Lecture VIII. Spinal Cord
... The size of white matter tracts (posterior, lateral and anterior columns) increases as more axons are added on the way TO the brain and decreases as axons end on the way FROM the the brain. September 27, 2010 ...
... The size of white matter tracts (posterior, lateral and anterior columns) increases as more axons are added on the way TO the brain and decreases as axons end on the way FROM the the brain. September 27, 2010 ...
The Crash Course in Head, Neck, and Arm By Mike Sughrue
... meets the scala tympani. I later read that this was false, however over time I have found that my error was actually rather helpful in describing the course of many nerves. Hence in this system, the term pre-trematic refers to a branch of each nerve that leaves the skull rostral to a plane through t ...
... meets the scala tympani. I later read that this was false, however over time I have found that my error was actually rather helpful in describing the course of many nerves. Hence in this system, the term pre-trematic refers to a branch of each nerve that leaves the skull rostral to a plane through t ...
2 m – 21. I, II, III, IV, VI, VIII pairs of cranial nerves
... common tendinous ring, and acts to abduct the eyeball (i.e. to rotate the gaze away from the midline). Vestibular cochlear nerve (VIII) The Vestibulocochlear Nerve is the eighth of the twelve cranial nerves. The fibers consist of only Afferent Sensory Fibers. The word Afferent means toward the centr ...
... common tendinous ring, and acts to abduct the eyeball (i.e. to rotate the gaze away from the midline). Vestibular cochlear nerve (VIII) The Vestibulocochlear Nerve is the eighth of the twelve cranial nerves. The fibers consist of only Afferent Sensory Fibers. The word Afferent means toward the centr ...
Physio
... If any of these shows weakness, it suggests BP injury is proximal This patient has brachial plexus injury, lesion is: Supraganglionic – if Horner’s positive At roots – if winging of scapula Distal to roots – i.e. trunks, divisions, cords Causes BP injury – avulsion from motorcycle accident ...
... If any of these shows weakness, it suggests BP injury is proximal This patient has brachial plexus injury, lesion is: Supraganglionic – if Horner’s positive At roots – if winging of scapula Distal to roots – i.e. trunks, divisions, cords Causes BP injury – avulsion from motorcycle accident ...
Clinically oriented anatomy of the brainstem
... cause of Parkinson disease is unclear, but it is probably not inherited; the Wallenberg syndrome is a brainstem lesion resulting from a vascular occlusion. ...
... cause of Parkinson disease is unclear, but it is probably not inherited; the Wallenberg syndrome is a brainstem lesion resulting from a vascular occlusion. ...
Short- and Long-Term Changes in Joint Co
... in decreases in the viscoelasticity. Although several studies have tried to model such a dual strategy (Flash and Gurevich 1997; Gribble and Ostry 2000; Katayama et al. 1998; Wang et al. 2001), no previous experimental study has clearly proven the existence of pure decreases in viscoelastic forces t ...
... in decreases in the viscoelasticity. Although several studies have tried to model such a dual strategy (Flash and Gurevich 1997; Gribble and Ostry 2000; Katayama et al. 1998; Wang et al. 2001), no previous experimental study has clearly proven the existence of pure decreases in viscoelastic forces t ...
Lecture VIII. Spinal Cord
... The size of white matter tracts (posterior, lateral and anterior columns) increases as more axons are added on the way TO the brain and decreases as axons end on the way FROM the the brain. September 21, 2009 ...
... The size of white matter tracts (posterior, lateral and anterior columns) increases as more axons are added on the way TO the brain and decreases as axons end on the way FROM the the brain. September 21, 2009 ...
HSAN I - Viktor`s Notes for the Neurosurgery Resident
... clinical presentations of CMT 1A and 1B are similar, although they are distinguishable. CMT 1A may have milder clinical course than 1B. age of onset ranges childhood ÷ early adulthood (2-3rd decades); may be earlier in X-linked CMT. progression is slow. cranial nerves are generally spared, ...
... clinical presentations of CMT 1A and 1B are similar, although they are distinguishable. CMT 1A may have milder clinical course than 1B. age of onset ranges childhood ÷ early adulthood (2-3rd decades); may be earlier in X-linked CMT. progression is slow. cranial nerves are generally spared, ...
Common and specific inhibitory motor neurons innervate
... motor control strategy (reviewed in Rathmayer, 1998) (see also Wolf, 1990). In keeping with this essential role, both limb (reviewed in Wiens, 1989) and body wall (Schmäh and Wolf, 2003a) muscles receive inhibitory innervation, in addition to their standard excitatory drive (e.g. Hoyle and Burrows, ...
... motor control strategy (reviewed in Rathmayer, 1998) (see also Wolf, 1990). In keeping with this essential role, both limb (reviewed in Wiens, 1989) and body wall (Schmäh and Wolf, 2003a) muscles receive inhibitory innervation, in addition to their standard excitatory drive (e.g. Hoyle and Burrows, ...
P.P.7
... Facet Pain • Stretching of the joint capsule may be a source of pain due to the presence of a nociceptive type IV receptor system. • Joint receptors (Type I, II, & III mechanoreceptors) provide information regarding such activities as the direction, velocity, and initiation of joint movements— achi ...
... Facet Pain • Stretching of the joint capsule may be a source of pain due to the presence of a nociceptive type IV receptor system. • Joint receptors (Type I, II, & III mechanoreceptors) provide information regarding such activities as the direction, velocity, and initiation of joint movements— achi ...
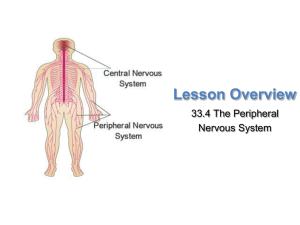
Autonomic Nervous System
... Somatic Nervous System The somatic nervous system regulates body activities that are under conscious control, such as the movement of skeletal muscles. Most of the time you have control over skeletal muscle movement, but when your body is in danger the central nervous system may take over. ...
... Somatic Nervous System The somatic nervous system regulates body activities that are under conscious control, such as the movement of skeletal muscles. Most of the time you have control over skeletal muscle movement, but when your body is in danger the central nervous system may take over. ...
Putting Pain in Perspective
... Nociceptor signals inhibit the SG neurons, therefore allowing pain signals to continue Increased signals from large diameter fibers results in increased firing of SG neurons, which ultimately decreases firing of T-cells (Result?) (Clinical application?) ...
... Nociceptor signals inhibit the SG neurons, therefore allowing pain signals to continue Increased signals from large diameter fibers results in increased firing of SG neurons, which ultimately decreases firing of T-cells (Result?) (Clinical application?) ...
The power of the mind: the cortex as a critical determinant of muscle
... The imagery script was digitized such that this person did not have to actually read the script. Rather, they were charged with monitoring the EMG recordings in real time on a computer monitor and to provide feedback to the subject if any interference EMG was subjectively noted (i.e., activity is ob ...
... The imagery script was digitized such that this person did not have to actually read the script. Rather, they were charged with monitoring the EMG recordings in real time on a computer monitor and to provide feedback to the subject if any interference EMG was subjectively noted (i.e., activity is ob ...
construction of a model demonstrating neural pathways and reflex arcs
... positions, new teaching methods must be developed that prepare tomorrow’s workforce for the challenges of the 2 1st century. One such method is the use of models. By actively building and manipulating concrete models that represent scientific concepts, students are involved in the most basic level o ...
... positions, new teaching methods must be developed that prepare tomorrow’s workforce for the challenges of the 2 1st century. One such method is the use of models. By actively building and manipulating concrete models that represent scientific concepts, students are involved in the most basic level o ...
construction of a model demonstrating neural pathways and reflex arcs
... positions, new teaching methods must be developed that prepare tomorrow’s workforce for the challenges of the 2 1st century. One such method is the use of models. By actively building and manipulating concrete models that represent scientific concepts, students are involved in the most basic level o ...
... positions, new teaching methods must be developed that prepare tomorrow’s workforce for the challenges of the 2 1st century. One such method is the use of models. By actively building and manipulating concrete models that represent scientific concepts, students are involved in the most basic level o ...
The neural encoding of self-generated and externally applied
... To date, the coding of vestibular information at the level of single vestibular nerve afferents and their target neurons in the vestibular nuclei has been well characterized in alert behaving m ...
... To date, the coding of vestibular information at the level of single vestibular nerve afferents and their target neurons in the vestibular nuclei has been well characterized in alert behaving m ...
nerve part 1
... • 1) It is localized to the site of stimulation and nearby area. • 2) During conduction, it decreases gradually with distance till it disappears (conducted with decrement) • 3) Its duration is very short (less than 1 m. sec). • 4) Can be graded: its magnitude is proportional with the strength of the ...
... • 1) It is localized to the site of stimulation and nearby area. • 2) During conduction, it decreases gradually with distance till it disappears (conducted with decrement) • 3) Its duration is very short (less than 1 m. sec). • 4) Can be graded: its magnitude is proportional with the strength of the ...
innervation of the ventral diaphragm of the locust
... pinned, ventral side up, on to the wax-floor of a Petri dish and continuously perfused with saline. One of the segmental nerves was then stained with CoCl8 (Pitman, Tweedle & Cohen, 1972) or NiCl2 via the cut axons (lies & Mulloney, 1971), by means of an oil gap electrode (Peters, 1976). Although Co ...
... pinned, ventral side up, on to the wax-floor of a Petri dish and continuously perfused with saline. One of the segmental nerves was then stained with CoCl8 (Pitman, Tweedle & Cohen, 1972) or NiCl2 via the cut axons (lies & Mulloney, 1971), by means of an oil gap electrode (Peters, 1976). Although Co ...
Vestibular System
... nerve (which hair cells of the spiral organ; what place along the basilar membrane) are maximally active (for > 200 Hz). As the pitch (Hz) of a sound increases, the peak amplitude of basilar membrane displacement regresses, from the apex (longest fibers) toward the base (shortest fibers) of the coch ...
... nerve (which hair cells of the spiral organ; what place along the basilar membrane) are maximally active (for > 200 Hz). As the pitch (Hz) of a sound increases, the peak amplitude of basilar membrane displacement regresses, from the apex (longest fibers) toward the base (shortest fibers) of the coch ...
Atonia-Related Regions in the Rodent Pons and Medulla
... Hajnik, T., Y. Y. Lai, and J. M. Siegel. Atonia-related regions in the rodent pons and medulla. J Neurophysiol 84: 1942–1948, 2000. Electrical stimulation of circumscribed areas of the pontine and medullary reticular formation inhibits muscle tone in cats. In this report, we present an analysis of t ...
... Hajnik, T., Y. Y. Lai, and J. M. Siegel. Atonia-related regions in the rodent pons and medulla. J Neurophysiol 84: 1942–1948, 2000. Electrical stimulation of circumscribed areas of the pontine and medullary reticular formation inhibits muscle tone in cats. In this report, we present an analysis of t ...
Chapter 14 - MDC Faculty Home Pages
... – Cell locations: axons are in spinal cord tracts; cell bodies are in ganglia, spinal cord gray horns, and brain gray matter – Each pathway is made of a chain of two or more neurons – Pathways are paired: there is a left and a right tract – Most pathways decussate: axons cross midline so brain proce ...
... – Cell locations: axons are in spinal cord tracts; cell bodies are in ganglia, spinal cord gray horns, and brain gray matter – Each pathway is made of a chain of two or more neurons – Pathways are paired: there is a left and a right tract – Most pathways decussate: axons cross midline so brain proce ...
Auris Nasus Larynx 34 (2008) 1-10
... In summary, the semicircular canal sense organs primarily project to the nuclei for VOR activation (nystagmus) while the otolith organs are responsible for activity in anti-gravity muscles of the neck, trunk and limbs (ataxia). However, compensatory eye muscle activation also occurs from stimulatio ...
... In summary, the semicircular canal sense organs primarily project to the nuclei for VOR activation (nystagmus) while the otolith organs are responsible for activity in anti-gravity muscles of the neck, trunk and limbs (ataxia). However, compensatory eye muscle activation also occurs from stimulatio ...
Somatic motor pathways
... All rights reserved. Reproduction or translation of this work beyond that permitted in section 117 of the 1976 United States Copyright Act without express permission of the copyright owner is unlawful. ...
... All rights reserved. Reproduction or translation of this work beyond that permitted in section 117 of the 1976 United States Copyright Act without express permission of the copyright owner is unlawful. ...
Proprioception
Proprioception (/ˌproʊpri.ɵˈsɛpʃən/ PRO-pree-o-SEP-shən), from Latin proprius, meaning ""one's own"", ""individual,"" and capio, capere, to take or grasp, is the sense of the relative position of neighbouring parts of the body and strength of effort being employed in movement. In humans, it is provided by proprioceptors in skeletal striated muscles (muscle spindles) and tendons (Golgi tendon organ) and the fibrous capsules in joints. It is distinguished from exteroception, by which one perceives the outside world, and interoception, by which one perceives pain, hunger, etc., and the movement of internal organs. The brain integrates information from proprioception and from the vestibular system into its overall sense of body position, movement, and acceleration. The word kinesthesia or kinæsthesia (kinesthetic sense) strictly means movement sense, but has been used inconsistently to refer either to proprioception alone or to the brain's integration of proprioceptive and vestibular inputs.