Bruenech, R., Ruskell, G., "Myotendinous Nerve Endings in Human
... numerous mitochondria with or without small clusters of small agranular vesicles (Fig. 3). The terminals had a Schwann cell investment which was continuous except at infrequent sites opposite the varicosities. Most of the varicosities were located in the tendon compartment of the complexes and other ...
... numerous mitochondria with or without small clusters of small agranular vesicles (Fig. 3). The terminals had a Schwann cell investment which was continuous except at infrequent sites opposite the varicosities. Most of the varicosities were located in the tendon compartment of the complexes and other ...
Motor System: Reflexes, Pyramidal Tract and Basal Ganglia
... than from MI; projection to midbrain and paramedian ...
... than from MI; projection to midbrain and paramedian ...
plexus injury after spinal cord implantation of avulsed ventral roots
... considerably impaired motor function in the arms and the hand/s is, however, the usual outcome of these injuries." In attempts to find ways to manage the motor deficits following complex nerve root injuries, the outcome of experimental studies of ventral root avulsion and reimplantation in the spina ...
... considerably impaired motor function in the arms and the hand/s is, however, the usual outcome of these injuries." In attempts to find ways to manage the motor deficits following complex nerve root injuries, the outcome of experimental studies of ventral root avulsion and reimplantation in the spina ...
Orthopedic and Physical Therapy Objectives in
... Each type requires a different approach in treatment. All three problems may be exhibited in one individual, or there may be three individuals each exhibiting a single treatment problem. Patients who, from the time of the first examination, show no weakness below 60 per cent or fair plus, fall into ...
... Each type requires a different approach in treatment. All three problems may be exhibited in one individual, or there may be three individuals each exhibiting a single treatment problem. Patients who, from the time of the first examination, show no weakness below 60 per cent or fair plus, fall into ...
Stretch reflexes. (Final).
... Signals sent to a whole muscle (like the biceps) causing it to contract, travel from the spinal cord through alpha motor neurons. When this occurs, only extrafusal muscle fibers would contract. Meanwhile, the intrafusal muscle fibers within the muscle spindles would go slack and information from the ...
... Signals sent to a whole muscle (like the biceps) causing it to contract, travel from the spinal cord through alpha motor neurons. When this occurs, only extrafusal muscle fibers would contract. Meanwhile, the intrafusal muscle fibers within the muscle spindles would go slack and information from the ...
Piriformis Syndrome. - Roland Jeffery Physiotherapy
... Piriformis syndrome is the name given to pain, if the muscle becomes ‘tight’ or irritated. The piriformis muscle can put strain on the sciatic nerve, which causes pain - this can radiate down the leg (sciatica). The majority of the pain however, is felt in the buttock (See Figure 2). The pain from p ...
... Piriformis syndrome is the name given to pain, if the muscle becomes ‘tight’ or irritated. The piriformis muscle can put strain on the sciatic nerve, which causes pain - this can radiate down the leg (sciatica). The majority of the pain however, is felt in the buttock (See Figure 2). The pain from p ...
What is Pelvic Pain? Pelvic pain is described as pain in the lower
... Pelvic pain can be caused by problems such as pelvic joint dysfunction, muscle imbalance within the muscles of the pelvic floor, trunk, and/or pelvis, incoordination in the muscles related to bowel and bladder function, tender points in the muscles of the pelvic floor, pressure on one or more nerves ...
... Pelvic pain can be caused by problems such as pelvic joint dysfunction, muscle imbalance within the muscles of the pelvic floor, trunk, and/or pelvis, incoordination in the muscles related to bowel and bladder function, tender points in the muscles of the pelvic floor, pressure on one or more nerves ...
Lab Activity 14 - Portland Community College
... • Lower motor neurons go from the spinal cord to a muscle. • The cell body of a lower motor neuron is in the spinal cord and its termination is in a skeletal muscle. • The loss of lower motor neurons leads to weakness, twitching of muscle (fasciculation), and loss of muscle mass (muscle atrophy). “F ...
... • Lower motor neurons go from the spinal cord to a muscle. • The cell body of a lower motor neuron is in the spinal cord and its termination is in a skeletal muscle. • The loss of lower motor neurons leads to weakness, twitching of muscle (fasciculation), and loss of muscle mass (muscle atrophy). “F ...
The power of the mind: the cortex as a critical determinant of muscle
... EMG recordings in real time on a computer monitor and to provide feedback to the subject if any interference EMG was subjectively noted (i.e., activity is observable above baseline noise with the y-axis scale such that very small increases in activity were noticeable). On a verbal signal to begin, s ...
... EMG recordings in real time on a computer monitor and to provide feedback to the subject if any interference EMG was subjectively noted (i.e., activity is observable above baseline noise with the y-axis scale such that very small increases in activity were noticeable). On a verbal signal to begin, s ...
Direct cortical control of muscle activation in voluntary arm movements
... problem is that most of the proposed movement parameters are related through the laws of physics, and therefore the spinal circuitry cannot control them independently even if it somehow managed to decode the mixed MI signal in real time. The other extreme is to question whether “movement parameters ...
... problem is that most of the proposed movement parameters are related through the laws of physics, and therefore the spinal circuitry cannot control them independently even if it somehow managed to decode the mixed MI signal in real time. The other extreme is to question whether “movement parameters ...
Muscle Receptor Organs in the Crayfish Abdomen: A Student
... The muscle spindle sensory neurons in mammals are challenging to investigate electrophysiologically because of the small nature of the sensory endings. It is also difficult to track the location of the cell bodies in the dorsal root ganglion to their peripheral endings. In comparison, the MRO neuron ...
... The muscle spindle sensory neurons in mammals are challenging to investigate electrophysiologically because of the small nature of the sensory endings. It is also difficult to track the location of the cell bodies in the dorsal root ganglion to their peripheral endings. In comparison, the MRO neuron ...
MS WORD file
... The muscle spindle sensory neurons in mammals are challenging to investigate electrophysiologically because of the small nature of the sensory endings. It is also difficult to track the location of the cell bodies in the dorsal root ganglion to their peripheral endings. In comparison, the MRO neuron ...
... The muscle spindle sensory neurons in mammals are challenging to investigate electrophysiologically because of the small nature of the sensory endings. It is also difficult to track the location of the cell bodies in the dorsal root ganglion to their peripheral endings. In comparison, the MRO neuron ...
successful transplantation of motoneurons into the peripheral nerve
... Cell transplantation therapies have become a major focus of pre-clinical research as a promising strategy for the treatment of neurological disorders.1-3) However, the large number of cells required to reconstruct the complex structures of the central nervous system results in a high risk of tumorig ...
... Cell transplantation therapies have become a major focus of pre-clinical research as a promising strategy for the treatment of neurological disorders.1-3) However, the large number of cells required to reconstruct the complex structures of the central nervous system results in a high risk of tumorig ...
Goals and Objectives of Training in Clinical Neurophysiology
... o Blink reflex (PC) o Brief exercise test for Lambert-Eaton Myasthenic Syndrome (PC) o The differentiation of subtypes of genetic neuromuscular diseases by history, physical examination, EMG/NCS and genetic testing (MK/PC/SBP) ...
... o Blink reflex (PC) o Brief exercise test for Lambert-Eaton Myasthenic Syndrome (PC) o The differentiation of subtypes of genetic neuromuscular diseases by history, physical examination, EMG/NCS and genetic testing (MK/PC/SBP) ...
Principles of Electrical Currents - Lectures
... causing a thermal effect. AC has a zero net charge (ZNC). The DC may have long term adverse physiological effects) ...
... causing a thermal effect. AC has a zero net charge (ZNC). The DC may have long term adverse physiological effects) ...
Online Textbook Worksheets
... 3. Contractions of skeletal muscle are voluntary, or under ________________ control 4. Cardiac muscle contains a great many mitochondria, which produce ___________________ for energy. 5. Skeletal muscles need a rich blood supply to provide them with __________________ and oxygen and to carry away th ...
... 3. Contractions of skeletal muscle are voluntary, or under ________________ control 4. Cardiac muscle contains a great many mitochondria, which produce ___________________ for energy. 5. Skeletal muscles need a rich blood supply to provide them with __________________ and oxygen and to carry away th ...
The Spinal Cord
... relaxation of the extensors is a case of reciprocal inhibition. The steps of the flexor withdrawal reflex response include: 1.Pain receptors are activated at the site of stimulation. 2. Afferent pain fibers enter the dorsal root and send collaterals to Excitatory interneurons that synapse with alp ...
... relaxation of the extensors is a case of reciprocal inhibition. The steps of the flexor withdrawal reflex response include: 1.Pain receptors are activated at the site of stimulation. 2. Afferent pain fibers enter the dorsal root and send collaterals to Excitatory interneurons that synapse with alp ...
D440-4 - Brochure - NEUROSPEC AG Research Neurosciences
... Amplified analog signals exit the D440 via BNC (Ch.1 only) or "D" connector (all channels) on the rear panel. ...
... Amplified analog signals exit the D440 via BNC (Ch.1 only) or "D" connector (all channels) on the rear panel. ...
5.4.1 Coordinated Movement
... 4. Each muscle fibre has many nuclei, described as multinucleate 5. There is an extensive system of ER called the sarcoplasmic reticulum, used to store Ca2+ for muscle contraction 6. At intervals, there are infoldings of the sarcolemma called T-tubules (transverse tubules) that penetrate the fibre 7 ...
... 4. Each muscle fibre has many nuclei, described as multinucleate 5. There is an extensive system of ER called the sarcoplasmic reticulum, used to store Ca2+ for muscle contraction 6. At intervals, there are infoldings of the sarcolemma called T-tubules (transverse tubules) that penetrate the fibre 7 ...
72 Deep Tendon Reflexes
... your forearm under both knees by contraction of the quadriceps with extension of the lower leg . If the reflex is hyperactive there is sometimes concomitant adduction of the ipsilateral thigh . Adduction of the opposite thigh and extension of the opposite lower leg also can occur simultaneously if t ...
... your forearm under both knees by contraction of the quadriceps with extension of the lower leg . If the reflex is hyperactive there is sometimes concomitant adduction of the ipsilateral thigh . Adduction of the opposite thigh and extension of the opposite lower leg also can occur simultaneously if t ...
15. ANS (Stick Figure) Anat Lecture
... What is the direct “effector tissue” for the bronchioles? Remember, basically, you only have 3 choices! ...
... What is the direct “effector tissue” for the bronchioles? Remember, basically, you only have 3 choices! ...
Functionally complex muscles of the cat hindlimb
... into four primary branches, each of which innervated all of and only muscle fibers contained within these "neuromuscular compartments". However, it was still possible that the axons of the individual motoneurons might bifurcate proximally and innervate more than one such primary nerve branch. In a s ...
... into four primary branches, each of which innervated all of and only muscle fibers contained within these "neuromuscular compartments". However, it was still possible that the axons of the individual motoneurons might bifurcate proximally and innervate more than one such primary nerve branch. In a s ...
Respiration and Proprioception - e
... The primary inspiration muscle, the diaphragm, shows a difference in proprioceptive innervation compared to other skeletal muscles including the intercostal muscles in terms of quantitative properties [21]. Work of Euler showed that there was a low ratio between the muscle spindle and tendon organ a ...
... The primary inspiration muscle, the diaphragm, shows a difference in proprioceptive innervation compared to other skeletal muscles including the intercostal muscles in terms of quantitative properties [21]. Work of Euler showed that there was a low ratio between the muscle spindle and tendon organ a ...
Table of Muscles: Actions and Invervations
... [A/L] aspect of globe, [P] to When eye adducted, elevates CN3 midline globe ...
... [A/L] aspect of globe, [P] to When eye adducted, elevates CN3 midline globe ...
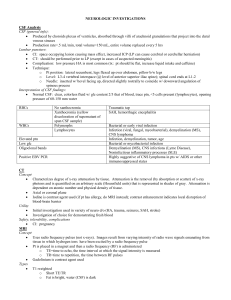
NEUROLOGIC INVESTIGATIONS
... o Sharp and spike wave discharges w/ or w/o accompanying slow wave interictal epileptiform findings o Rhythmic spike or sharp and slow wave discharges or rhythmic slow waves focal or generalized electrographic seizures Nerve Conduction Studies (NCS) Electrical stimulus applied over a nerve, and ...
... o Sharp and spike wave discharges w/ or w/o accompanying slow wave interictal epileptiform findings o Rhythmic spike or sharp and slow wave discharges or rhythmic slow waves focal or generalized electrographic seizures Nerve Conduction Studies (NCS) Electrical stimulus applied over a nerve, and ...
Electromyography

Electromyography (EMG) is an electrodiagnostic medicine technique for evaluating and recording the electrical activity produced by skeletal muscles. EMG is performed using an instrument called an electromyograph, to produce a record called an electromyogram. An electromyograph detects the electrical potential generated by muscle cells when these cells are electrically or neurologically activated. The signals can be analyzed to detect medical abnormalities, activation level, or recruitment order, or to analyze the biomechanics of human or animal movement.