Unit 3 - PGS Science
... Freshwater bony fish use their kidneys to overcome a water balance problem. Describe this problem and one method used by the kidneys to overcome it. ...
... Freshwater bony fish use their kidneys to overcome a water balance problem. Describe this problem and one method used by the kidneys to overcome it. ...
intermediate 2 biology
... Freshwater bony fish use their kidneys to overcome a water balance problem. Describe this problem and one method used by the kidneys to overcome it. ...
... Freshwater bony fish use their kidneys to overcome a water balance problem. Describe this problem and one method used by the kidneys to overcome it. ...
Body In Action Notes
... because they have air in them. They are pinky red in colour because they have a good blood supply. Describe the mechanism of breathing in humans Movements of the chest wall help us to inhale (take in air) and exhale (give out air). The diaphragm and the intercostal muscles between the ribs are used ...
... because they have air in them. They are pinky red in colour because they have a good blood supply. Describe the mechanism of breathing in humans Movements of the chest wall help us to inhale (take in air) and exhale (give out air). The diaphragm and the intercostal muscles between the ribs are used ...
capillaries
... • sensory structures in the walls of certain vessels that monitor blood pressure and chemistry – send info to brainstem that serves to regulate heart rate, vasomotion, and respiration – carotid sinuses – baroreceptors (pressure sensors) • in walls of internal carotid artery • monitor blood pressure ...
... • sensory structures in the walls of certain vessels that monitor blood pressure and chemistry – send info to brainstem that serves to regulate heart rate, vasomotion, and respiration – carotid sinuses – baroreceptors (pressure sensors) • in walls of internal carotid artery • monitor blood pressure ...
the structure of the human body
... - groups of organs that perform a complex body function e.g. Cardiovascular system organ: - different tissues arranged to perform a specific function e.g. kidney ...
... - groups of organs that perform a complex body function e.g. Cardiovascular system organ: - different tissues arranged to perform a specific function e.g. kidney ...
Full Text - Life Science Journal
... of substance levels that have a general toxic and cerebrotoxic action. Bile enzymes also contribute to the toxicity: unconjugated bilirubin provides a pathogenic effect on cell membranes of tissues and organs. In connection with the general intoxication, there is impaired a systemic hemodynamics [28 ...
... of substance levels that have a general toxic and cerebrotoxic action. Bile enzymes also contribute to the toxicity: unconjugated bilirubin provides a pathogenic effect on cell membranes of tissues and organs. In connection with the general intoxication, there is impaired a systemic hemodynamics [28 ...
File
... 23. Sperm are MADE in the:_testes______which are located in the __scrotum_______? 24. Which cell structure directs the cell’s activities and houses genetic information? The nucleus 25. What specific type of muscle is only found in the heart? Cardiac ...
... 23. Sperm are MADE in the:_testes______which are located in the __scrotum_______? 24. Which cell structure directs the cell’s activities and houses genetic information? The nucleus 25. What specific type of muscle is only found in the heart? Cardiac ...
Slide 1
... Lack of water is the #1 trigger of daytime fatigue Preliminary research indicates that 8-10 glasses of water a day could significantly ease back/joint pain for up to 80% of ...
... Lack of water is the #1 trigger of daytime fatigue Preliminary research indicates that 8-10 glasses of water a day could significantly ease back/joint pain for up to 80% of ...
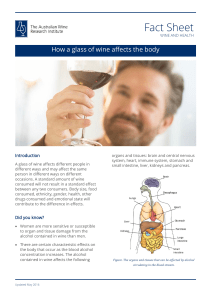
How a glass of wine affects the body
... A glass of wine affects different people in different ways and may affect the same person in different ways on different occasions. A standard amount of wine consumed will not result in a standard effect between any two consumers. Body size, food consumed, ethnicity, gender, health, other drugs cons ...
... A glass of wine affects different people in different ways and may affect the same person in different ways on different occasions. A standard amount of wine consumed will not result in a standard effect between any two consumers. Body size, food consumed, ethnicity, gender, health, other drugs cons ...
THE CIRCULATORY AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS
... • Respiratory diseases could include emphysema and lung cancer. Emphysema causes the alveoli walls to lose their elasticity. This may make breathing very difficult. • Smoking also destroys the cilia lining your respiratory ...
... • Respiratory diseases could include emphysema and lung cancer. Emphysema causes the alveoli walls to lose their elasticity. This may make breathing very difficult. • Smoking also destroys the cilia lining your respiratory ...
Human Body Systems Final Assessment
... Pepsin-found in digestive juice along with HCl (hydrochloric acid) breaks down proteins • Bile-made in liver and stored in the gall bladder, breaks down fats • Pancreatic juice-contains several enzymes that break down fats, starches and proteins You will need to recall how to do a test for starch (u ...
... Pepsin-found in digestive juice along with HCl (hydrochloric acid) breaks down proteins • Bile-made in liver and stored in the gall bladder, breaks down fats • Pancreatic juice-contains several enzymes that break down fats, starches and proteins You will need to recall how to do a test for starch (u ...
Human Body Systems Interactions Test Review
... • When you are dehydrated, the pituitary releases a hormone into your bloodstream to tell you kidneys to hold onto water. • When you have too much water, the pituitary stops releasing the hormone, so that you can excrete the excess water (pee…) ...
... • When you are dehydrated, the pituitary releases a hormone into your bloodstream to tell you kidneys to hold onto water. • When you have too much water, the pituitary stops releasing the hormone, so that you can excrete the excess water (pee…) ...
Structure and Function of Blood Vessels
... a. drains from the superior vena cava (from the head and arms) or inferior vena cava (from the lower trunk and legs) into the right atrium, b. moves out to the lungs via the pulmonary artery, c. returns to the left atrium through the pulmonary vein, and d. leaves the heart through the aorta. ...
... a. drains from the superior vena cava (from the head and arms) or inferior vena cava (from the lower trunk and legs) into the right atrium, b. moves out to the lungs via the pulmonary artery, c. returns to the left atrium through the pulmonary vein, and d. leaves the heart through the aorta. ...
the PDF file
... The blood vessels (arteries, veins, and capillaries) carry blood either away from the heart to various organs or from various organs back to the heart. Question 15: Why is it necessary to separate oxygenated and deoxygenated blood in mammals and birds? Answer: Warm-blooded animals such as birds and ...
... The blood vessels (arteries, veins, and capillaries) carry blood either away from the heart to various organs or from various organs back to the heart. Question 15: Why is it necessary to separate oxygenated and deoxygenated blood in mammals and birds? Answer: Warm-blooded animals such as birds and ...
BioE Example: Artificial Heart
... on patient activity level Should not evoke an immune response No wires or tubes that penetrate the skin Should not produce blood clots Should not damage red blood cells Ideally should have pulsatile blood flow Many others we haven’t thought of! We bring life to engineering! ...
... on patient activity level Should not evoke an immune response No wires or tubes that penetrate the skin Should not produce blood clots Should not damage red blood cells Ideally should have pulsatile blood flow Many others we haven’t thought of! We bring life to engineering! ...
This type of blood vessel carries blood away from the heart. What is
... Vein carries blood to heart (atrium) Artery carries blood away from heart (ventricle) ...
... Vein carries blood to heart (atrium) Artery carries blood away from heart (ventricle) ...
circulatory webquest
... 3. Your blood pressure is at its ______________________________ when the heart __________________________, pumping the blood. This is called _____________________________________________________________________. 4. When the heart is at ______________________, between __________________________, your ...
... 3. Your blood pressure is at its ______________________________ when the heart __________________________, pumping the blood. This is called _____________________________________________________________________. 4. When the heart is at ______________________, between __________________________, your ...
Blood Transport System
... diffuses into tissue capillaries and enter the blood stream where it combines with water to form carbonic acid – carbonic acid is weak and quickly dissociates into hydrogen ions – in this form majority of CO2 is transported back to the lungs and expired 23% combines with haemoglobin in red blood cel ...
... diffuses into tissue capillaries and enter the blood stream where it combines with water to form carbonic acid – carbonic acid is weak and quickly dissociates into hydrogen ions – in this form majority of CO2 is transported back to the lungs and expired 23% combines with haemoglobin in red blood cel ...
Key - Wilson`s Web Page
... monitors CO2 and H+ levels in the blood, and stimulates increased breathing when levels increase. Sends and receives signals to and from the diaphragm/intercostal muscles to coordinate breathing. Pleural membrane: membrane which contains the lungs, and surrounds the thoracic cavity. This secretes ...
... monitors CO2 and H+ levels in the blood, and stimulates increased breathing when levels increase. Sends and receives signals to and from the diaphragm/intercostal muscles to coordinate breathing. Pleural membrane: membrane which contains the lungs, and surrounds the thoracic cavity. This secretes ...
Cells, Tissues, Organs, and Systems
... Tissues are groups of cells working together to perform a certain job. Organs are groups of tissues that perform a certain function. Organs working together to carry out a certain life function are an organ system. ...
... Tissues are groups of cells working together to perform a certain job. Organs are groups of tissues that perform a certain function. Organs working together to carry out a certain life function are an organ system. ...
hypoalbuminemia – when the blood albumin level gets
... When we eat food containing proteins, the digestion process breaks them into small enough sized molecules to allow passage through the intestinal lining and into the bloodstream. The liver grabs these molecules as they flow through it, and transforms them into albumin, which the body can then remanu ...
... When we eat food containing proteins, the digestion process breaks them into small enough sized molecules to allow passage through the intestinal lining and into the bloodstream. The liver grabs these molecules as they flow through it, and transforms them into albumin, which the body can then remanu ...
circulatory system
... passageways and fills up our lungs. Within each lung, the tiny alveoli are surrounded by blood vessels and oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse in and out of the vessels. ...
... passageways and fills up our lungs. Within each lung, the tiny alveoli are surrounded by blood vessels and oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse in and out of the vessels. ...
Homeostasis

Homeostasis or homoeostasis (homeo- + -stasis) is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH). It is a process that maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment in response to changes in external conditions.The concept was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1865 and the word was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. Although the term was originally used to refer to processes within living organisms, it is frequently applied to automatic control systems such as thermostats. Homeostasis requires a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.