Unit 18: Genetics and Genetic Engineering
... covered in the Biochemistry and Biochemical Techniques unit, this unit will enable learners to appreciate that genes control all of the characteristics of living organisms. Learners will also understand how the mechanisms of cell division and chromosome replication lead to complex patterns of inheri ...
... covered in the Biochemistry and Biochemical Techniques unit, this unit will enable learners to appreciate that genes control all of the characteristics of living organisms. Learners will also understand how the mechanisms of cell division and chromosome replication lead to complex patterns of inheri ...
Chapter_9_Student
... Producing New Kinds of Plants Mutations in some plant cells produce cells that have double or triple the normal number of chromosomes. This condition, known as polyploidy, produces new species of plants that are often larger and stronger than their diploid relatives. Polyploidy in animals is usuall ...
... Producing New Kinds of Plants Mutations in some plant cells produce cells that have double or triple the normal number of chromosomes. This condition, known as polyploidy, produces new species of plants that are often larger and stronger than their diploid relatives. Polyploidy in animals is usuall ...
Wool Tech. and Sheep Breed. 50
... reviewed. The molecular technologies are unlikely to completely replace traditional genetic evaluations for these product-quality traits for a number of reasons. For sheep selection, using protein markers detected by the use of two-dimensionalpolyacrylamide gel electrophoresis technology is probably ...
... reviewed. The molecular technologies are unlikely to completely replace traditional genetic evaluations for these product-quality traits for a number of reasons. For sheep selection, using protein markers detected by the use of two-dimensionalpolyacrylamide gel electrophoresis technology is probably ...
ppt - Chair of Computational Biology
... Greater power in fine-mapping is obtained by haplotype analysis, in which all markers are considered simultaneously as haplotypes rather than individually. Haplotype analysis allows the inference of likely historical crossover points, which localize the disease mutation. New algorithms based on hapl ...
... Greater power in fine-mapping is obtained by haplotype analysis, in which all markers are considered simultaneously as haplotypes rather than individually. Haplotype analysis allows the inference of likely historical crossover points, which localize the disease mutation. New algorithms based on hapl ...
lecture15
... exonuclease activities, but lacks a 5' -> 3' exonuclease domain. It is thus very similar in activity to Klenow fragment and T4 DNA polymerase. The claim to fame for T7 DNA polymerase is it's processivity. That is to say, the average length of DNA synthesized before the enzyme dissociates from the te ...
... exonuclease activities, but lacks a 5' -> 3' exonuclease domain. It is thus very similar in activity to Klenow fragment and T4 DNA polymerase. The claim to fame for T7 DNA polymerase is it's processivity. That is to say, the average length of DNA synthesized before the enzyme dissociates from the te ...
Quant-iT™ Assay Kits for microplate
... of RNA. The x-axis gives the mass of nucleic acid when DNA or RNA is assayed alone; in the 1:1 mixture, the total mass of nucleic acid is double the amount shown. The inset shows the sensitivity of the assay for DNA. B The Quant-iT™ RNA Assay Kit has a linear detection range of 5–100 ng and is selec ...
... of RNA. The x-axis gives the mass of nucleic acid when DNA or RNA is assayed alone; in the 1:1 mixture, the total mass of nucleic acid is double the amount shown. The inset shows the sensitivity of the assay for DNA. B The Quant-iT™ RNA Assay Kit has a linear detection range of 5–100 ng and is selec ...
Biological Modelling Gene Expression Data
... but will not bond to the slide itself or to other spots. ...
... but will not bond to the slide itself or to other spots. ...
Genes Are DNA
... The difference between DNA and RNA is in the group at the 2′ position of the sugar. ...
... The difference between DNA and RNA is in the group at the 2′ position of the sugar. ...
Types of DNA Mutations - University of Minnesota
... 1) DNA synthesis in eukaryotes is mechanistically similar to replication in bacteria. 2) Eukaryotic replication is much slower and uses multiple replication origins. 3) Chromosomal DNA is associated with histones which need to be biosynthesized at the time of replication. 4) DNA Polymerases are more ...
... 1) DNA synthesis in eukaryotes is mechanistically similar to replication in bacteria. 2) Eukaryotic replication is much slower and uses multiple replication origins. 3) Chromosomal DNA is associated with histones which need to be biosynthesized at the time of replication. 4) DNA Polymerases are more ...
Section 14. Pedigree Analysis and Molecular Markers
... disease and actually show symptoms by this age ...
... disease and actually show symptoms by this age ...
MAKING RNA AND PROTEIN
... RNA differs from DNA 1. RNA has a sugar ribose DNA has a sugar deoxyribose 2. RNA contains uracil (U) DNA has thymine (T) 3. RNA molecule is single-stranded DNA is double-stranded ...
... RNA differs from DNA 1. RNA has a sugar ribose DNA has a sugar deoxyribose 2. RNA contains uracil (U) DNA has thymine (T) 3. RNA molecule is single-stranded DNA is double-stranded ...
Untitled
... Hershey and Chase grew one batch of E. coli in a medium containing 32P and infected the bacteria with T2 phage so that all the new phages would have DNA labeled with 32P (Figure 10.5). They grew a second batch of E. coli in a medium containing 35S and infected these bacteria with T2 phage so that ...
... Hershey and Chase grew one batch of E. coli in a medium containing 32P and infected the bacteria with T2 phage so that all the new phages would have DNA labeled with 32P (Figure 10.5). They grew a second batch of E. coli in a medium containing 35S and infected these bacteria with T2 phage so that ...
Biotechnology Laboratory (Kallas)
... sites. In array design 2, most genes in Synechococcus are covered with 3 probes repeated three times on each array, but high-density UTR probes are included for all of the predicted genes. As one example: RNAs would be isolated from wild type Synechococcus and one or two mutants of the cytochrome bf ...
... sites. In array design 2, most genes in Synechococcus are covered with 3 probes repeated three times on each array, but high-density UTR probes are included for all of the predicted genes. As one example: RNAs would be isolated from wild type Synechococcus and one or two mutants of the cytochrome bf ...
chapter 16: the molecular basis of inheritance
... 10) Explain how RNA polymerase recognizes where transcription should begin. Describe the promoter, the terminator, and the transcription unit. 11) Explain the general process of transcription, including the three major steps of initiation, elongation, and termination. 12) Explain how RNA is modified ...
... 10) Explain how RNA polymerase recognizes where transcription should begin. Describe the promoter, the terminator, and the transcription unit. 11) Explain the general process of transcription, including the three major steps of initiation, elongation, and termination. 12) Explain how RNA is modified ...
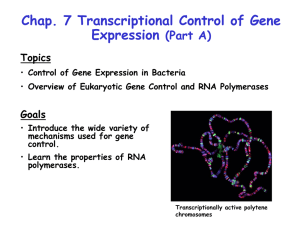
Chapter 7A
... polymerase further requires activators that bind to upstream enhancer sequences for initiation. As shown in Fig. 7.4, these "enhancer binding proteins" (e.g., NtrC) contact s54-RNA polymerase by looping of the DNA between them. The mechanism of transcription activation by s54-RNA polymerase is simil ...
... polymerase further requires activators that bind to upstream enhancer sequences for initiation. As shown in Fig. 7.4, these "enhancer binding proteins" (e.g., NtrC) contact s54-RNA polymerase by looping of the DNA between them. The mechanism of transcription activation by s54-RNA polymerase is simil ...
Cancer Lab p53 – Teacher Background
... the p53 tumor suppressor gene. These somatic mutations are differently encountered within the body. In some cases, differences in frequencies of mutations at a specific site may reflect an enhanced growth advantage for a tumor in a particular tissue. For example, the mutation of p53 at amino acid 17 ...
... the p53 tumor suppressor gene. These somatic mutations are differently encountered within the body. In some cases, differences in frequencies of mutations at a specific site may reflect an enhanced growth advantage for a tumor in a particular tissue. For example, the mutation of p53 at amino acid 17 ...
Plasmid
... Artificial plasmids are widely used as vectors in molecular cloning, in order to drive the replication of recombinant DNA sequences within host organisms. ...
... Artificial plasmids are widely used as vectors in molecular cloning, in order to drive the replication of recombinant DNA sequences within host organisms. ...