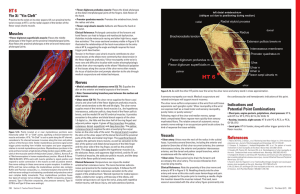
Corticomuscular Contributions to the Control of Rhythmic Movement
... were linked to specific phases in the pedaling cycle. Lastly, simultaneous recordings of muscular and cortical activity showed a significant coherence between EEG signals and EMG signals. This corticospinal coupling was weakened as fatigue developed throughout the pedaling exercise. On the contrary, ...
... were linked to specific phases in the pedaling cycle. Lastly, simultaneous recordings of muscular and cortical activity showed a significant coherence between EEG signals and EMG signals. This corticospinal coupling was weakened as fatigue developed throughout the pedaling exercise. On the contrary, ...
Preview from Notesale.co.uk Page 10 of 12
... Skeletal Muscle Tissue and Cardiac Muscle Tissue Skeletal tissues are attached to the skeletal bones of the body; however, cardiac muscle tissue is located in the walls of the heart. Cardiac muscle tissue is involuntary, while skeletal muscle tissue is voluntary. Cardiac muscle tissue striations are ...
... Skeletal Muscle Tissue and Cardiac Muscle Tissue Skeletal tissues are attached to the skeletal bones of the body; however, cardiac muscle tissue is located in the walls of the heart. Cardiac muscle tissue is involuntary, while skeletal muscle tissue is voluntary. Cardiac muscle tissue striations are ...
Sciatica - Axelson Chiropractic
... a specific diagnosis and does not indicate what is actually causing the nerve irritation. Actually, there are many distinct conditions that can cause the Sciatic nerve to become injured. One common misconception is that Sciatica always results from a Disc Herniation of the lower back. Although Disc ...
... a specific diagnosis and does not indicate what is actually causing the nerve irritation. Actually, there are many distinct conditions that can cause the Sciatic nerve to become injured. One common misconception is that Sciatica always results from a Disc Herniation of the lower back. Although Disc ...
THE NEUROMUSCULAR SYSTEM CHAPTER 5: 1.3.1 The
... • Hence if the shorter of the two motor units is stimulated all the muscle fibres connected to that motor unit will contract - this is the ‘all-or-none law’. • But at the same time the longer of the two motor units could be resting and so those muscle fibres connected to that motor neurone would b ...
... • Hence if the shorter of the two motor units is stimulated all the muscle fibres connected to that motor unit will contract - this is the ‘all-or-none law’. • But at the same time the longer of the two motor units could be resting and so those muscle fibres connected to that motor neurone would b ...
The Science Behind Balance Training
... movement patterns through training and repetition that is specific to the movement(s) being undertaken. Activity like this is usually referred to as “skill practice,” “sport specific training” or “rehearsal.” The principle of skill-rehearsal encompasses specificity – specific practice and repetition ...
... movement patterns through training and repetition that is specific to the movement(s) being undertaken. Activity like this is usually referred to as “skill practice,” “sport specific training” or “rehearsal.” The principle of skill-rehearsal encompasses specificity – specific practice and repetition ...
Ativity 13 - PCC - Portland Community College
... • Lower motor neurons go from the spinal cord to a muscle. • The cell body of a lower motor neuron is in the spinal cord and its termination is in a skeletal muscle. • The loss of lower motor neurons leads to weakness, twitching of muscle (fasciculation), and loss of muscle mass (muscle atrophy). “F ...
... • Lower motor neurons go from the spinal cord to a muscle. • The cell body of a lower motor neuron is in the spinal cord and its termination is in a skeletal muscle. • The loss of lower motor neurons leads to weakness, twitching of muscle (fasciculation), and loss of muscle mass (muscle atrophy). “F ...
Testing upper motor neuron function in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
... Clinical signs of upper motor neuron involvement are an essential observation to support the diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. However, clinical signs of upper motor neuron can be difficult to elicit in patients with motor neuron disease. One postulated reason for this problem is the prese ...
... Clinical signs of upper motor neuron involvement are an essential observation to support the diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. However, clinical signs of upper motor neuron can be difficult to elicit in patients with motor neuron disease. One postulated reason for this problem is the prese ...
Synaptic Competition during the Reformation of a Neuromuscular Map
... C6 (ASI 5 1.03). Similar results were observed in sector III (data not shown). ...
... C6 (ASI 5 1.03). Similar results were observed in sector III (data not shown). ...
Recruitment properties of intramuscular and nerve
... of large motoneurons become more similar in size to those of smaller motoneurons as they approach their target muscle-fibers. Stimulation applied in the vicinity of these terminal axonal branches would then tend to be equally effective at recruiting small, fatigue-resistant motor units as large, fat ...
... of large motoneurons become more similar in size to those of smaller motoneurons as they approach their target muscle-fibers. Stimulation applied in the vicinity of these terminal axonal branches would then tend to be equally effective at recruiting small, fatigue-resistant motor units as large, fat ...
Repetitive Strain Injuries - Working
... icing to prevent injury. 2 Do not use ice on your hands or fingers if you are aware that you have Raynaud's disease or Reflex Sympathetic Dysfunction (RSD). Use ice no longer than 20 minutes. Allow 30 minutes between 20-minute icing sessions. This cycle can be repeated several times without harm to ...
... icing to prevent injury. 2 Do not use ice on your hands or fingers if you are aware that you have Raynaud's disease or Reflex Sympathetic Dysfunction (RSD). Use ice no longer than 20 minutes. Allow 30 minutes between 20-minute icing sessions. This cycle can be repeated several times without harm to ...
Optical Control of Muscle Function by Transplantation of Stem Cell
... output. Analysis of muscle contractile characteristics also revealed that the latency to peak twitch contraction from initiation of the electrical trigger to the LED unit, or direct stimulation of the nerve, was identical for both optical and electrical stimulation (Fig. 3F). This finding indicates ...
... output. Analysis of muscle contractile characteristics also revealed that the latency to peak twitch contraction from initiation of the electrical trigger to the LED unit, or direct stimulation of the nerve, was identical for both optical and electrical stimulation (Fig. 3F). This finding indicates ...
COLLEGE OF PHYSICIANS AND SURGEONS
... Alberta’s Health Professions Act provides for the accreditation of medical services in non-hospital facilities by the College of Physicians and Surgeons of Alberta. Section 8.1 in Schedule 21 of the Act states: 8.1(1) A regulated member shall not provide a prescribed health service, or cause a presc ...
... Alberta’s Health Professions Act provides for the accreditation of medical services in non-hospital facilities by the College of Physicians and Surgeons of Alberta. Section 8.1 in Schedule 21 of the Act states: 8.1(1) A regulated member shall not provide a prescribed health service, or cause a presc ...
SOME OBSERVATIONS UPON THE PERIPHERAL NERVOUS
... condition is found in the parietal muscles, as will be described below, and it seems that the overlap of innervation between segments (also found in petromyzonts, see Peters & Mackay, 1961), reflected in the absence of strict segmentation in the motoneurons of the cord, must imply that the animal is ...
... condition is found in the parietal muscles, as will be described below, and it seems that the overlap of innervation between segments (also found in petromyzonts, see Peters & Mackay, 1961), reflected in the absence of strict segmentation in the motoneurons of the cord, must imply that the animal is ...
absence of an intact nerve terminal in the motor end
... axons to sprout and reinnervate denervated muscle fibres (Van Harreveld, 1945; Edds, 1950; Brown, Holland & Hopkins, 1982). If the damaged motor axons are allowed to regenerate, re-formation of neuromuscular junctions occurs. In lower vertebrates, the regenerating motor axons may retrieve all of the ...
... axons to sprout and reinnervate denervated muscle fibres (Van Harreveld, 1945; Edds, 1950; Brown, Holland & Hopkins, 1982). If the damaged motor axons are allowed to regenerate, re-formation of neuromuscular junctions occurs. In lower vertebrates, the regenerating motor axons may retrieve all of the ...
The Peripheral Nervous System and Reflex Activity
... All spinal nerves except C1 participate in dermatomes Extent of spinal cord injuries ascertained by affected dermatomes Most dermatomes overlap, so destruction of a single spinal nerve will not cause complete numbness ...
... All spinal nerves except C1 participate in dermatomes Extent of spinal cord injuries ascertained by affected dermatomes Most dermatomes overlap, so destruction of a single spinal nerve will not cause complete numbness ...
HT 6 References
... bones on the ulnar side of the wrist. The dorsal branch supplies the skin on the ulnar aspect of the dorsal hand and the proximal parts of the little and medial ring finger. The superficial branch supplies the palmaris brevis muscle, as well as sensation to the skin of the palmar and distal dorsal a ...
... bones on the ulnar side of the wrist. The dorsal branch supplies the skin on the ulnar aspect of the dorsal hand and the proximal parts of the little and medial ring finger. The superficial branch supplies the palmaris brevis muscle, as well as sensation to the skin of the palmar and distal dorsal a ...
Document
... Types of smooth muscles • A. Multi-unit smooth muscle • Composed of discrete,separate smooth muscle fibers • Each fiber operate/contract independently of others • Often innerveted by a single nerve ending as occurs for skeletal muscles • Their control is exerted mainly by the nerve signals • Outer ...
... Types of smooth muscles • A. Multi-unit smooth muscle • Composed of discrete,separate smooth muscle fibers • Each fiber operate/contract independently of others • Often innerveted by a single nerve ending as occurs for skeletal muscles • Their control is exerted mainly by the nerve signals • Outer ...
Smooth Muscle - Judith Brown CPD
... sodium channels are not significant. Spike depolarisations associated with calcium ion entry are seen in some types of smooth muscle, but the fast action potentials associated with nerves and striated muscles are not observed. Receptors are distributed fairly evenly over the surface of smooth muscle ...
... sodium channels are not significant. Spike depolarisations associated with calcium ion entry are seen in some types of smooth muscle, but the fast action potentials associated with nerves and striated muscles are not observed. Receptors are distributed fairly evenly over the surface of smooth muscle ...
CNS learns Stable, Accurate and Efficient Movements using a
... the muscle would be expected than for the single joint elbow muscles. Because of the high trial-to-trial variability in the EMG due to its stochastic nature, the signal to noise ratio is low. Therefore, of the two antagonistic muscle pairs acting at the shoulder, the pair undergoing the greatest cha ...
... the muscle would be expected than for the single joint elbow muscles. Because of the high trial-to-trial variability in the EMG due to its stochastic nature, the signal to noise ratio is low. Therefore, of the two antagonistic muscle pairs acting at the shoulder, the pair undergoing the greatest cha ...
Traumatic Nerve Injuries
... Exercise after Nerve Injury Edx showed recovery of CMAP and decreasing fibs at ...
... Exercise after Nerve Injury Edx showed recovery of CMAP and decreasing fibs at ...
Deep Tendon Reflex
... spinal nerves carry the sensory impulses from the muscle spindles to the spinal cord. In the spinal cord, the sensory fibers stimulate the motor neurons that send their motor fibers (efferents) to the muscle causing its contraction. ...
... spinal nerves carry the sensory impulses from the muscle spindles to the spinal cord. In the spinal cord, the sensory fibers stimulate the motor neurons that send their motor fibers (efferents) to the muscle causing its contraction. ...
Reflexes
... contract, withdrawing the leg. The reflex is protective as contraction of the flexor muscles moves the limb to avoid pain. The flexor reflex is ipsilateral. Incoming and outgoing impulses are on the same side of the spinal cord. The flexor reflex illustrates another feature of polysynaptic reflex ar ...
... contract, withdrawing the leg. The reflex is protective as contraction of the flexor muscles moves the limb to avoid pain. The flexor reflex is ipsilateral. Incoming and outgoing impulses are on the same side of the spinal cord. The flexor reflex illustrates another feature of polysynaptic reflex ar ...
neuropharmacology of spasticity
... An increased tonic stretch reflex resulting in velocity- and length-dependent hypertonia due to abnormal spinal processing of proprioceptive input ...
... An increased tonic stretch reflex resulting in velocity- and length-dependent hypertonia due to abnormal spinal processing of proprioceptive input ...
Evaluation of ventral root reimplantation as a treatment of
... nerves arise only from those roots that were reimplanted. To evaluate the benefits of VRR, we used 3 groups of dogs. Group 1 was formed of 6 dogs in which VRR was performed. Group 2 (3 dogs) was a sham control group. A surgical approach and VRR was performed but the reimplanted roots were cut distal ...
... nerves arise only from those roots that were reimplanted. To evaluate the benefits of VRR, we used 3 groups of dogs. Group 1 was formed of 6 dogs in which VRR was performed. Group 2 (3 dogs) was a sham control group. A surgical approach and VRR was performed but the reimplanted roots were cut distal ...
Electromyography

Electromyography (EMG) is an electrodiagnostic medicine technique for evaluating and recording the electrical activity produced by skeletal muscles. EMG is performed using an instrument called an electromyograph, to produce a record called an electromyogram. An electromyograph detects the electrical potential generated by muscle cells when these cells are electrically or neurologically activated. The signals can be analyzed to detect medical abnormalities, activation level, or recruitment order, or to analyze the biomechanics of human or animal movement.