Unit 5 Answers - Iowa State University
... Phylogenetic Species Concept (PSC): Species are defined as the smallest monophyletic groups based on their evolutionary history Disadvantage: subspecies How is allopatric speciation different from sympatric speciation? Allopatric: different areas ...
... Phylogenetic Species Concept (PSC): Species are defined as the smallest monophyletic groups based on their evolutionary history Disadvantage: subspecies How is allopatric speciation different from sympatric speciation? Allopatric: different areas ...
Chapter 13 Theory of Evolution Darwin
... 1. All organisms have variations of traits 2. Some variations allow the organism to be successful in a particular environment and produce more offspring 3. Less successful organisms tend to die out rapidly producing little if any offspring. 4. Competition for survival weeds out inferior specie ...
... 1. All organisms have variations of traits 2. Some variations allow the organism to be successful in a particular environment and produce more offspring 3. Less successful organisms tend to die out rapidly producing little if any offspring. 4. Competition for survival weeds out inferior specie ...
Paedomorphosis
... all organisms have descended with modification from a common ancestor, and thus built a strong case for evolution 2. Suggested natural selection as a mechanism of evolution The Modern Synthesis attempts to explain how evolution works at the level of genes, phenotypes, and populations whereas Darwini ...
... all organisms have descended with modification from a common ancestor, and thus built a strong case for evolution 2. Suggested natural selection as a mechanism of evolution The Modern Synthesis attempts to explain how evolution works at the level of genes, phenotypes, and populations whereas Darwini ...
Document
... 1. Directional Selection: environment favors traits that are at ONE extreme of a range of traits a. Ex. peppered moths in Manchester, England b. humans artificially select crops for agriculture and animals for breeding which accelerates this 2. Stabilizing Selection: intermediate forms of a trait ha ...
... 1. Directional Selection: environment favors traits that are at ONE extreme of a range of traits a. Ex. peppered moths in Manchester, England b. humans artificially select crops for agriculture and animals for breeding which accelerates this 2. Stabilizing Selection: intermediate forms of a trait ha ...
Evolution Definitions
... Disruptive Selection – Natural selection that favors both extremes (White limpets blend with light colored rocks, dark brown limpets blend with dark colored rocks, and tan limpets don’t blend at all and are eaten) Speciation – The evolution of a new species occurs when members of similar populations ...
... Disruptive Selection – Natural selection that favors both extremes (White limpets blend with light colored rocks, dark brown limpets blend with dark colored rocks, and tan limpets don’t blend at all and are eaten) Speciation – The evolution of a new species occurs when members of similar populations ...
Evolution PowerPoint Lecture Notes
... beneficial and are added to gene pool. 2) Genetic Drift - Changes due to chance events (Small populations) Ex. Amish; short arms/legs 3) Gene flow - Movement of genes into or out of a population; causes the gain or loss of genetic info. ...
... beneficial and are added to gene pool. 2) Genetic Drift - Changes due to chance events (Small populations) Ex. Amish; short arms/legs 3) Gene flow - Movement of genes into or out of a population; causes the gain or loss of genetic info. ...
Evolution chapters 16-17 test review sheet 1. Biologists in Darwin`s
... 6. Describe artificial selection and give example that humans may have used. Choosing individuals to m ate to change offspring (example: dog breeding) 7. Organisms that live long enough, may become more adapted to their environment may be led to greater fitness how will this affect their offspring? ...
... 6. Describe artificial selection and give example that humans may have used. Choosing individuals to m ate to change offspring (example: dog breeding) 7. Organisms that live long enough, may become more adapted to their environment may be led to greater fitness how will this affect their offspring? ...
Evolution Essays
... 1994: Genetic variation is the raw material for evolution. a. Explain three cellular and/or molecular mechanisms that introduce variation into the gene pool of a plant or animal population. b. Explain the evolutionary mechanisms that can change the composition of the gene pool. 2004: Darwin is consi ...
... 1994: Genetic variation is the raw material for evolution. a. Explain three cellular and/or molecular mechanisms that introduce variation into the gene pool of a plant or animal population. b. Explain the evolutionary mechanisms that can change the composition of the gene pool. 2004: Darwin is consi ...
Evolutionary Theory
... 3. Over time, traits that make some individuals better tend to spread in that population 4. LOTS of fossil evidence that living species evolved from organisms that are now extinct ...
... 3. Over time, traits that make some individuals better tend to spread in that population 4. LOTS of fossil evidence that living species evolved from organisms that are now extinct ...
Darwin proposed natural selection as the mechanism of evolution
... More Observations Lead to an Idea • Based his theory on 2 key sets of observations – Only small % of offspring will survive each generation – Population VARIATION differences among members of the SAME species ...
... More Observations Lead to an Idea • Based his theory on 2 key sets of observations – Only small % of offspring will survive each generation – Population VARIATION differences among members of the SAME species ...
Evolution
... • Well-accepted theory of how organisms have changed over time by natural selection. • Darwin based his ideas on: • 1. observations of nature • 2. Malthus’s theory about exponential population growth • 3. his experience breeding animals ...
... • Well-accepted theory of how organisms have changed over time by natural selection. • Darwin based his ideas on: • 1. observations of nature • 2. Malthus’s theory about exponential population growth • 3. his experience breeding animals ...
Evolution 2011-2012
... 2. DNA by comparing the DNA sequences of two organisms or the amino acid sequences made from the DNA, scientists can learn which organisms are related; the more DNA two organisms have in common, the more closely related they are ...
... 2. DNA by comparing the DNA sequences of two organisms or the amino acid sequences made from the DNA, scientists can learn which organisms are related; the more DNA two organisms have in common, the more closely related they are ...
Brain Squeeze
... O Is when one species gives rise to many different species. O Occurs in a relatively short time span. O Usually occurs in response to the creation of a new ...
... O Is when one species gives rise to many different species. O Occurs in a relatively short time span. O Usually occurs in response to the creation of a new ...
Unit 6: Evolution
... 5. Work out these practice problems. Find both the gene and genotype frequencies: a. In Drosophilia, the allele for normal length wings is dominant over the allele for vestigial wings. In a population of 1,000 individuals, 160 show the recessive phenotype. b. The allele for the hair pattern called " ...
... 5. Work out these practice problems. Find both the gene and genotype frequencies: a. In Drosophilia, the allele for normal length wings is dominant over the allele for vestigial wings. In a population of 1,000 individuals, 160 show the recessive phenotype. b. The allele for the hair pattern called " ...
Icons of Science - Evolution video worksheet
... 15) What are examples of species that experiences convergent evolution (appear similar, but aren’t)? ...
... 15) What are examples of species that experiences convergent evolution (appear similar, but aren’t)? ...
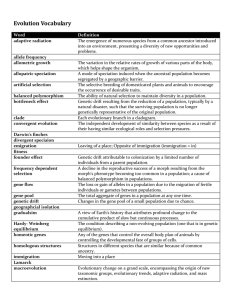
Evolution Vocabulary
... Differential success in the reproduction of different phenotypes resulting from the interaction of organisms with their environment. Evolution occurs when natural selection causes changes in relative frequencies of alleles in the gene pool. The supercontinent formed near the end of the Paleozoic era ...
... Differential success in the reproduction of different phenotypes resulting from the interaction of organisms with their environment. Evolution occurs when natural selection causes changes in relative frequencies of alleles in the gene pool. The supercontinent formed near the end of the Paleozoic era ...
Chapter 15 Notes Darwin on the HMS Beagle The Galápagos
... Chapter 15 Notes Darwin on the HMS Beagle ...
... Chapter 15 Notes Darwin on the HMS Beagle ...
Evolution Test Study Guide Answers
... • What would happen to the populations of the same species living in different areas? – They would evolve differently over time because of their different environments ...
... • What would happen to the populations of the same species living in different areas? – They would evolve differently over time because of their different environments ...
File
... A plant or animal that reproduces usually makes more offspring than can possibly survive (than the environment can support): Ex: several thousand salmon eggs, not all hatch, a few hundred survive disease or predation, several dozen reach adulthood, and few will successfully reproduce Genetic var ...
... A plant or animal that reproduces usually makes more offspring than can possibly survive (than the environment can support): Ex: several thousand salmon eggs, not all hatch, a few hundred survive disease or predation, several dozen reach adulthood, and few will successfully reproduce Genetic var ...
Natural Selection and Evolution notes
... On the Galapagos islands Darwin studied many plants and animals, but specifically a type of bird—finches. *He discovered the birds had changed due to isolation on each island, and had evolved different traits to meet survival needs of each island (ex: beak size, coloration, wing span, etc.) *He prop ...
... On the Galapagos islands Darwin studied many plants and animals, but specifically a type of bird—finches. *He discovered the birds had changed due to isolation on each island, and had evolved different traits to meet survival needs of each island (ex: beak size, coloration, wing span, etc.) *He prop ...
Evolution Terms to Know
... Allopatric speciation disruptive selection analogous structures domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, artificial selection family, genus, species binomial nomenclature (genus, species) Evidence of evolution biogeography evolutionary adaptation bottleneck effect founder effect ...
... Allopatric speciation disruptive selection analogous structures domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, artificial selection family, genus, species binomial nomenclature (genus, species) Evidence of evolution biogeography evolutionary adaptation bottleneck effect founder effect ...
Ch. 22-Student Note Sheet
... Natural selection is a major mechanism of evolution Natural selection acts on phenotypic variations within populations. Evolutionary change is also driven by random processes. Biological evolution is supported by scientific evidence from many disciplines including mathematics Organisms share many co ...
... Natural selection is a major mechanism of evolution Natural selection acts on phenotypic variations within populations. Evolutionary change is also driven by random processes. Biological evolution is supported by scientific evidence from many disciplines including mathematics Organisms share many co ...
Speciation
Speciation is the evolutionary process by which new biological species arise. The biologist Orator F. Cook was the first to coin the term 'speciation' for the splitting of lineages or ""cladogenesis,"" as opposed to ""anagenesis"" or ""phyletic evolution"" occurring within lineages. Charles Darwin was the first to describe the role of natural selection in speciation. There is research comparing the intensity of sexual selection in different clades with their number of species.There are four geographic modes of speciation in nature, based on the extent to which speciating populations are isolated from one another: allopatric, peripatric, parapatric, and sympatric. Speciation may also be induced artificially, through animal husbandry, agriculture, or laboratory experiments. Whether genetic drift is a minor or major contributor to speciation is the subject matter of much ongoing discussion.