tn8_ch-04_win-mine - Dr. Bruce Packard
... • Separation Speciation is believed to begin when a part of a population becomes separated from the rest. • Adaptation Populations constantly undergo natural selection. After two groups have separated, natural selection continues to act on the groups. • If the environmental conditions for each group ...
... • Separation Speciation is believed to begin when a part of a population becomes separated from the rest. • Adaptation Populations constantly undergo natural selection. After two groups have separated, natural selection continues to act on the groups. • If the environmental conditions for each group ...
The Peppered Moth – A case of Natural Selection and Adaptation
... Breeding dogs, breeding horses to produce the fastest possible horse etc. ...
... Breeding dogs, breeding horses to produce the fastest possible horse etc. ...
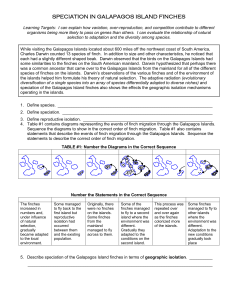
ACTIVITY: GALAPAGOS FINCHES
... While visiting the Galapagos Islands located about 600 miles off the northwest coast of South America, Charles Darwin counted 13 species of finch. In addition to size and other characteristics, he noticed that each had a slightly different shaped beak. Darwin observed that the birds on the Galapagos ...
... While visiting the Galapagos Islands located about 600 miles off the northwest coast of South America, Charles Darwin counted 13 species of finch. In addition to size and other characteristics, he noticed that each had a slightly different shaped beak. Darwin observed that the birds on the Galapagos ...
11.1 Genetic Variation Within Population
... – It occurs when a few individuals start a new population. – The founder effect is genetic drift that occurs after start of new population. ...
... – It occurs when a few individuals start a new population. – The founder effect is genetic drift that occurs after start of new population. ...
The evolutionary reality of species and higher taxa in plants: a
... Fig. 1 Three theoretical models for the structure of diversity that make different predictions about the structure of genetic and phenotypic variation within clades. (a, d) Individuals within a wider clade form a continuous hierarchy. No processes are operating that create independently evolving sub ...
... Fig. 1 Three theoretical models for the structure of diversity that make different predictions about the structure of genetic and phenotypic variation within clades. (a, d) Individuals within a wider clade form a continuous hierarchy. No processes are operating that create independently evolving sub ...
Evolution Objectives Natural Selection: 1. State the 2 major points
... 28. Distinguish between prezygotic and postzygotic isolating mechanisms 29. Describe 5 prezygotic isolating mechanisms and give an example of each 30. Explain why many hybrids are sterile 31. Explain how hybrid breakdown maintains separate species even if gene flow occurs 32. Distinguish between all ...
... 28. Distinguish between prezygotic and postzygotic isolating mechanisms 29. Describe 5 prezygotic isolating mechanisms and give an example of each 30. Explain why many hybrids are sterile 31. Explain how hybrid breakdown maintains separate species even if gene flow occurs 32. Distinguish between all ...
EVOLUTION OF POPOULATIONS
... • How does genetic drift take place? • In small populations, individuals that carry a particular allele may leave more descendants than other individuals do, just by chance • Over time, a series of chance occurrences of this type can cause an allele to become common in a population ...
... • How does genetic drift take place? • In small populations, individuals that carry a particular allele may leave more descendants than other individuals do, just by chance • Over time, a series of chance occurrences of this type can cause an allele to become common in a population ...
EVOLUTION OF POPOULATIONS
... • How does genetic drift take place? • In small populations, individuals that carry a particular allele may leave more descendants than other individuals do, just by chance • Over time, a series of chance occurrences of this type can cause an allele to become common in a population ...
... • How does genetic drift take place? • In small populations, individuals that carry a particular allele may leave more descendants than other individuals do, just by chance • Over time, a series of chance occurrences of this type can cause an allele to become common in a population ...
Darwin II
... laws, taken in the largest sense, being Growth with Reproduction; Inheritance which is almost implied by reproduction; Variability from the indirect and direct action of the external conditions of life, and from use and disuse; a Ratio of Increase so high as to lead to a Struggle for Life, and as a ...
... laws, taken in the largest sense, being Growth with Reproduction; Inheritance which is almost implied by reproduction; Variability from the indirect and direct action of the external conditions of life, and from use and disuse; a Ratio of Increase so high as to lead to a Struggle for Life, and as a ...
Big Idea 1 intro
... • In central Florida they feed on goldenrain tree with smaller fruit; they have shorter beaks • Correlation between fruit size and beak size has also been observed in Louisiana, Oklahoma, and ...
... • In central Florida they feed on goldenrain tree with smaller fruit; they have shorter beaks • Correlation between fruit size and beak size has also been observed in Louisiana, Oklahoma, and ...
Evolution and alleles
... record of recent changes in heritable characteristics. By watching mating of males and females, and the offspring, breeders select the desirable traits they want. After practicing selective breeding for hundreds of dozens of years, certain varieties of animals had unique combinations of traits not s ...
... record of recent changes in heritable characteristics. By watching mating of males and females, and the offspring, breeders select the desirable traits they want. After practicing selective breeding for hundreds of dozens of years, certain varieties of animals had unique combinations of traits not s ...
Chapter 15: The Theory of Evolution
... Organisms without these variations are less likely to survive and reproduce. As a result, each generation consists largely of offspring from parents with these variations that aid survival. ...
... Organisms without these variations are less likely to survive and reproduce. As a result, each generation consists largely of offspring from parents with these variations that aid survival. ...
bioknowledgy ppt - Peoria Public Schools
... Natural selection can only occur if there is variation among members of the same species. Mutation, meiosis and sexual reproduction cause variation between individuals in a species. Adaptations are characteristics that make an individual suited to its environment and way of life. Species tend to pro ...
... Natural selection can only occur if there is variation among members of the same species. Mutation, meiosis and sexual reproduction cause variation between individuals in a species. Adaptations are characteristics that make an individual suited to its environment and way of life. Species tend to pro ...
Docx - NSW Syllabus
... outline the process of natural selection with diagrams and/or an animation such as Evolution lab, using Darwin’s postulates, which are: individuals within a population vary in their traits. some of these variable traits are heritable more offspring are produced than can survive because of limi ...
... outline the process of natural selection with diagrams and/or an animation such as Evolution lab, using Darwin’s postulates, which are: individuals within a population vary in their traits. some of these variable traits are heritable more offspring are produced than can survive because of limi ...
evolution - Net Start Class
... eventually washes up on an island off the coast of the mainland. The fruit flies mature and emerge from their slimy nursery onto the lonely island. The two portions of the population, mainland and island, are now too far apart for gene flow to unite them. At this point, speciation has not occurred — ...
... eventually washes up on an island off the coast of the mainland. The fruit flies mature and emerge from their slimy nursery onto the lonely island. The two portions of the population, mainland and island, are now too far apart for gene flow to unite them. At this point, speciation has not occurred — ...
AP Biology 2006-2007 Evolution by Natural Selection AP Biology
... food successfully in the different environments ...
... food successfully in the different environments ...
How Populations Evolve
... traits most suitable to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce and pass those traits on to the next generation. Tuesday, January 22, 2013 ...
... traits most suitable to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce and pass those traits on to the next generation. Tuesday, January 22, 2013 ...
Natural Selection - Napa Valley College
... Individuals with certain heritable characteristics survive and reproduce at a higher rate than other individuals Natural selection increases the adaptation of organisms to their environment over time If an environment changes over time, natural selection may result in adaptation to these new c ...
... Individuals with certain heritable characteristics survive and reproduce at a higher rate than other individuals Natural selection increases the adaptation of organisms to their environment over time If an environment changes over time, natural selection may result in adaptation to these new c ...
Darwin`s bridge between microevolution and
... have “individual variations” that are faithfully transmitted from parent to offspring; second, that all organisms produce more offspring than are required to replace themselves in the next generation; third, that limited resources create a “struggle for existence” that regulates population size, suc ...
... have “individual variations” that are faithfully transmitted from parent to offspring; second, that all organisms produce more offspring than are required to replace themselves in the next generation; third, that limited resources create a “struggle for existence” that regulates population size, suc ...
Kawamiya, Nobuo
... This character displacement has been interpreted in terms of adaptive evolution: where one has attributed the accelerated evolution to enhanced “struggle for life” among close kin species. In fact the rapid cichlids' speciation seems to have been driven not by struggle for life but by struggle for s ...
... This character displacement has been interpreted in terms of adaptive evolution: where one has attributed the accelerated evolution to enhanced “struggle for life” among close kin species. In fact the rapid cichlids' speciation seems to have been driven not by struggle for life but by struggle for s ...
Biol 112 LAB REMINDERS Variation in populations Heritability of
... reproducing in a particular habitat leave more offspring than others • Inference #2 This unequal ability of individuals to survive and reproduce leads to an accumulation of these traits in a population over generations ...
... reproducing in a particular habitat leave more offspring than others • Inference #2 This unequal ability of individuals to survive and reproduce leads to an accumulation of these traits in a population over generations ...
Evolution practice questions
... In the early 1800's, peppered moths living in England rested on tree trunks that were covered with whitish lichens. The moths were also whitish in color and so matched the color of the background on which they rested. This made the moths less visible to the birds that preyed on them. In the late 184 ...
... In the early 1800's, peppered moths living in England rested on tree trunks that were covered with whitish lichens. The moths were also whitish in color and so matched the color of the background on which they rested. This made the moths less visible to the birds that preyed on them. In the late 184 ...
1 Bio 1B Evolution (Mishler) Practice questions Fall 2008 *Answers
... In the early 1800's, peppered moths living in England rested on tree trunks that were covered with whitish lichens. The moths were also whitish in color and so matched the color of the background on which they rested. This made the moths less visible to the birds that preyed on them. In the late 184 ...
... In the early 1800's, peppered moths living in England rested on tree trunks that were covered with whitish lichens. The moths were also whitish in color and so matched the color of the background on which they rested. This made the moths less visible to the birds that preyed on them. In the late 184 ...
Speciation
Speciation is the evolutionary process by which new biological species arise. The biologist Orator F. Cook was the first to coin the term 'speciation' for the splitting of lineages or ""cladogenesis,"" as opposed to ""anagenesis"" or ""phyletic evolution"" occurring within lineages. Charles Darwin was the first to describe the role of natural selection in speciation. There is research comparing the intensity of sexual selection in different clades with their number of species.There are four geographic modes of speciation in nature, based on the extent to which speciating populations are isolated from one another: allopatric, peripatric, parapatric, and sympatric. Speciation may also be induced artificially, through animal husbandry, agriculture, or laboratory experiments. Whether genetic drift is a minor or major contributor to speciation is the subject matter of much ongoing discussion.