Pneumonia
... in most cases of community-acquired pneumonia, the most common causes are Streptococcus pneumoniae, Legionella species, aerobic gram-negative bacilli, Haemophilus influenzae, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, and respiratory viruses. Pseudomonas aeruginosa is more common among patients with structural lung dis ...
... in most cases of community-acquired pneumonia, the most common causes are Streptococcus pneumoniae, Legionella species, aerobic gram-negative bacilli, Haemophilus influenzae, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, and respiratory viruses. Pseudomonas aeruginosa is more common among patients with structural lung dis ...
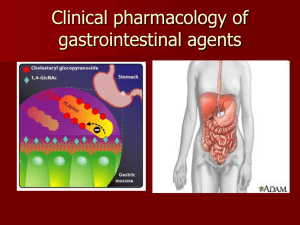
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY OF GASTROINTESTINAL AGENTS
... Therapy of PUD has undergone profound changes. There are now available very effective medications to supress and almost eliminate the outpouring of stomach acid. These acidsuppresssing drugs have been dramatically effective in relieving symptoms and allowing ulcers to heal. If an ulcer has been caus ...
... Therapy of PUD has undergone profound changes. There are now available very effective medications to supress and almost eliminate the outpouring of stomach acid. These acidsuppresssing drugs have been dramatically effective in relieving symptoms and allowing ulcers to heal. If an ulcer has been caus ...
Population Health Curriculum for Health Professionals
... Describe the public health approach to emerging issues. Identify roles and responsibilities of public health system components. Describe linkages needed to address challenges. ...
... Describe the public health approach to emerging issues. Identify roles and responsibilities of public health system components. Describe linkages needed to address challenges. ...
AIDS etická problematika
... The number of people living with HIV rose from around 8 million in 1990 to 34 million by the end of 2010. The overall growth of the epidemic has stabilised in recent years. The annual number of new HIV infections has steadily declined and due to the significant increase in people receiving antiretr ...
... The number of people living with HIV rose from around 8 million in 1990 to 34 million by the end of 2010. The overall growth of the epidemic has stabilised in recent years. The annual number of new HIV infections has steadily declined and due to the significant increase in people receiving antiretr ...
Autoimmunity QA RP - APS Foundation of America, Inc
... interests to be with you. Learn as much as you can about your disease. Share what you learn with your family. Involve them in counseling or a support group. It may help them better understand the disease and how they can help. • Sexual relations—Sexual relationships can also be affected. For men, di ...
... interests to be with you. Learn as much as you can about your disease. Share what you learn with your family. Involve them in counseling or a support group. It may help them better understand the disease and how they can help. • Sexual relations—Sexual relationships can also be affected. For men, di ...
Epidemiology 231 - UCLA School of Public Health
... Infectious disease is one of the few genuine adventures left in the world. The dragons are all dead and the lance grows rusty in the chimney corner . . . About the only sporting proposition that remains unimpaired by the relentless domestication of a once free-living human species is the war agains ...
... Infectious disease is one of the few genuine adventures left in the world. The dragons are all dead and the lance grows rusty in the chimney corner . . . About the only sporting proposition that remains unimpaired by the relentless domestication of a once free-living human species is the war agains ...
Predicting the Spread of an Infectious Disease
... SARS coughs or sneezes droplets onto themselves, other people, or nearby surfaces. It also is possible that SARS can be spread more broadly through the air or by other ways that are currently not known. ...
... SARS coughs or sneezes droplets onto themselves, other people, or nearby surfaces. It also is possible that SARS can be spread more broadly through the air or by other ways that are currently not known. ...
Legionella
... comprised their body’s immunity. Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is one such condition and in Las Vegas approximately 3,773 individuals suffer from HIV. Cancer is another form of an immunodeficiency that makes individuals more susceptible to Legionnaires’ Disease, and in Las Vegas there have been ...
... comprised their body’s immunity. Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is one such condition and in Las Vegas approximately 3,773 individuals suffer from HIV. Cancer is another form of an immunodeficiency that makes individuals more susceptible to Legionnaires’ Disease, and in Las Vegas there have been ...
M. tuberculosis
... Because of long incubation period for active disease, travel-related TB may be greatly underestimated ...
... Because of long incubation period for active disease, travel-related TB may be greatly underestimated ...
Ocular Cicatricial Pemphigoid - University of Louisville Ophthalmology
... Alkilating agents: Mitomycin C in treatment after surgical lysis ...
... Alkilating agents: Mitomycin C in treatment after surgical lysis ...
Communicable Disease Control
... immunization as a means of protecting community health. As described in chapter 8, it is the immunity level present in a particular population of people (Chin, 1999). If there are few immune persons within a community, there is low herd immunity and the spread of disease is more likely. Vaccination ...
... immunization as a means of protecting community health. As described in chapter 8, it is the immunity level present in a particular population of people (Chin, 1999). If there are few immune persons within a community, there is low herd immunity and the spread of disease is more likely. Vaccination ...
September 2014 Monitoring International Trends
... A meta-analysis and systematic review has found that restrictive red blood cell transfusion thresholds are associated with a decreased risk of acquiring healthcareassociated infections compared with liberal transfusion thresholds (page 12). A US study found that severe combined immunodeficiency ...
... A meta-analysis and systematic review has found that restrictive red blood cell transfusion thresholds are associated with a decreased risk of acquiring healthcareassociated infections compared with liberal transfusion thresholds (page 12). A US study found that severe combined immunodeficiency ...
Table of Contents
... payments for 2 years, and persons with end-stage renal disease. Medicare consists of two separate but coordinated programs—hospital insurance (Part A) and supplementary medical insurance (Part B). Health insurance protection is available to insured persons without regard to income. Monoclinal antibo ...
... payments for 2 years, and persons with end-stage renal disease. Medicare consists of two separate but coordinated programs—hospital insurance (Part A) and supplementary medical insurance (Part B). Health insurance protection is available to insured persons without regard to income. Monoclinal antibo ...
ii. infection control
... 1. Isolation places barriers between the infected patient and others 2. Standard precautions include the use of gowns and gloves when in contact with patient blood or secretions. 3. Application to all patients protects health care workers from HIV 4. Transmission precautions block airborne, droplet, ...
... 1. Isolation places barriers between the infected patient and others 2. Standard precautions include the use of gowns and gloves when in contact with patient blood or secretions. 3. Application to all patients protects health care workers from HIV 4. Transmission precautions block airborne, droplet, ...
Document
... 1/3 of adults produce methane in the colon unrelated to food ingestion Ex. Beans contain oligosaccharides that can’t be split by intestinal mucosal enzymes, but are metabolised by colonic bacteria Increased intraluminal gas may result from abnormal bacterial colonization of the small intestine or in ...
... 1/3 of adults produce methane in the colon unrelated to food ingestion Ex. Beans contain oligosaccharides that can’t be split by intestinal mucosal enzymes, but are metabolised by colonic bacteria Increased intraluminal gas may result from abnormal bacterial colonization of the small intestine or in ...
Pneumonia
... pathogens. Community-acquired pneumonia with typical clinical features is most often caused by encapsulated bacteria, particularly Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus species. Risk factors for community-acquired pneumonia in patients with HIV infection include cigarette smoking and using inject ...
... pathogens. Community-acquired pneumonia with typical clinical features is most often caused by encapsulated bacteria, particularly Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus species. Risk factors for community-acquired pneumonia in patients with HIV infection include cigarette smoking and using inject ...
Comm isease Summary 2012 unicable D
... (http://www.cdc.gov/dpdx//) is a diagnostic reference resource for laboratorians and healthcare professionals that also provide training and free consultation with CDC staff. Whenever possible, conduct confirmatory laboratory testing for potential cases of parasitic disease. All suspect cases should ...
... (http://www.cdc.gov/dpdx//) is a diagnostic reference resource for laboratorians and healthcare professionals that also provide training and free consultation with CDC staff. Whenever possible, conduct confirmatory laboratory testing for potential cases of parasitic disease. All suspect cases should ...
IMMUNE SYSTEM. PECULIARITIES of ITS FUNCTIONING
... protection against most viral, fungal, and protozoan infections and slow-growing bacterial infections, such as tuberculosis, rejection of histoincompatible grafts, mediation of cutaneous delayed hypersensitivity reactions, such as in tuberculin testing, and probably immune surveillance for mal ...
... protection against most viral, fungal, and protozoan infections and slow-growing bacterial infections, such as tuberculosis, rejection of histoincompatible grafts, mediation of cutaneous delayed hypersensitivity reactions, such as in tuberculin testing, and probably immune surveillance for mal ...
3. Morbidity and Mortality
... during the period 1980-2003. Another noteworthy feature is that the patients getting treatment for diseases of the eye and adnexa has also doubled during the last twenty years A substantial increase is seen in hospitalization for injury and poisoning. It has increased from 1,732 cases per 100,000 po ...
... during the period 1980-2003. Another noteworthy feature is that the patients getting treatment for diseases of the eye and adnexa has also doubled during the last twenty years A substantial increase is seen in hospitalization for injury and poisoning. It has increased from 1,732 cases per 100,000 po ...
Moyamoya disease and migraine-like headaches
... Each episode lasted about 30 minutes to 2 hours. In November 1989, she had girdle headache episodes in the right frontal temple and the retroorbital region accompanied again by anorexia, nausea and vomiting. About 10–30 minutes before the headache, there were prodromi including bright sparkles and s ...
... Each episode lasted about 30 minutes to 2 hours. In November 1989, she had girdle headache episodes in the right frontal temple and the retroorbital region accompanied again by anorexia, nausea and vomiting. About 10–30 minutes before the headache, there were prodromi including bright sparkles and s ...
Blood-borne viruses – what they are and how they spread
... The blood-borne viruses .................................................................................... 7 Human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV-1 and HIV-2) ........................................ 8 Pathogenesis of HIV infection ................................................................... ...
... The blood-borne viruses .................................................................................... 7 Human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV-1 and HIV-2) ........................................ 8 Pathogenesis of HIV infection ................................................................... ...
MODELING THE EFFECTS OF CARRIERS ON TRANSMISSION
... are completely determined by the values of R0 . Since R0 explicitly involves parameters related to disease carriage, we are able to discuss the impact of disease carriage on R0 . We have also carried out numerical simulations of the model using parameter values that are pertinent to hepatitis B infe ...
... are completely determined by the values of R0 . Since R0 explicitly involves parameters related to disease carriage, we are able to discuss the impact of disease carriage on R0 . We have also carried out numerical simulations of the model using parameter values that are pertinent to hepatitis B infe ...
Infection control-week 2
... Increased exposure to the number and types of disease causing microorganisms Invasive procedures NON ...
... Increased exposure to the number and types of disease causing microorganisms Invasive procedures NON ...
The Problem of Securing Health
... mners have constituted potential future events as biosecurity threats, and have ;ponded by criticizing, redeploying, or reworking existing apparatuses. The chapters in this volume provide a guide to the various ways in which the :ld of biosecurity is being problematized today. On the one hand, they ...
... mners have constituted potential future events as biosecurity threats, and have ;ponded by criticizing, redeploying, or reworking existing apparatuses. The chapters in this volume provide a guide to the various ways in which the :ld of biosecurity is being problematized today. On the one hand, they ...
08 Obstructive Airway Disease
... • Obstructive diseases are 2 types : • Reversible = Asthma • Irreversible: Bronchiectasis because the membrane is destroyed therefore the obstruction is permanent. They present with productive cough with high amount of sputum that are more in the morning with clubbing (indicating pus formation). v ...
... • Obstructive diseases are 2 types : • Reversible = Asthma • Irreversible: Bronchiectasis because the membrane is destroyed therefore the obstruction is permanent. They present with productive cough with high amount of sputum that are more in the morning with clubbing (indicating pus formation). v ...