Document
... significant bleeding that is unseen inside a body cavity or region. • Significant amounts of blood loss cause hypoperfusion, or shock. – In penetrating trauma, the patient may have only a small amount of bleeding that is visible. ...
... significant bleeding that is unseen inside a body cavity or region. • Significant amounts of blood loss cause hypoperfusion, or shock. – In penetrating trauma, the patient may have only a small amount of bleeding that is visible. ...
FROG DISSECTION Objectives
... BLADDER, AND CLOACA The kidneys are organs that filter wastes from the blood and excrete urine. Connected to each kidney is a ureter, a tube through which urine passes into the urinary bladder. The urinary bladder is a sac that stores urine until it passes out of the body through the cloaca. ...
... BLADDER, AND CLOACA The kidneys are organs that filter wastes from the blood and excrete urine. Connected to each kidney is a ureter, a tube through which urine passes into the urinary bladder. The urinary bladder is a sac that stores urine until it passes out of the body through the cloaca. ...
P4.3.2.VaricoseVeins - Life Science Academy
... An estimated 62,000 miles of blood vessels ensure that oxygen and nutrients are delivered to the trillions of cells in your body, and that waste products are taken away for disposal. If all of these blood vessels were laid out end to end, they would wrap around the Earth twice! This transportation s ...
... An estimated 62,000 miles of blood vessels ensure that oxygen and nutrients are delivered to the trillions of cells in your body, and that waste products are taken away for disposal. If all of these blood vessels were laid out end to end, they would wrap around the Earth twice! This transportation s ...
13. Effects of Exercise File
... Immediate effects on the respiratory system Exercise causes the muscles to use more oxygen. This means that the lungs must work harder and faster to keep the body supplied with oxygen and also to exhale the carbon dioxide that is produced. This is why exercise makes you out-of-breath. Breathing rat ...
... Immediate effects on the respiratory system Exercise causes the muscles to use more oxygen. This means that the lungs must work harder and faster to keep the body supplied with oxygen and also to exhale the carbon dioxide that is produced. This is why exercise makes you out-of-breath. Breathing rat ...
Connective Tissue
... • Our bodies are kept in a narrow temperature range. • When we exercise, our bodies are cooled by – evaporation of sweat on the skin and ...
... • Our bodies are kept in a narrow temperature range. • When we exercise, our bodies are cooled by – evaporation of sweat on the skin and ...
Lab Procedure (External and Internal Anatomy)
... 7. The ileum is held together by mesentery. In the small intestine, further digestion occurs and nutrients are absorbed through the arteries in the mesentery. These arteries are called mesenteric arteries. 8. Pancreas: a bumpy organ located along the underside of the stomach, a pancreatic duct leads ...
... 7. The ileum is held together by mesentery. In the small intestine, further digestion occurs and nutrients are absorbed through the arteries in the mesentery. These arteries are called mesenteric arteries. 8. Pancreas: a bumpy organ located along the underside of the stomach, a pancreatic duct leads ...
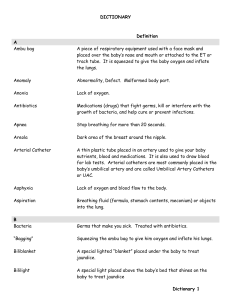
dictionary - Mother Baby University
... everyday events that goes with having a premature or critically ill baby and perhaps being a distance from your family and friends. They can help with things like: finding a place to stay, dealing with insurance or financial concerns, parking and/or meals. They provide spiritual and emotional suppor ...
... everyday events that goes with having a premature or critically ill baby and perhaps being a distance from your family and friends. They can help with things like: finding a place to stay, dealing with insurance or financial concerns, parking and/or meals. They provide spiritual and emotional suppor ...
Chapter 20 and 21 – Human Body and Digestion/Nutrition
... cancer is common, especially in low fiber diets (too slow fecal movement). (Fig. ...
... cancer is common, especially in low fiber diets (too slow fecal movement). (Fig. ...
Unit 4 Conclusion Questions 100 points possible Activity 4.1.1 How
... responsible for doing so many tasks. This nerve controls movement in the triceps and sensation in a portion of the hand while also allowing the wrist and fingers to move. When damage to the radial nerve occurs, all of these functions are put in jeopardy. 5. Describe at least three different jobs tha ...
... responsible for doing so many tasks. This nerve controls movement in the triceps and sensation in a portion of the hand while also allowing the wrist and fingers to move. When damage to the radial nerve occurs, all of these functions are put in jeopardy. 5. Describe at least three different jobs tha ...
EXAMPLE Histology Compendium
... Neutrophils are normally found in the blood stream. Neutrophils are recruited to neutrophils play a key role in the front-line defense against invading the site of injury within minutes following trauma and are the hallmark of acute pathogens. Neutrophils have three strategies for directly attacking ...
... Neutrophils are normally found in the blood stream. Neutrophils are recruited to neutrophils play a key role in the front-line defense against invading the site of injury within minutes following trauma and are the hallmark of acute pathogens. Neutrophils have three strategies for directly attacking ...
Your Body`s Systems
... The rhythm of arterial expansion and contraction is called the pulse. Your pulse rate is the same as your heartbeat rate because it's a single beat of the heart that causes each expansion and contraction of the artery. Arteries are much thicker than veins and most are located deep within our bodies. ...
... The rhythm of arterial expansion and contraction is called the pulse. Your pulse rate is the same as your heartbeat rate because it's a single beat of the heart that causes each expansion and contraction of the artery. Arteries are much thicker than veins and most are located deep within our bodies. ...
Functional Renal Imaging Vivian S. Lee The kidneys
... Vivian S. Lee The kidneys maintain homeostasis by filtering and excreting metabolic waste products, regulating acid-base balance, and moderating blood pressure and fluid volume. Since decreasing renal function accompanies renal disease, monitoring renal function permits assessment of disease progres ...
... Vivian S. Lee The kidneys maintain homeostasis by filtering and excreting metabolic waste products, regulating acid-base balance, and moderating blood pressure and fluid volume. Since decreasing renal function accompanies renal disease, monitoring renal function permits assessment of disease progres ...
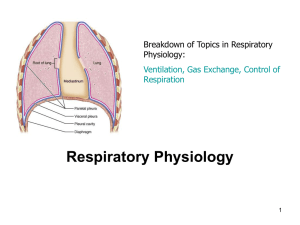
Respiratory Physiology
... •The weight of the lungs produces uneven inflation of alveoli. Lungs weight make different alveolar volume at the top and bottom of the lungs (e.g. alveoli at the top of the lungs are at a larger volume (more negative intrapleural pressure) than those at the base (less negative intrapleural pressure ...
... •The weight of the lungs produces uneven inflation of alveoli. Lungs weight make different alveolar volume at the top and bottom of the lungs (e.g. alveoli at the top of the lungs are at a larger volume (more negative intrapleural pressure) than those at the base (less negative intrapleural pressure ...
CHAPTER 39
... of 16 breaths, the excess gas still has not been completely removed from the alveoli. ...
... of 16 breaths, the excess gas still has not been completely removed from the alveoli. ...
Nerve activates contraction
... Most is transported in the plasma as bicarbonate ion (HCO3–) A small amount is carried inside red blood cells on hemoglobin, but at different binding sites than those of oxygen ...
... Most is transported in the plasma as bicarbonate ion (HCO3–) A small amount is carried inside red blood cells on hemoglobin, but at different binding sites than those of oxygen ...
Chapter 7 Structural Organisation in Animals Question
... In frog, when it is in water, skin acts as a aquatic respiratory organs and it is called cutaneous respiration. Frog when on land respire through lungs and it is called pulmonary respiration. 44.What do the blood vascular system and lymphatic system consist in frog ? Blood vascular system consist of ...
... In frog, when it is in water, skin acts as a aquatic respiratory organs and it is called cutaneous respiration. Frog when on land respire through lungs and it is called pulmonary respiration. 44.What do the blood vascular system and lymphatic system consist in frog ? Blood vascular system consist of ...
11 Respiratory physiology
... hydrogen ions on the oxygen and turns it into water). This excess water leaves the cell and enters the tissues. • The removal of oxygen from the plasma and the addition of water in the tissues creates a driving force (known as the Starling principle) to continuously draw oxygen into the tissues, sin ...
... hydrogen ions on the oxygen and turns it into water). This excess water leaves the cell and enters the tissues. • The removal of oxygen from the plasma and the addition of water in the tissues creates a driving force (known as the Starling principle) to continuously draw oxygen into the tissues, sin ...
(II) Human Body(2015)
... The jelly-like part outside the nucleus of a cell. It comprises 90% of water and different organelles. The type and numbers of organelles vary according to the functions of the cell. ...
... The jelly-like part outside the nucleus of a cell. It comprises 90% of water and different organelles. The type and numbers of organelles vary according to the functions of the cell. ...
Slide 1
... • Air has weight; atmospheric pressure is 760 mmHg at sea level (much less weight and pressure at high altitudes). • Since air will flow from higher pressure to lower pressure areas, to get the air to flow into our lungs, we need to have a lower pressure in our lungs. • We can decrease the pressure ...
... • Air has weight; atmospheric pressure is 760 mmHg at sea level (much less weight and pressure at high altitudes). • Since air will flow from higher pressure to lower pressure areas, to get the air to flow into our lungs, we need to have a lower pressure in our lungs. • We can decrease the pressure ...
The Human Body
... Anatomy is the study of the structure and shape of the body and its parts, and their relationship to one another. Gross anatomy (large body structures) can be observed with the naked eye, while microscopic anatomy (small structures within the body) requires a magnifying instrument. Physiology is the ...
... Anatomy is the study of the structure and shape of the body and its parts, and their relationship to one another. Gross anatomy (large body structures) can be observed with the naked eye, while microscopic anatomy (small structures within the body) requires a magnifying instrument. Physiology is the ...
Evidence for Endothermic Ancestors of Crocodiles at the Stem of
... it is only 0.19%–0.32% in most reptiles (Poupa and Lindström 1983; Seymour 1987; Farrell et al. 1998). In alligators, heart mass decreases from 0.25% at 1 kg body mass to 0.15% at 70 kg and 0.125% at 124 kg (Coulson et al. 1989). The level of systemic arterial blood pressure is related not only to ...
... it is only 0.19%–0.32% in most reptiles (Poupa and Lindström 1983; Seymour 1987; Farrell et al. 1998). In alligators, heart mass decreases from 0.25% at 1 kg body mass to 0.15% at 70 kg and 0.125% at 124 kg (Coulson et al. 1989). The level of systemic arterial blood pressure is related not only to ...
Homeostasis

Homeostasis or homoeostasis (homeo- + -stasis) is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH). It is a process that maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment in response to changes in external conditions.The concept was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1865 and the word was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. Although the term was originally used to refer to processes within living organisms, it is frequently applied to automatic control systems such as thermostats. Homeostasis requires a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.