keynesian economics
... So having moved along the Phillips Curve from U to V, the firms now begin to lay people off once again and unemployment moves back to W. Next time around the firms and consumers are ready for this, and anticipate the inflation. If the government insist on trying again the economy will do the same th ...
... So having moved along the Phillips Curve from U to V, the firms now begin to lay people off once again and unemployment moves back to W. Next time around the firms and consumers are ready for this, and anticipate the inflation. If the government insist on trying again the economy will do the same th ...
a well-defined analytical concept or one more arbitrary straightjacket?
... 1. Labour market ‘full employment/natural unemployment’ equilibrium 2. Private sector equilibrium between savings and real investment 3. Deviations are cleared via the financial capital markets, domestically 4. Internationally via the balance of payments, capital account (especially within a monetar ...
... 1. Labour market ‘full employment/natural unemployment’ equilibrium 2. Private sector equilibrium between savings and real investment 3. Deviations are cleared via the financial capital markets, domestically 4. Internationally via the balance of payments, capital account (especially within a monetar ...
Module History and Alternative Views of
... The Revival of Monetary Policy The main practical consequence of Keynes’s work was that it legitimized macroeconomic policy activism—the use of monetary and fiscal policy is to smooth out the business cycle. In the 1930s, economists were divided on the issue of government policy that would affect th ...
... The Revival of Monetary Policy The main practical consequence of Keynes’s work was that it legitimized macroeconomic policy activism—the use of monetary and fiscal policy is to smooth out the business cycle. In the 1930s, economists were divided on the issue of government policy that would affect th ...
Wapshott Interview on Keynes Hayek
... because of money printing and this is what caused political instability (Keynes claim it was a failure of capitalism). This began the Nazi rise to power. • Keynes stated: “There is no subtler, no surer way means to overturning the existing basis of society than to debauch the currency” [Note: curren ...
... because of money printing and this is what caused political instability (Keynes claim it was a failure of capitalism). This began the Nazi rise to power. • Keynes stated: “There is no subtler, no surer way means to overturning the existing basis of society than to debauch the currency” [Note: curren ...
FT.com print article
... seriously. “A sound banker, alas, is not one who foresees danger and avoids it, but one who, when he is ruined, is ruined in a conventional way along with his fellows, so that no one can really blame him.” Not for him, then, was the notion of “efficient markets”. The second lesson is that the econom ...
... seriously. “A sound banker, alas, is not one who foresees danger and avoids it, but one who, when he is ruined, is ruined in a conventional way along with his fellows, so that no one can really blame him.” Not for him, then, was the notion of “efficient markets”. The second lesson is that the econom ...
The Long Swings in Economic Understanding
... The growing inequality of incomes in recent years is, of course, attracting the attention of prominent economists but hardly within the real business cycle school. In the United States, James K. Galbraith (1998) has played a role corresponding to that of Fitoussi in France. ...
... The growing inequality of incomes in recent years is, of course, attracting the attention of prominent economists but hardly within the real business cycle school. In the United States, James K. Galbraith (1998) has played a role corresponding to that of Fitoussi in France. ...
Eco 202 Course Outline for 2015-2016
... ELEMENTS OF ECONOMICS II (ECO 202) SECOND SEMESTER 2015/2016 CREDIT HOURS: 3 COURSE DESCRIPTION This course in macroeconomics analyses the aggregate economic activity in the national economy and its link with the rest of the world. Emphasis is placed on basic principles involved in the determination ...
... ELEMENTS OF ECONOMICS II (ECO 202) SECOND SEMESTER 2015/2016 CREDIT HOURS: 3 COURSE DESCRIPTION This course in macroeconomics analyses the aggregate economic activity in the national economy and its link with the rest of the world. Emphasis is placed on basic principles involved in the determination ...
Download pdf | 407 KB |
... Reading Keynes III Now if for a given value of N the expected proceeds are greater than the aggregate supply price, i.e. if D is greater than Z, there will be an incentive to entrepreneurs to increase employment beyond N and, if necessary, to raise costs by competing with one another for the factor ...
... Reading Keynes III Now if for a given value of N the expected proceeds are greater than the aggregate supply price, i.e. if D is greater than Z, there will be an incentive to entrepreneurs to increase employment beyond N and, if necessary, to raise costs by competing with one another for the factor ...
Document
... that provides a passive path over which aggregate demand can roam. The short-run aggregate supply curve can shift in ways that clearly affect real GDP, unemployment, and the price level. Money matters more than Keynesians had previously suspected. The work of monetarists showing a close corresponden ...
... that provides a passive path over which aggregate demand can roam. The short-run aggregate supply curve can shift in ways that clearly affect real GDP, unemployment, and the price level. Money matters more than Keynesians had previously suspected. The work of monetarists showing a close corresponden ...
Quiz 1
... what causes a nation’s economic activity to fluctuate? d. why are women paid less on average than men with the same qualifications and experience? e. can government policies be used successfully to manage a nation’s economic performance? ...
... what causes a nation’s economic activity to fluctuate? d. why are women paid less on average than men with the same qualifications and experience? e. can government policies be used successfully to manage a nation’s economic performance? ...
Spending Is Not Stimulus
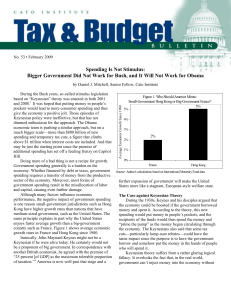
... Government spending generally is a burden on the economy. Whether financed by debt or taxes, government Source: Author's calculations based on International Monetary Fund data. spending requires a transfer of money from the productive sector of the economy. Moreover, most forms of further expansion ...
... Government spending generally is a burden on the economy. Whether financed by debt or taxes, government Source: Author's calculations based on International Monetary Fund data. spending requires a transfer of money from the productive sector of the economy. Moreover, most forms of further expansion ...
- Kennedy HS
... no one had enough money to buy its products. o How do unemployed consumers spend money they don’t have. o The only way to end the Depression would be if someone, somewhere, started spending. A New Role for Government o Keynes thought the spender should be the ___________________. o In the early 1930 ...
... no one had enough money to buy its products. o How do unemployed consumers spend money they don’t have. o The only way to end the Depression would be if someone, somewhere, started spending. A New Role for Government o Keynes thought the spender should be the ___________________. o In the early 1930 ...
ECON 2020-200 Principles of Macroeconomics
... A few other reading assignments will be distributed and referred to in the class. Use of new technology such as website search and reference is required. Course Description and Objectives: This course focuses on the overall economic issues of GDP calculation, working · of ·market system in a capital ...
... A few other reading assignments will be distributed and referred to in the class. Use of new technology such as website search and reference is required. Course Description and Objectives: This course focuses on the overall economic issues of GDP calculation, working · of ·market system in a capital ...
Economic Rent
... maximum which he/she would have been willing to pay rather than going without it. ...
... maximum which he/she would have been willing to pay rather than going without it. ...
Chapter 10
... If a shift in the aggregate demand curve from AD to AD1 in Figure 10.4 causes a movement from point a to point d in the long run, will a shift in the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD cause a movement from point d back to point a in the long run? Yes, if there were disinvestment as the result of ...
... If a shift in the aggregate demand curve from AD to AD1 in Figure 10.4 causes a movement from point a to point d in the long run, will a shift in the aggregate demand curve from AD1 to AD cause a movement from point d back to point a in the long run? Yes, if there were disinvestment as the result of ...
Breaking from Orthodoxy: Responses to the Great Depression
... stay low, factories stay idle, workers stay unemployed, and workers don’t have income to consume products. Demand therefore stays low • A “vicious circle” created by investors acting rationally as individuals, but irrationally as a group. Implied a role for government to help shift investor expectat ...
... stay low, factories stay idle, workers stay unemployed, and workers don’t have income to consume products. Demand therefore stays low • A “vicious circle” created by investors acting rationally as individuals, but irrationally as a group. Implied a role for government to help shift investor expectat ...
File
... an entire school of modern thought bears his name. Many of his ideas were revolutionary; almost all were controversial. KEYNESIAN ECONOMICS serves as a sort of yardstick that can define virtually all economists who came after him. Keynes became a celebrity before becoming one of the most respected e ...
... an entire school of modern thought bears his name. Many of his ideas were revolutionary; almost all were controversial. KEYNESIAN ECONOMICS serves as a sort of yardstick that can define virtually all economists who came after him. Keynes became a celebrity before becoming one of the most respected e ...
Chapter 11 Classical & Keynesian Economics What You Will Learn
... Price Stability (1970’s) – Federal Government took responsibility to ensure the economy has stable prices – CPI increase at no more than 3%/year So, from no role prior to the great depression to comprehensive responsibilities post depression ...
... Price Stability (1970’s) – Federal Government took responsibility to ensure the economy has stable prices – CPI increase at no more than 3%/year So, from no role prior to the great depression to comprehensive responsibilities post depression ...
Fiscal Policy: Incentives and Secondary Effects
... disagreements about fiscal policy among modern macroeconomists ...
... disagreements about fiscal policy among modern macroeconomists ...
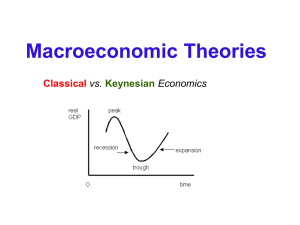
Classical versus Keynesian Economics
... Macroeconomic Theories Classical vs. Keynesian Economics ...
... Macroeconomic Theories Classical vs. Keynesian Economics ...