CHAPTER
... solute concentration (high water concentration) to one with a high solute concentration (low water concentration). Because cell membranes are relatively impermeable to most solutes but highly permeable to water (i.e., selectively permeable), whenever there is a higher concentration of solute on one ...
... solute concentration (high water concentration) to one with a high solute concentration (low water concentration). Because cell membranes are relatively impermeable to most solutes but highly permeable to water (i.e., selectively permeable), whenever there is a higher concentration of solute on one ...
Heart - Frank`s Hospital Workshop
... rapidly through the walls of the artria, causing both artria to contract in unison. The impulses also pass to another region of specialized cardiac muscle tissue, a relay point called the atrioventricular node, located in the wall between the right artrium and the right ventricle. Here, the impulses ...
... rapidly through the walls of the artria, causing both artria to contract in unison. The impulses also pass to another region of specialized cardiac muscle tissue, a relay point called the atrioventricular node, located in the wall between the right artrium and the right ventricle. Here, the impulses ...
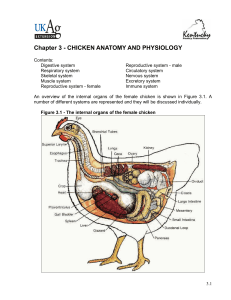
Chapter 3 - CHICKEN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
... muscle of the heart. The skeletal muscle is the type of muscle responsible for the shape of the bird and for its voluntary movement. This is the muscle type that makes up the edible portions of the carcass. The most valuable skeletal muscles in a poultry carcass are the breast, thigh and leg. The br ...
... muscle of the heart. The skeletal muscle is the type of muscle responsible for the shape of the bird and for its voluntary movement. This is the muscle type that makes up the edible portions of the carcass. The most valuable skeletal muscles in a poultry carcass are the breast, thigh and leg. The br ...
Heart Chambers - Cloudfront.net
... influenced by temperature • For this reason, essential life functions can be carried out most efficiently when an animal's internal body temperature is within a particular “operating range” • For muscles to operate quickly and efficiently, for example, their temperature can neither be too low nor to ...
... influenced by temperature • For this reason, essential life functions can be carried out most efficiently when an animal's internal body temperature is within a particular “operating range” • For muscles to operate quickly and efficiently, for example, their temperature can neither be too low nor to ...
PHYSIOLOGY OF VENOUS AND LYMPHATIC SYSTEM
... muscles and efferent impulsation from autonomic nerve centers, which control arterial pressure. Partial state of contraction in blood vessels caused by continual slow firing of vasoconstrictor area is called vasculomotor tone. ...
... muscles and efferent impulsation from autonomic nerve centers, which control arterial pressure. Partial state of contraction in blood vessels caused by continual slow firing of vasoconstrictor area is called vasculomotor tone. ...
RAAS Basic physiology and Pathophysiolgy
... ACE2 is regarded as the central regulator of the RAAS. As its changes can affect not only Ang II detrimental actions but also Ang 1–7 protective effects. For instance, a decrease in ACE2 results in activation of the Ang II/AT1R axis with a parallel reduction of Ang 1– ...
... ACE2 is regarded as the central regulator of the RAAS. As its changes can affect not only Ang II detrimental actions but also Ang 1–7 protective effects. For instance, a decrease in ACE2 results in activation of the Ang II/AT1R axis with a parallel reduction of Ang 1– ...
505C Heart evolution - Précis d`anesthésie cardiaque
... adequate, because the distances between cells were very short. Diffusion is still appropriate for gas exchange and transport if the body diameter is less than 1 mm, and if the envelope is freely permeable to gases [14]. But as soon as the organisms started to grow in size and multiplied the internal ...
... adequate, because the distances between cells were very short. Diffusion is still appropriate for gas exchange and transport if the body diameter is less than 1 mm, and if the envelope is freely permeable to gases [14]. But as soon as the organisms started to grow in size and multiplied the internal ...
Investigating the Human Body - Classroom
... have recorded from Part 2 to write labels, and an explanation of how that body part works, around the outside of the body outline. The posters should be hung around the room. Part 4: Using their model-poster as a prop each group should prepare a short presentation about their body part or system, an ...
... have recorded from Part 2 to write labels, and an explanation of how that body part works, around the outside of the body outline. The posters should be hung around the room. Part 4: Using their model-poster as a prop each group should prepare a short presentation about their body part or system, an ...
Chapter 17 PPT - Blair Community Schools
... and flows in veins to the heart E. This blood flows to the lungs where it releases CO2 and picks up O2 F. The oxygen-rich blood returns to the heart ...
... and flows in veins to the heart E. This blood flows to the lungs where it releases CO2 and picks up O2 F. The oxygen-rich blood returns to the heart ...
Respiratory Physio Detailed File
... – Venous blood Po2 = 40 mm Hg – Alveolar Po2 = 104 mm Hg • O2 partial pressures reach equilibrium of 104 mm Hg in ~0.25 seconds, about 1/3 the time a red blood cell is in a pulmonary capillary ...
... – Venous blood Po2 = 40 mm Hg – Alveolar Po2 = 104 mm Hg • O2 partial pressures reach equilibrium of 104 mm Hg in ~0.25 seconds, about 1/3 the time a red blood cell is in a pulmonary capillary ...
Diuretics
... drug of choice: non-toxic, freely filtered, nonreabsorbable and non-metabolized administered prophylatically for acute renal failure secondary to trauma, CVS disease, surgery or nephrotoxic drugs short-term treatment of acute glaucoma infused to lower intracranial pressure Urea, glycerol and isosorb ...
... drug of choice: non-toxic, freely filtered, nonreabsorbable and non-metabolized administered prophylatically for acute renal failure secondary to trauma, CVS disease, surgery or nephrotoxic drugs short-term treatment of acute glaucoma infused to lower intracranial pressure Urea, glycerol and isosorb ...
Animal Diversity – I (Invertebrate Phyla)
... Spermathecae receive and store spermatozoa in the form of bundles known as spermatophores during copulation. ...
... Spermathecae receive and store spermatozoa in the form of bundles known as spermatophores during copulation. ...
Arthropods - OG
... • Green Glands – Filter waste out of the crayfish – work similar to our kidneys – Green glands secrete uric acid near the ...
... • Green Glands – Filter waste out of the crayfish – work similar to our kidneys – Green glands secrete uric acid near the ...
For each of the statements below decide which two
... 10. The pancreas creates digestive enzymes that are secreted into the small intestines along with several hormones including insulin. The pancreas belongs to the ______________________ & ______________________ systems. ...
... 10. The pancreas creates digestive enzymes that are secreted into the small intestines along with several hormones including insulin. The pancreas belongs to the ______________________ & ______________________ systems. ...
every day cancer words and terms: a to z
... consumers and staff with plain language meanings of complex medical words and terms. The information contained within this booklet is given as a guide to help support patients, carers, families and consumers understand their health and support their health decision making process. The information gi ...
... consumers and staff with plain language meanings of complex medical words and terms. The information contained within this booklet is given as a guide to help support patients, carers, families and consumers understand their health and support their health decision making process. The information gi ...
Chapter 42 Internal Transport
... • Right ventricle pumps blood into the pulmonary arteries, one going to each lung • Blood circulates through pulmonary capillaries in the lung • Blood is conducted to the left ...
... • Right ventricle pumps blood into the pulmonary arteries, one going to each lung • Blood circulates through pulmonary capillaries in the lung • Blood is conducted to the left ...
The Cardiovascular System: Blood
... Red Blood Cells • Stimulating Hormones – Erythropoietin (EPO): • Also called erythropoiesis-stimulating hormone • Secreted when oxygen in peripheral tissues is low (hypoxia) • Due to disease or high altitude ...
... Red Blood Cells • Stimulating Hormones – Erythropoietin (EPO): • Also called erythropoiesis-stimulating hormone • Secreted when oxygen in peripheral tissues is low (hypoxia) • Due to disease or high altitude ...
Critical Care Case Report Sara
... Nursing: Continue to monitor respirations, including the pattern, rate and depth. Assess for signs of distressed breathing, anxiety and restlessness. Interpret the ABG readings. Monitor oxygen saturation, capillary refill and for signs of cyanosis/pallor. Auscultate lung sounds for any worsening or ...
... Nursing: Continue to monitor respirations, including the pattern, rate and depth. Assess for signs of distressed breathing, anxiety and restlessness. Interpret the ABG readings. Monitor oxygen saturation, capillary refill and for signs of cyanosis/pallor. Auscultate lung sounds for any worsening or ...
Renal lecture problems
... cells. K secretion into the lumen requires the development of a negative transepithelial potential. If Na does not enter the cell on the apical surface, then the transepithelial potential does not develop, and K does not cross the apical surface into the lumen. ...
... cells. K secretion into the lumen requires the development of a negative transepithelial potential. If Na does not enter the cell on the apical surface, then the transepithelial potential does not develop, and K does not cross the apical surface into the lumen. ...
The Respiratory System - Palm Beach State College
... Wander the lumens of alveoli and the connective tissue between them Keep alveoli free from debris by phagocytizing dust particles 100 million dust cells die each day as they ride up the mucociliary escalator to be swallowed and digested with their load of debris ...
... Wander the lumens of alveoli and the connective tissue between them Keep alveoli free from debris by phagocytizing dust particles 100 million dust cells die each day as they ride up the mucociliary escalator to be swallowed and digested with their load of debris ...
Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
... One scientist is known above all others for his contributions to our understanding of the human circulatory system. That scientist is William Harvey, an English physician, whose 1628 book on the circulation of blood was a landmark publication. Up until Harvey’s time, there were many misconceptions a ...
... One scientist is known above all others for his contributions to our understanding of the human circulatory system. That scientist is William Harvey, an English physician, whose 1628 book on the circulation of blood was a landmark publication. Up until Harvey’s time, there were many misconceptions a ...
Homeostasis

Homeostasis or homoeostasis (homeo- + -stasis) is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH). It is a process that maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment in response to changes in external conditions.The concept was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1865 and the word was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. Although the term was originally used to refer to processes within living organisms, it is frequently applied to automatic control systems such as thermostats. Homeostasis requires a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.