Protein Synthesis I
... 3. Where coupling between amino acids and protein takes place II. GENETIC CODES AS THEY OCCUR IN mRNA’S [S2] a. mRNA is a message that contains the codes for the amino acids b. Codes can be very different- you can have a nucleic acid polymer which has a code at every segment of the nucleic acid i. F ...
... 3. Where coupling between amino acids and protein takes place II. GENETIC CODES AS THEY OCCUR IN mRNA’S [S2] a. mRNA is a message that contains the codes for the amino acids b. Codes can be very different- you can have a nucleic acid polymer which has a code at every segment of the nucleic acid i. F ...
Biochemistry 2000 Sample Questions Proteins
... Please Note: In the above table the net charge has been reported as the nearest integer. To be completely accurate, the net charge at pH 2.2 is +0.5, then net charge at pH 4.2 is -0.5 and the net charge at 9.4 is -1.5. (18) The peptide bonds are shown in red. ...
... Please Note: In the above table the net charge has been reported as the nearest integer. To be completely accurate, the net charge at pH 2.2 is +0.5, then net charge at pH 4.2 is -0.5 and the net charge at 9.4 is -1.5. (18) The peptide bonds are shown in red. ...
protein review 2 - Ms. Hart WHS Science
... structures, resulting in a wide range of functions • Proteins account for more than 50% of the dry mass of most cells • Protein functions include structural support, storage, transport, cellular communications, movement, and defense against foreign substances ...
... structures, resulting in a wide range of functions • Proteins account for more than 50% of the dry mass of most cells • Protein functions include structural support, storage, transport, cellular communications, movement, and defense against foreign substances ...
Introduction to Carbohydrates
... Removing the α-amino group is essential for producing energy from any amino acid, and is an obligatory step in the catabolism of all amino acids. Once removed, this nitrogen can be incorporated into other compounds or excreted, with the carbon skeletons being metabolized. This section describe ...
... Removing the α-amino group is essential for producing energy from any amino acid, and is an obligatory step in the catabolism of all amino acids. Once removed, this nitrogen can be incorporated into other compounds or excreted, with the carbon skeletons being metabolized. This section describe ...
QUIZ #4 LIPID STRUCTURES AND METABOLISM
... You have two 6-carbon compounds; one is glucose and the other is caproic acid (6:0). If both are complexely oxidized to CO2 and H2O, what is the ratio of their potential maximum ATPs generated? a. Glucose yields 38 ATP where as caproic acid yields 28 ATP b. Glucose yields 28 ATP where as caproic aci ...
... You have two 6-carbon compounds; one is glucose and the other is caproic acid (6:0). If both are complexely oxidized to CO2 and H2O, what is the ratio of their potential maximum ATPs generated? a. Glucose yields 38 ATP where as caproic acid yields 28 ATP b. Glucose yields 28 ATP where as caproic aci ...
Design and Operation of Large Scale RNA production v2
... • Cleavage off the beads is the first step of the postsynthesis procedure ...
... • Cleavage off the beads is the first step of the postsynthesis procedure ...
Amino acid - Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research
... epistaxis, haematuria and haemolysis), Cnestic ferruginea (used in the treatment of migraine and sinusitis and anaemia for woman with abortion and ovarian problems) and in the treatment of gonorrhea, joint and waist pains, arthritis, rheumatism, stroke and syphilis [3] and Cussonia arborea used for ...
... epistaxis, haematuria and haemolysis), Cnestic ferruginea (used in the treatment of migraine and sinusitis and anaemia for woman with abortion and ovarian problems) and in the treatment of gonorrhea, joint and waist pains, arthritis, rheumatism, stroke and syphilis [3] and Cussonia arborea used for ...
الشريحة 1
... Reaction of amino acids 1) Amphoteric character of amino acid Amino acids are amphoteric because it contains both acidic –COOH thus it is present in an inner salt (B) which is , group and basic group –NH2 Zeitter ion called ...
... Reaction of amino acids 1) Amphoteric character of amino acid Amino acids are amphoteric because it contains both acidic –COOH thus it is present in an inner salt (B) which is , group and basic group –NH2 Zeitter ion called ...
Introduction 1
... Lk = linking number: Number of times one edge of ribbon linked around other – topological property cannot change w/o cutting. (calculate by Lk = Tw+Wr) Twist = winding of Watson around Crick – integrated angle of twist/2p along length, not an integer, necessarily (calculate by Tw = (number of base ...
... Lk = linking number: Number of times one edge of ribbon linked around other – topological property cannot change w/o cutting. (calculate by Lk = Tw+Wr) Twist = winding of Watson around Crick – integrated angle of twist/2p along length, not an integer, necessarily (calculate by Tw = (number of base ...
الشريحة 1
... Reaction of amino acids 1) Amphoteric character of amino acid Amino acids are amphoteric because it contains both acidic –COOH thus it is present in an inner salt (B) which is , group and basic group –NH2 Zeitter ion called ...
... Reaction of amino acids 1) Amphoteric character of amino acid Amino acids are amphoteric because it contains both acidic –COOH thus it is present in an inner salt (B) which is , group and basic group –NH2 Zeitter ion called ...
Chapter 5 The Structure and Function of Macromolecules
... groups that are charged (ionized) at cellular pH. Some acidic R groups are negative in charge due to the presence of a carboxyl group. Basic R groups have amino groups that are positive in charge. Note that all amino acids have carboxyl and amino groups. The terms acidic and basic in this cont ...
... groups that are charged (ionized) at cellular pH. Some acidic R groups are negative in charge due to the presence of a carboxyl group. Basic R groups have amino groups that are positive in charge. Note that all amino acids have carboxyl and amino groups. The terms acidic and basic in this cont ...
Regents Chemistry
... o Be able to explain BP and Solubility in terms of intermolecular forces of attraction o When give several compounds containing different functional groups be able to arrange them in order of BP ...
... o Be able to explain BP and Solubility in terms of intermolecular forces of attraction o When give several compounds containing different functional groups be able to arrange them in order of BP ...
Translation: DNA to mRNA to Protein
... second codon can then bind to the A site, a step that requires elongation factors (in E. coli, these are called EF-Tu and EF-Ts), as well as guanosine triphosphate (GTP) as an energy source for the process. Upon binding of the tRNA-amino acid complex in the A site, GTP is cleaved to form guanosine d ...
... second codon can then bind to the A site, a step that requires elongation factors (in E. coli, these are called EF-Tu and EF-Ts), as well as guanosine triphosphate (GTP) as an energy source for the process. Upon binding of the tRNA-amino acid complex in the A site, GTP is cleaved to form guanosine d ...
Year 12 ATAR Chemistry Course Outline 2017
... Equilibrium, Acids and Bases, and Redox Reactions ...
... Equilibrium, Acids and Bases, and Redox Reactions ...
word - My eCoach
... One strand of DNA (the anti-sense strand) is used as a template to produce a single strand of mRNA. The bases in the mRNA strand are opposite (complimentary) to the bases in the DNA template strand; it resembles the sense strand of DNA except that the base thymine is replaced by uracil. The mRNA con ...
... One strand of DNA (the anti-sense strand) is used as a template to produce a single strand of mRNA. The bases in the mRNA strand are opposite (complimentary) to the bases in the DNA template strand; it resembles the sense strand of DNA except that the base thymine is replaced by uracil. The mRNA con ...
Protein Folding Activity
... Amino acids are small molecules that link together in long chains to form proteins. They are often referred to as the "building blocks" of proteins. The sequence of amino acids in a protein, and hence the protein function, are determined by the genetic code, defined by the sequence of nucleotides in ...
... Amino acids are small molecules that link together in long chains to form proteins. They are often referred to as the "building blocks" of proteins. The sequence of amino acids in a protein, and hence the protein function, are determined by the genetic code, defined by the sequence of nucleotides in ...
Structure and Function of Macromolecules
... groups that are charged (ionized) at cellular pH. Some acidic R groups are negative in charge due to the presence of a carboxyl group. Basic R groups have amino groups that are positive in charge. Note that all amino acids have carboxyl and amino groups. The terms acidic and basic in this cont ...
... groups that are charged (ionized) at cellular pH. Some acidic R groups are negative in charge due to the presence of a carboxyl group. Basic R groups have amino groups that are positive in charge. Note that all amino acids have carboxyl and amino groups. The terms acidic and basic in this cont ...
Advances in Amino Acid Analysis
... using several specialized AAA methods (described below), which improve recovery over typical 6N HCl and phenol hydrolysis. Amino acid composition. Compositional analysis of each amino acid is commonly expressed in the mole percentage (mol %) of the amino acid relative to all other residues in the pr ...
... using several specialized AAA methods (described below), which improve recovery over typical 6N HCl and phenol hydrolysis. Amino acid composition. Compositional analysis of each amino acid is commonly expressed in the mole percentage (mol %) of the amino acid relative to all other residues in the pr ...
Carbon-Based Molecules
... Proteins differ in the number and order of amino acids. The specific sequence of amino acids determines a protein’s structure and function. Two types of interactions between the side groups of some amino acids are especially important in protein structure. First, some side groups contain sulfur ato ...
... Proteins differ in the number and order of amino acids. The specific sequence of amino acids determines a protein’s structure and function. Two types of interactions between the side groups of some amino acids are especially important in protein structure. First, some side groups contain sulfur ato ...
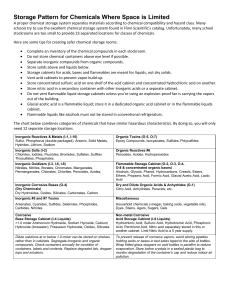
Storage Pattern for Chemicals Where Space is Limited
... Store concentrated sulfuric acid on one shelf of the acid cabinet and concentrated hydrochloric acid on another. Store nitric acid in a secondary container with other inorganic acids or a separate cabinet. Do not vent flammable liquid storage cabinets unless you’re using an explosion-proof fan is ca ...
... Store concentrated sulfuric acid on one shelf of the acid cabinet and concentrated hydrochloric acid on another. Store nitric acid in a secondary container with other inorganic acids or a separate cabinet. Do not vent flammable liquid storage cabinets unless you’re using an explosion-proof fan is ca ...
On the Importance of Amino Acid Sequence and Spatial Proximity of
... analysis is done is the range of interaction distances studied, which is mostly irrelevant to protein structure. The authors measure the cumulative distribution of the number of Cα-Cα interactions over the range 0–60 Å for specific residue types and fit this to simple sigmoids. The fits show no clea ...
... analysis is done is the range of interaction distances studied, which is mostly irrelevant to protein structure. The authors measure the cumulative distribution of the number of Cα-Cα interactions over the range 0–60 Å for specific residue types and fit this to simple sigmoids. The fits show no clea ...