introduction
... balanced protein is the main reason for high rate of sickness and death in developing countries (Fontanel, 1972). It is reported that ...
... balanced protein is the main reason for high rate of sickness and death in developing countries (Fontanel, 1972). It is reported that ...
FREE Sample Here
... thereby, introducing a number of double bonds between the carbon atoms. 2. The double bonds would physically put a kink in the long chain of carbons. This kink would not allow the molecules to associate in a manner necessary to produce a solid. In essence, the molecules would not pack together as ni ...
... thereby, introducing a number of double bonds between the carbon atoms. 2. The double bonds would physically put a kink in the long chain of carbons. This kink would not allow the molecules to associate in a manner necessary to produce a solid. In essence, the molecules would not pack together as ni ...
Macromolecules
... acids together toAmino Side make proteins The process is called dehydration synthesis Peptide bonds form to hold the amino acids together ...
... acids together toAmino Side make proteins The process is called dehydration synthesis Peptide bonds form to hold the amino acids together ...
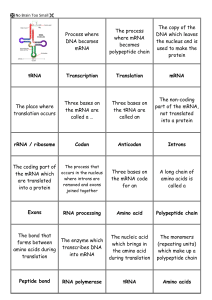
Gene expression flash cards
... The process that The coding part of the mRNA which occurs in the nucleus where introns are are translated removed and exons into a protein joined together ...
... The process that The coding part of the mRNA which occurs in the nucleus where introns are are translated removed and exons into a protein joined together ...
Building Protein Models
... d. Would both of these small polypeptides form the same shape and have the same function? ...
... d. Would both of these small polypeptides form the same shape and have the same function? ...
Study Guide Nucleotide metabolism 2015
... Study Guide for the following Chapters; Nucleotide Synthesis 1. In the synthesis of IMP, why is the second reaction the first committed step? What other pathways utilize PRPP? 2. What is the rate-limiting step of purine synthesis? 3. How is the purine synthetic pathway controlled? 4. What are the am ...
... Study Guide for the following Chapters; Nucleotide Synthesis 1. In the synthesis of IMP, why is the second reaction the first committed step? What other pathways utilize PRPP? 2. What is the rate-limiting step of purine synthesis? 3. How is the purine synthetic pathway controlled? 4. What are the am ...
Topic guide 1.1: Amino acids and proteins
... molecules. Sulfur molecules may be present in the R groups of some amino acids so, when they are close together, a disulfide bond forms. Ionic bonds form because some R groups carry a charge; when oppositely charged amino acids are close together an ionic bond forms. Hydrogen bonds occur where there ...
... molecules. Sulfur molecules may be present in the R groups of some amino acids so, when they are close together, a disulfide bond forms. Ionic bonds form because some R groups carry a charge; when oppositely charged amino acids are close together an ionic bond forms. Hydrogen bonds occur where there ...
Sorting the Fatty Acid Chaff from the Toxin Wheat, or is it All
... Success in identifying genes and enzymes that are involved in the biosynthesis of toxins by dinoflagellates has been limited thus far, despite considerable efforts by many groups. The chemical structures of dinoflagellate polyketides suggest that they are produced by modular type I PKS enzymes in so ...
... Success in identifying genes and enzymes that are involved in the biosynthesis of toxins by dinoflagellates has been limited thus far, despite considerable efforts by many groups. The chemical structures of dinoflagellate polyketides suggest that they are produced by modular type I PKS enzymes in so ...
This exam has 8 pages, including this one.
... i) In the space below draw the structure of a dipeptide. The first amino acid can be any polar, but not charged, amino acid and the second amino acid can be any amino acid that is predominately or completely non-polar, except for Tyrosine. Provide the name for each amino acid that you have drawn (6 ...
... i) In the space below draw the structure of a dipeptide. The first amino acid can be any polar, but not charged, amino acid and the second amino acid can be any amino acid that is predominately or completely non-polar, except for Tyrosine. Provide the name for each amino acid that you have drawn (6 ...
Ch 5 Macromolecules
... – glycerol: three-carbon alcohol w/ hydroxyl attached to each carbon – fatty acid: carboxyl group attached to long carbon skeleton ...
... – glycerol: three-carbon alcohol w/ hydroxyl attached to each carbon – fatty acid: carboxyl group attached to long carbon skeleton ...
Amino Acids and Peptides
... water from 2 amino acids resulting in CONH linkage. Can have di-, tri-, oligo- and polypeptides. Proteins composed of linear polymer of amino acids. ...
... water from 2 amino acids resulting in CONH linkage. Can have di-, tri-, oligo- and polypeptides. Proteins composed of linear polymer of amino acids. ...
SP7+ P7 (1+3) Energetics and kinetics of chemical reaction.
... Seminar practicals (SP) and practicals (P) SP1+P1 (1+3) Basic stoichiometry. Preparation of solutions. SP2+ P2 (1+3) Optical methods in medical chemistry. SP3+ P3 (1+3) Gas laws. Ions in solution. Osmotic pressure. ...
... Seminar practicals (SP) and practicals (P) SP1+P1 (1+3) Basic stoichiometry. Preparation of solutions. SP2+ P2 (1+3) Optical methods in medical chemistry. SP3+ P3 (1+3) Gas laws. Ions in solution. Osmotic pressure. ...
Re-identification of the N-terminal amino acid residue and its
... interpreted in terms of stability of proteins in a living cell. According to the N-end rule (Tobias et al. 1991; Varshavsky 1992), both Ala and Glu in bacteria are stabilizing residues that protect proteins against intracellular proteolytic degradation. The Ala residue does not prevent the removal o ...
... interpreted in terms of stability of proteins in a living cell. According to the N-end rule (Tobias et al. 1991; Varshavsky 1992), both Ala and Glu in bacteria are stabilizing residues that protect proteins against intracellular proteolytic degradation. The Ala residue does not prevent the removal o ...
Macromolecules
... • Simple units called nucleotides, connected in long chains • Nucleotides have 3 parts: 1- 5-Carbon sugar (pentose) 2- Nitrogen containing base (made of C, H and N) 3- A phosphate group ( P ) • The P groups make the links that unite the sugars (hence a “sugarphosphate backbone” ...
... • Simple units called nucleotides, connected in long chains • Nucleotides have 3 parts: 1- 5-Carbon sugar (pentose) 2- Nitrogen containing base (made of C, H and N) 3- A phosphate group ( P ) • The P groups make the links that unite the sugars (hence a “sugarphosphate backbone” ...
Chirality in Chemistry
... The fact that amino acids are chiral means that they exist in two forms, the two isomers. These two optical isomers are called enantiomers. In fact, in nature, only one of these enantiomers exist meaning that all of the amino acids in our cells have the same “handedness” (i.e. they are all like, for ...
... The fact that amino acids are chiral means that they exist in two forms, the two isomers. These two optical isomers are called enantiomers. In fact, in nature, only one of these enantiomers exist meaning that all of the amino acids in our cells have the same “handedness” (i.e. they are all like, for ...
www.stat.tamu.edu
... become inactive. When solvent condition is changed back, the protein refolds and becomes active again. ...
... become inactive. When solvent condition is changed back, the protein refolds and becomes active again. ...
Method S1.
... sonication (five 30 s pulses with intermitted one-min-cooling periods in Soniprep 150, UK) in 50 mM Tris-HCl, 100 mM NaCl (pH 7.4; 900 µl), and cell debris was removed by centrifugation (30 min at 10000 g). Reaction was initiated adding 2.8 U of bovine liver glutamate dehydrogenase (type II, 40 U mg ...
... sonication (five 30 s pulses with intermitted one-min-cooling periods in Soniprep 150, UK) in 50 mM Tris-HCl, 100 mM NaCl (pH 7.4; 900 µl), and cell debris was removed by centrifugation (30 min at 10000 g). Reaction was initiated adding 2.8 U of bovine liver glutamate dehydrogenase (type II, 40 U mg ...
macromolecules notes
... c. Some side chains are nonpolar (examples: proline, tryptophan, valine) d. Some side chains are acidic (examples: aspartic acid, glutamine acid) e. Some side chains are basic (examples: lysine, histidine) ...
... c. Some side chains are nonpolar (examples: proline, tryptophan, valine) d. Some side chains are acidic (examples: aspartic acid, glutamine acid) e. Some side chains are basic (examples: lysine, histidine) ...
Modeling with Toobers
... and 2 differences you see? How do you explain the differences you observed? ...
... and 2 differences you see? How do you explain the differences you observed? ...
Protein Synthesis Notes File
... 5. The t-RNA molecule is 80 nucleotides long in the shape of a cloverleaf. a) the 3' end at the top of the molecule contain the _____________________ b) The other end t-RNA molecule has a 3 base sequence called the _____________________ where the t-RNA binds with the m-RNA codon c) The enzyme ______ ...
... 5. The t-RNA molecule is 80 nucleotides long in the shape of a cloverleaf. a) the 3' end at the top of the molecule contain the _____________________ b) The other end t-RNA molecule has a 3 base sequence called the _____________________ where the t-RNA binds with the m-RNA codon c) The enzyme ______ ...