of wh ...
Digitally Programmed Cells
... • Characteristics small (E.coli: 1x2m , 109/ml) self replicating energy efficient ...
... • Characteristics small (E.coli: 1x2m , 109/ml) self replicating energy efficient ...
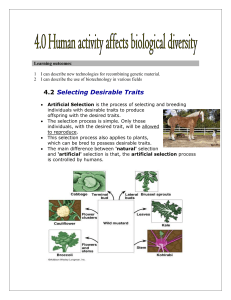
Artificial Selection
... Artificial Selection is the process of selecting and breeding individuals with desirable traits to produce offspring with the desired traits. The selection process is simple - only those individuals (animals or plants) with the desired trait are allowed to reproduce. Some people in history have trie ...
... Artificial Selection is the process of selecting and breeding individuals with desirable traits to produce offspring with the desired traits. The selection process is simple - only those individuals (animals or plants) with the desired trait are allowed to reproduce. Some people in history have trie ...
Standard 3
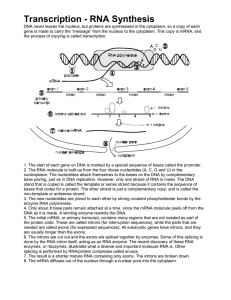
... the two strands from each other. The main enzyme involved with DNA replication is DNA polymerase. o Since each nitrogenous base has a complementary nitrogenous base, base pairing allows for two identical sets of DNA to be formed from the two strands of one set of DNA. o By forming identical sets of ...
... the two strands from each other. The main enzyme involved with DNA replication is DNA polymerase. o Since each nitrogenous base has a complementary nitrogenous base, base pairing allows for two identical sets of DNA to be formed from the two strands of one set of DNA. o By forming identical sets of ...
Slide 1
... Replicators that can evolve by natural selection must: (i) multiply and (ii) have heredity that, however, is not perfectly accurate (variability). However, these qualities are necessary but not sufficient to be "life". Viruses and even computer codes are also replicators. ...
... Replicators that can evolve by natural selection must: (i) multiply and (ii) have heredity that, however, is not perfectly accurate (variability). However, these qualities are necessary but not sufficient to be "life". Viruses and even computer codes are also replicators. ...
Big Idea 1: The process of evolution drives the diversity and unity of
... differential survival. Individuals with more favorable phenotypes are more likely to survive and produce more offspring, thus passing traits to subsequent generations. b. Evolutionary fitness is measured by reproductive success. c. Genetic variation and mutation play roles in natural selection. A di ...
... differential survival. Individuals with more favorable phenotypes are more likely to survive and produce more offspring, thus passing traits to subsequent generations. b. Evolutionary fitness is measured by reproductive success. c. Genetic variation and mutation play roles in natural selection. A di ...
Genetic Engineering Notes
... 1) __________________________________________= The process by which desired traits of certain plants and animals are selected and passed on to their future generations. Breed only those plants or animals with desirable traits 2) People have been using selective breeding for 1000’s of years with fa ...
... 1) __________________________________________= The process by which desired traits of certain plants and animals are selected and passed on to their future generations. Breed only those plants or animals with desirable traits 2) People have been using selective breeding for 1000’s of years with fa ...
forensic_biology
... nucleotide "letters" A (adenine), C (cytosine), T (thymine), and G (guanine). SNP variation occurs when a single nucleotide, such as an A, replaces one of the other three nucleotide letters—C, G, or T. Each person's genetic material contains a unique SNP pattern that is made up of many different gen ...
... nucleotide "letters" A (adenine), C (cytosine), T (thymine), and G (guanine). SNP variation occurs when a single nucleotide, such as an A, replaces one of the other three nucleotide letters—C, G, or T. Each person's genetic material contains a unique SNP pattern that is made up of many different gen ...