Powerpoint
... cerebral cortex – frontal, parietal, temporal and occipital lobe Grey matter on outer surface, white matter inner surface Cerebral cortex is highly folded to increase the surface area for holding more neurones for more complicated coordination. ...
... cerebral cortex – frontal, parietal, temporal and occipital lobe Grey matter on outer surface, white matter inner surface Cerebral cortex is highly folded to increase the surface area for holding more neurones for more complicated coordination. ...
Objectives 34
... 3. Lateral vestibulospinal tract from the lateral vestibular nuclei in medulla; activate anti-gravity muscles for postural responses - Each brainstem nuclei receives input from motor cortex (corticobulbar) - CST carries axons with cell bodies in motor cortex, premotor cortex, and supplementary motor ...
... 3. Lateral vestibulospinal tract from the lateral vestibular nuclei in medulla; activate anti-gravity muscles for postural responses - Each brainstem nuclei receives input from motor cortex (corticobulbar) - CST carries axons with cell bodies in motor cortex, premotor cortex, and supplementary motor ...
LPN-C
... • consists of sensory neurons from the head, body wall, extremities, and motor neurons to skeletal muscle. • The motor responses are under conscious control and therefore the SNS is voluntary. • Certain peripheral nerves perform specialized functions and form the autonomic nervous system; they contr ...
... • consists of sensory neurons from the head, body wall, extremities, and motor neurons to skeletal muscle. • The motor responses are under conscious control and therefore the SNS is voluntary. • Certain peripheral nerves perform specialized functions and form the autonomic nervous system; they contr ...
18 The Somatosensory System II: Touch, Thermal Sense, and Pain
... Central Sensitization and Secondary Hyperalgesia • Secondary hyperalgesia occurs in the skin bordering the damaged tissue. Although receptor sensitization may contribute to secondary hyperalgesia, there is likely to be a central (e.g., spinal) component as well. • There is hyper-activation of the c ...
... Central Sensitization and Secondary Hyperalgesia • Secondary hyperalgesia occurs in the skin bordering the damaged tissue. Although receptor sensitization may contribute to secondary hyperalgesia, there is likely to be a central (e.g., spinal) component as well. • There is hyper-activation of the c ...
Nervous System Worksheets
... exit the spinal cord through openings between the vertebrae. The part of the nerve that exits the spinal cord is called the nerve root. It then branches into smaller nerves that control different parts of the body called the peripheral nerves. ...
... exit the spinal cord through openings between the vertebrae. The part of the nerve that exits the spinal cord is called the nerve root. It then branches into smaller nerves that control different parts of the body called the peripheral nerves. ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM AND REFLEXES Introduction:
... interneuron within the spinal cord. Motor neuron cell bodies lie within the spinal cord and their axons extend from the spinal cord as the ventral root. Both the dorsal and ventral roots merge, to form a mixed nerve, carrying both sensory and motor information between the body and the spinal cord. W ...
... interneuron within the spinal cord. Motor neuron cell bodies lie within the spinal cord and their axons extend from the spinal cord as the ventral root. Both the dorsal and ventral roots merge, to form a mixed nerve, carrying both sensory and motor information between the body and the spinal cord. W ...
Introduction to the Cervical Spine
... needles are placed along the spine and along certain muscles. The electrical response between the nerves and the muscles can determine which nerves are not functioning properly. ...
... needles are placed along the spine and along certain muscles. The electrical response between the nerves and the muscles can determine which nerves are not functioning properly. ...
motor neurons
... 2. Inhibitory area –medullary reticular system (1) Extend the entire extent to the medulla, lying ventrally and medially near the middle. (2) Transmit inhibitory signals to the same antigravity anterior ...
... 2. Inhibitory area –medullary reticular system (1) Extend the entire extent to the medulla, lying ventrally and medially near the middle. (2) Transmit inhibitory signals to the same antigravity anterior ...
Slide 1
... Neurons runs from CNS directly to muscle Consists of single neuron plus skeletal ...
... Neurons runs from CNS directly to muscle Consists of single neuron plus skeletal ...
Diencephalon - People Server at UNCW
... • http://science.discovery.com/videos/whensenses-collide-origins.html • Synesthesia • Check it out Dawgs! ...
... • http://science.discovery.com/videos/whensenses-collide-origins.html • Synesthesia • Check it out Dawgs! ...
Modeling the spinal cord neural circuitry controlling cat hindlimb
... patterns that drive locomotor movements even in the absence of descending inputs from higher brain centers and sensory feedback [3,6]. This supports the concept of the central pattern generator (CPG), which presumably is located in the spinal cord and generates a basic locomotor rhythm (for review s ...
... patterns that drive locomotor movements even in the absence of descending inputs from higher brain centers and sensory feedback [3,6]. This supports the concept of the central pattern generator (CPG), which presumably is located in the spinal cord and generates a basic locomotor rhythm (for review s ...
Motor_lesions2009-04-18 00:3983 KB
... paralysis of the muscles of the left half of the face & the left upper & lower limbs. ● MUSCLE TONE: there is hypertonia & hyperreflexia due to block of the extrapyramidal inhibitory discharge on the gamma efferents & hence the excitatory reticular formation because unopposed . So, spasticity is a r ...
... paralysis of the muscles of the left half of the face & the left upper & lower limbs. ● MUSCLE TONE: there is hypertonia & hyperreflexia due to block of the extrapyramidal inhibitory discharge on the gamma efferents & hence the excitatory reticular formation because unopposed . So, spasticity is a r ...
PNS and Reflexes
... Nerve IX is a mixed nerve with motor and sensory functions Motor – innervates part of the tongue and pharynx, and provides motor fibers to the parotid salivary gland Sensory – fibers conduct taste and general sensory impulses from the tongue and pharynx ...
... Nerve IX is a mixed nerve with motor and sensory functions Motor – innervates part of the tongue and pharynx, and provides motor fibers to the parotid salivary gland Sensory – fibers conduct taste and general sensory impulses from the tongue and pharynx ...
ssep anatomy handout
... more lateral than the higher (cervical) ones Fasciculus (nucleus) gracilis- is part of the dorsal or posterior columns. It contains input from the lower half of the body with fibers that arise from the lumbrosacral region.(more medial segments) Ganglia- term used to designate a group of nerve cells ...
... more lateral than the higher (cervical) ones Fasciculus (nucleus) gracilis- is part of the dorsal or posterior columns. It contains input from the lower half of the body with fibers that arise from the lumbrosacral region.(more medial segments) Ganglia- term used to designate a group of nerve cells ...
Control and Coordination
... misses or does not occur in time then the body will not get nutrition. In case of animals, including man, the chemicals produced by ductless (endocrine) glands also bring about coordination. This coordination by chemicals is brought about by the endocrine system. On the other hand the nervous system ...
... misses or does not occur in time then the body will not get nutrition. In case of animals, including man, the chemicals produced by ductless (endocrine) glands also bring about coordination. This coordination by chemicals is brought about by the endocrine system. On the other hand the nervous system ...
Nervous System PPT 4 - PNS
... (for example, a sharp pin) causes sensory receptors in the skin to generate nerve impulses that travel in sensory axons to the spinal cord. Interneurons integrate data from sensory neurons and then relay signals to motor axons. Motor axons convey nerve impulses from the spinal cord to a sketetal mus ...
... (for example, a sharp pin) causes sensory receptors in the skin to generate nerve impulses that travel in sensory axons to the spinal cord. Interneurons integrate data from sensory neurons and then relay signals to motor axons. Motor axons convey nerve impulses from the spinal cord to a sketetal mus ...
Sensation and Perception
... What is sensation? Sensation allows us to receive information from the world ...
... What is sensation? Sensation allows us to receive information from the world ...
lower back pain
... Indications for Surgery Surgery may be recommended: 1. If the conservative treatment options do not provide relief within two to three months. 2. If leg or back pain limits normal activity 3. If there is weakness or numbness in the legs 4. If it is difficult to walk or stand, or if medication or ph ...
... Indications for Surgery Surgery may be recommended: 1. If the conservative treatment options do not provide relief within two to three months. 2. If leg or back pain limits normal activity 3. If there is weakness or numbness in the legs 4. If it is difficult to walk or stand, or if medication or ph ...
Slide ()
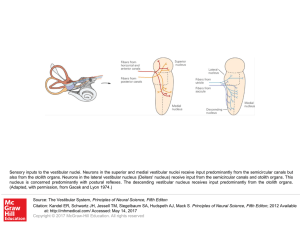
... Sensory inputs to the vestibular nuclei. Neurons in the superior and medial vestibular nuclei receive input predominantly from the semicircular canals but also from the otolith organs. Neurons in the lateral vestibular nucleus (Deiters' nucleus) receive input from the semicircular canals and otolith ...
... Sensory inputs to the vestibular nuclei. Neurons in the superior and medial vestibular nuclei receive input predominantly from the semicircular canals but also from the otolith organs. Neurons in the lateral vestibular nucleus (Deiters' nucleus) receive input from the semicircular canals and otolith ...
Micro Muscle: Muscle signal response and myosin activity
... so. Many different aspects of physiology interact to allow this to take place. Recall from the nervous system is made up of networks of nervous tissue. This nervous tissue is made of cells called neurons that can interact with other types of tissue. Neurons that control muscle tissue are called moto ...
... so. Many different aspects of physiology interact to allow this to take place. Recall from the nervous system is made up of networks of nervous tissue. This nervous tissue is made of cells called neurons that can interact with other types of tissue. Neurons that control muscle tissue are called moto ...
Nerves, structures, and organs of the head 1. Left cerebral
... Cerebellum (17) The second largest part of the brain. It has three functions, the unconscious maintenance of muscle coordination, equilibrium, and posture. Cerebral cortex (3) The outer layer, or "gray matter/' of the cerebrum that is composed mainly of nerve cell bodies which gives it the gray appe ...
... Cerebellum (17) The second largest part of the brain. It has three functions, the unconscious maintenance of muscle coordination, equilibrium, and posture. Cerebral cortex (3) The outer layer, or "gray matter/' of the cerebrum that is composed mainly of nerve cell bodies which gives it the gray appe ...
Proprioception
Proprioception (/ˌproʊpri.ɵˈsɛpʃən/ PRO-pree-o-SEP-shən), from Latin proprius, meaning ""one's own"", ""individual,"" and capio, capere, to take or grasp, is the sense of the relative position of neighbouring parts of the body and strength of effort being employed in movement. In humans, it is provided by proprioceptors in skeletal striated muscles (muscle spindles) and tendons (Golgi tendon organ) and the fibrous capsules in joints. It is distinguished from exteroception, by which one perceives the outside world, and interoception, by which one perceives pain, hunger, etc., and the movement of internal organs. The brain integrates information from proprioception and from the vestibular system into its overall sense of body position, movement, and acceleration. The word kinesthesia or kinæsthesia (kinesthetic sense) strictly means movement sense, but has been used inconsistently to refer either to proprioception alone or to the brain's integration of proprioceptive and vestibular inputs.