122 переведення працівника на більш високу
... go up, aggregate supply goes down. The average tax rate does not matter; c) this shift in aggregate supply is more important for predicting what taxes will do than is the shift in aggregate demand. Rational expectations – expectations that are unbiased and based upon the best available information. ...
... go up, aggregate supply goes down. The average tax rate does not matter; c) this shift in aggregate supply is more important for predicting what taxes will do than is the shift in aggregate demand. Rational expectations – expectations that are unbiased and based upon the best available information. ...
Keynesian economics
... While consumption is the most stable component of GDP, investment is the least stable. According to Keynesian theory, the volatility of investment (due, in part, to “animal spirits”) is the root cause of most ...
... While consumption is the most stable component of GDP, investment is the least stable. According to Keynesian theory, the volatility of investment (due, in part, to “animal spirits”) is the root cause of most ...
John Maynard Keynes: The Man Who Transformed the Economic
... Keynesian ideas began to gain favor during the Great Depression when many of his proposals influenced the American and British governments, particularly Roosevelt's New Deal policies. And while it took some time for Keynes' ideas to take hold, they eventually gained ground and became a dominant scho ...
... Keynesian ideas began to gain favor during the Great Depression when many of his proposals influenced the American and British governments, particularly Roosevelt's New Deal policies. And while it took some time for Keynes' ideas to take hold, they eventually gained ground and became a dominant scho ...
Modeling Dynamics Of Dividend Policy, Capital Structure And
... Classical economic theory has always claimed that the economy is always at full-employment. Guarantee that, all output produced by firms will be taken up by consumers on the principles that, supply creates its own demand. In the short-run there will be temporary disequilibrium in the capital, ...
... Classical economic theory has always claimed that the economy is always at full-employment. Guarantee that, all output produced by firms will be taken up by consumers on the principles that, supply creates its own demand. In the short-run there will be temporary disequilibrium in the capital, ...
the fed, fiscal, monetary policy, keynes
... tell economists and politicians how to get out of and avoid economic crisis ...
... tell economists and politicians how to get out of and avoid economic crisis ...
Economic Ups and Downs
... Prices rise for 2 quarters or (6 months) Prices tend to rise during periods of ...
... Prices rise for 2 quarters or (6 months) Prices tend to rise during periods of ...
Macro Theory
... That markets can’t clear is sign of government intervention. Existence of unions & gov’t price fixing policies worsen outcome. ...
... That markets can’t clear is sign of government intervention. Existence of unions & gov’t price fixing policies worsen outcome. ...
What Would Keynes D ould Keynes D ould Keynes Do?
... Identify one president who relied on Keynes’s ideas to solve an economic crisis. Was his strategy generally thought to be successful? Why or why not? ____________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ ...
... Identify one president who relied on Keynes’s ideas to solve an economic crisis. Was his strategy generally thought to be successful? Why or why not? ____________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ ...
January 12th Agenda CBM In the News
... regarding taxing and spending • Monetary Policy: The FED policy aimed at regulating amount of money in circulation and interest rates • Before 1930, government rarely intervened in the economy – good or bad times included ...
... regarding taxing and spending • Monetary Policy: The FED policy aimed at regulating amount of money in circulation and interest rates • Before 1930, government rarely intervened in the economy – good or bad times included ...
No Slide Title
... 1) Classical economics is the body of macroeconomics thought associated primarily with nineteenth-century British economist David Ricardo. It emphasized the ability of flexible wages and prices to keep the economy at or near its natural level of employment. ...
... 1) Classical economics is the body of macroeconomics thought associated primarily with nineteenth-century British economist David Ricardo. It emphasized the ability of flexible wages and prices to keep the economy at or near its natural level of employment. ...
Booms and busts, the accelerator, and Keynesian fiscal policy
... • Keynesians believe that investment (I) demand is not sensitive to the interest rate, instead it is primarily linked to aggregate demand (AD). • Increases in AD and economic growth will accelerate investment by businesses, while decreases in AD and growth will decelerate it. ...
... • Keynesians believe that investment (I) demand is not sensitive to the interest rate, instead it is primarily linked to aggregate demand (AD). • Increases in AD and economic growth will accelerate investment by businesses, while decreases in AD and growth will decelerate it. ...
Two school of Economics 1. Neo-classical * Free
... Key Keynesian insight – Increase in exogenous spending increased household income and encourages higher I by Firms. For eg, ↑Go causes additional in C and I. Final ∆∆YYmust greater than initial ∆ Go. ∆ Y = ∆Go + ∆C + ∆I Small fiscal or monetary stimulus can return economy to Yfe, full employment NB. ...
... Key Keynesian insight – Increase in exogenous spending increased household income and encourages higher I by Firms. For eg, ↑Go causes additional in C and I. Final ∆∆YYmust greater than initial ∆ Go. ∆ Y = ∆Go + ∆C + ∆I Small fiscal or monetary stimulus can return economy to Yfe, full employment NB. ...
Modern neoclassical economics
... of consumption, savings and investment decisions of different categories of economic agents. - Analyse the determinants of aggregate demand and aggregate supply - Explore the effects of fiscal policy on ...
... of consumption, savings and investment decisions of different categories of economic agents. - Analyse the determinants of aggregate demand and aggregate supply - Explore the effects of fiscal policy on ...
keynes1
... was cheated of his 5 shillings. It is not well suited for classroom use. It is arrogant, bad-tempered, polemical, and not overlygenerous in its acknowledgements... In it the Keynesian system stands out indistinctly, as if the author were hardly aware of its existence or cognizant of its properties; ...
... was cheated of his 5 shillings. It is not well suited for classroom use. It is arrogant, bad-tempered, polemical, and not overlygenerous in its acknowledgements... In it the Keynesian system stands out indistinctly, as if the author were hardly aware of its existence or cognizant of its properties; ...
First Lecture Powerpoint Slides in Acrobat Format
... was cheated of his 5 shillings. It is not well suited for classroom use. It is arrogant, bad-tempered, polemical, and not overlygenerous in its acknowledgements... In it the Keynesian system stands out indistinctly, as if the author were hardly aware of its existence or cognizant of its properties; ...
... was cheated of his 5 shillings. It is not well suited for classroom use. It is arrogant, bad-tempered, polemical, and not overlygenerous in its acknowledgements... In it the Keynesian system stands out indistinctly, as if the author were hardly aware of its existence or cognizant of its properties; ...
Chapter 17 Economic Policymaking
... • Private individuals own the principal means of production • Prices and wages determined by Supply and Demand • “Free Market” = no government intervention of economy ...
... • Private individuals own the principal means of production • Prices and wages determined by Supply and Demand • “Free Market” = no government intervention of economy ...
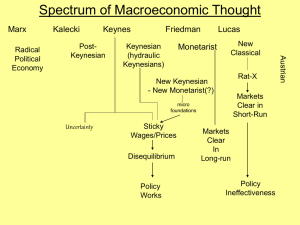
Macro Spectrum
... would enable them to compute perfectly the relative prices they care about, agents make errors…[A]gents temporarily mistake a general increase in all absolute prices as an increase in the relative price of the good they are selling, leading them to increase their supply of that good…Since everyone i ...
... would enable them to compute perfectly the relative prices they care about, agents make errors…[A]gents temporarily mistake a general increase in all absolute prices as an increase in the relative price of the good they are selling, leading them to increase their supply of that good…Since everyone i ...
Notes on Economics
... GDP – Gross Domestic Product – the total production inside the United States for all businesses from all countries. Aggregate Demand – percentage of income that people spend instead of saving or investing. Unemployment – the number of people without jobs Inflation/Deflation – the change of p ...
... GDP – Gross Domestic Product – the total production inside the United States for all businesses from all countries. Aggregate Demand – percentage of income that people spend instead of saving or investing. Unemployment – the number of people without jobs Inflation/Deflation – the change of p ...
Fiscal Policy and the Federal Reserve
... The United States government largely adhered to free market practices throughout the 18th and 19th century The American economy was marked but rapid growth during this time period, but also periodic sometimes intense downturns, frequently referred to as “panics”; banking was not highly regulated The ...
... The United States government largely adhered to free market practices throughout the 18th and 19th century The American economy was marked but rapid growth during this time period, but also periodic sometimes intense downturns, frequently referred to as “panics”; banking was not highly regulated The ...
John Maynard Keynes - Washington State University
... John Maynard Keynes The Rise of Keynesianism and Challenges to Keynesianism ...
... John Maynard Keynes The Rise of Keynesianism and Challenges to Keynesianism ...
The implications of Mr. Sraffa for economic policy
... the short and in the long run. In the short-run by a fuller exploitation of existing capacity; in the long-run by increasing capacity. • In a demand-led theory, resources (capital and population) adjust to demand growth, not the other way round. • Monetary and fiscal policy affects output also in th ...
... the short and in the long run. In the short-run by a fuller exploitation of existing capacity; in the long-run by increasing capacity. • In a demand-led theory, resources (capital and population) adjust to demand growth, not the other way round. • Monetary and fiscal policy affects output also in th ...
Big Government Causes Slow Growth
... In 1930, Pluto was declared the ninth planet. In 2007, it was demoted to "dwarf planet" status by astronomers after considering new evidence. There are now only eight planets. Also in the 1930s, the ideas of John Maynard Keynes came of age. In spite of a massive amount of evidence that these ideas d ...
... In 1930, Pluto was declared the ninth planet. In 2007, it was demoted to "dwarf planet" status by astronomers after considering new evidence. There are now only eight planets. Also in the 1930s, the ideas of John Maynard Keynes came of age. In spite of a massive amount of evidence that these ideas d ...