View/Open
... water of the tissues to form carbonic acid, which dissociates into hydrogen and bicarbonate ions; the hydrogen ions then have a potent direct stimulatory effect on respiration. These reactions are shown in Figure 41-2. Why does blood carbon dioxide have a more potent effect in stimulating the chemos ...
... water of the tissues to form carbonic acid, which dissociates into hydrogen and bicarbonate ions; the hydrogen ions then have a potent direct stimulatory effect on respiration. These reactions are shown in Figure 41-2. Why does blood carbon dioxide have a more potent effect in stimulating the chemos ...
Human Body Systems Flip Book
... Name ____________________Period ___ Human Body Systems Book This is an in class, individual project- not a group project. Your textbook, paper, net book, colored pencils and anything else needed to fit the requirements of the project should be brought to class each day. The latest the book will be a ...
... Name ____________________Period ___ Human Body Systems Book This is an in class, individual project- not a group project. Your textbook, paper, net book, colored pencils and anything else needed to fit the requirements of the project should be brought to class each day. The latest the book will be a ...
Document
... • Occurs when heart stops contracting • Without supply of blood, cells will die because they cannot get oxygen or nutrients. • As cells die, organ damage occurs. • Brain damage occurs within 4 to 6 minutes. ...
... • Occurs when heart stops contracting • Without supply of blood, cells will die because they cannot get oxygen or nutrients. • As cells die, organ damage occurs. • Brain damage occurs within 4 to 6 minutes. ...
Physiological changes in pregnancy
... Pregnancy problem due these changes • Physiological edema • Renin and aldosterone activity are increased by oestrogens, progesterone and prostaglandins, leading to increased fluid and electrolyte retention. ...
... Pregnancy problem due these changes • Physiological edema • Renin and aldosterone activity are increased by oestrogens, progesterone and prostaglandins, leading to increased fluid and electrolyte retention. ...
Mechanics of Ventilation (cont`d)
... Respiratory membrane: 2 cell membranes that aid diffusion • Membrane of alveolar cells • Membrane of cells of capillary wall Copyright © 2012 Wolters Kluwer Health | Lippincott Williams & Wilkins ...
... Respiratory membrane: 2 cell membranes that aid diffusion • Membrane of alveolar cells • Membrane of cells of capillary wall Copyright © 2012 Wolters Kluwer Health | Lippincott Williams & Wilkins ...
Bod} @
... maintain their boundaries, move, respond to environmental changes, take in and digest nutrients, carry out metabolism, dispose of wastes, reproduce themselves, and grow. We will discuss each ...
... maintain their boundaries, move, respond to environmental changes, take in and digest nutrients, carry out metabolism, dispose of wastes, reproduce themselves, and grow. We will discuss each ...
Life Functions - duncanbiology
... wormlike larva encloses itself within a protective capsule called a chrysalis. Here, it passes through a pupa stage, in which it changes into an adult. – A complete metamorphosis is a complex life cycle. The larvae can, however, exploit different habitats and food sources than adults. ...
... wormlike larva encloses itself within a protective capsule called a chrysalis. Here, it passes through a pupa stage, in which it changes into an adult. – A complete metamorphosis is a complex life cycle. The larvae can, however, exploit different habitats and food sources than adults. ...
6085634245
... Fig. 4.1 shows the cycling of phosphate ions in living organisms and the environment. ...
... Fig. 4.1 shows the cycling of phosphate ions in living organisms and the environment. ...
lecture outline - St. Louis Community College
... 6. What are prostaglandins? What are they made of? Give examples of prostaglandins and some of their functions. 7. How are hormones transported from the place of secretion to the target structure? Describe the mechanism of action of lipid-soluble hormones. 8. Describe the mechanism of action of pept ...
... 6. What are prostaglandins? What are they made of? Give examples of prostaglandins and some of their functions. 7. How are hormones transported from the place of secretion to the target structure? Describe the mechanism of action of lipid-soluble hormones. 8. Describe the mechanism of action of pept ...
Interactions of Human Body Systems
... This process works well for most skin injuries. But sometimes a wound is too large, and the skin can’t heal on its own. When this happens, doctors can treat the area with a skin graft. In this process, the injured skin is replaced with healthy skin taken from another part of the injured person’s bod ...
... This process works well for most skin injuries. But sometimes a wound is too large, and the skin can’t heal on its own. When this happens, doctors can treat the area with a skin graft. In this process, the injured skin is replaced with healthy skin taken from another part of the injured person’s bod ...
COVENANT UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF
... The body is long, pointed at both ends and compressed It has a dorsal fin, caudal fin and ventral fin The lateral edges of the body project out as two longitudinal fin-like folds called the metapleural folds Below the anterior end of the body, there is a funnel shaped cavity called the vesti ...
... The body is long, pointed at both ends and compressed It has a dorsal fin, caudal fin and ventral fin The lateral edges of the body project out as two longitudinal fin-like folds called the metapleural folds Below the anterior end of the body, there is a funnel shaped cavity called the vesti ...
Nonvertebrate Chordates, Fishes, and Amphibians
... • Medulla oblongata: area of the brain that controls the functioning of many internal organs ...
... • Medulla oblongata: area of the brain that controls the functioning of many internal organs ...
4.01 - Nursing Fundamentals
... and right pulmonary veins –left ventricle (4) - pumps blood to aorta, which delivers blood to all body parts (except lungs) ...
... and right pulmonary veins –left ventricle (4) - pumps blood to aorta, which delivers blood to all body parts (except lungs) ...
231 - Bossier Parish Community College
... 68. Explain the significance of the plateau phase of cardiac muscle physiology. (B) 69. Identify the components of the ECG recording. (B) 70. List the five events of the cardiac cycle. (B) 71. Define cardiac output. (B) 72. Define chronotropic agents and describe how they affect heart rate. (B) 73. ...
... 68. Explain the significance of the plateau phase of cardiac muscle physiology. (B) 69. Identify the components of the ECG recording. (B) 70. List the five events of the cardiac cycle. (B) 71. Define cardiac output. (B) 72. Define chronotropic agents and describe how they affect heart rate. (B) 73. ...
Chapter 10: Circulatory System and Lymphatic
... involves artificially boosting the blood’s ability to bring more oxygen to muscles. Aerobic capacity and endurance improve where there are additional red blood cells available to carry oxygen. ...
... involves artificially boosting the blood’s ability to bring more oxygen to muscles. Aerobic capacity and endurance improve where there are additional red blood cells available to carry oxygen. ...
Chapter 10: Circulatory System and Lymphatic
... involves artificially boosting the blood’s ability to bring more oxygen to muscles. Aerobic capacity and endurance improve where there are additional red blood cells available to carry oxygen. ...
... involves artificially boosting the blood’s ability to bring more oxygen to muscles. Aerobic capacity and endurance improve where there are additional red blood cells available to carry oxygen. ...
Human Physiology An Integrated Approach 6/E
... area, and barrier permeability in the body are constants and are maximized to facilitate diffusion. Gas exchange in the lungs is rapid, blood flow through pulmonary capillaries is slow, and diffusion reaches equilibrium in less than 1 second. This leaves the concentration gradient between alveoli an ...
... area, and barrier permeability in the body are constants and are maximized to facilitate diffusion. Gas exchange in the lungs is rapid, blood flow through pulmonary capillaries is slow, and diffusion reaches equilibrium in less than 1 second. This leaves the concentration gradient between alveoli an ...
Lobsters - csnmarsci
... arteries and veins, so the blood just passes through the tissue spaces. •Therefore, lobster and all other arthropods have an open circulatory system. •The lobster’s nervous system enables it to carry out a variety of responses. •Its eyes are mounted on movable stalks. •Two pairs of antennae actively ...
... arteries and veins, so the blood just passes through the tissue spaces. •Therefore, lobster and all other arthropods have an open circulatory system. •The lobster’s nervous system enables it to carry out a variety of responses. •Its eyes are mounted on movable stalks. •Two pairs of antennae actively ...
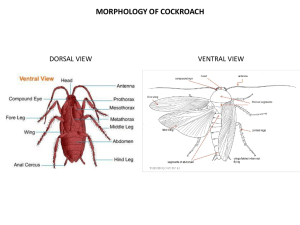
anatomy-of-cockroach
... images of an object. This kind of vision is known as mosaic vision with more sensitivity but less resolution, being common during night (hence called nocturnal vision). ...
... images of an object. This kind of vision is known as mosaic vision with more sensitivity but less resolution, being common during night (hence called nocturnal vision). ...
Homeostasis pH
... amino acid can act as weak bases and accept additional hydrogen ions, forming a carboxyl group (—COOH) and an amino ion (—NH3), respectively. Many of the R-groups can also accept hydrogen ions, ...
... amino acid can act as weak bases and accept additional hydrogen ions, forming a carboxyl group (—COOH) and an amino ion (—NH3), respectively. Many of the R-groups can also accept hydrogen ions, ...
atoms
... • Electrolytes are ionic substances (Na+, K+, Ca2+, Mg2+, Cl-, HCO3 -) or substances which form ions when they dissolve. • Electrolytes are ions released through dissociation of inorganic compounds • Can conduct electrical current in solution ...
... • Electrolytes are ionic substances (Na+, K+, Ca2+, Mg2+, Cl-, HCO3 -) or substances which form ions when they dissolve. • Electrolytes are ions released through dissociation of inorganic compounds • Can conduct electrical current in solution ...
Homeostasis

Homeostasis or homoeostasis (homeo- + -stasis) is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH). It is a process that maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment in response to changes in external conditions.The concept was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1865 and the word was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. Although the term was originally used to refer to processes within living organisms, it is frequently applied to automatic control systems such as thermostats. Homeostasis requires a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.