The Primary Structure of a 4.0-kDa Photosystem I Polypeptide
... Photosystem I (PS I)’ in plants and cyanobacteriacatalyzes the photochemical transfer of electrons from plastocyanin to carried out by dissolving the lyophilized PSI-I polypeptide (5 nmol) in 100 p l of 0.2% acetic acid (adjusted to pH 2.0 with HCl) and ferredoxin. Pigments and theelectron acceptors ...
... Photosystem I (PS I)’ in plants and cyanobacteriacatalyzes the photochemical transfer of electrons from plastocyanin to carried out by dissolving the lyophilized PSI-I polypeptide (5 nmol) in 100 p l of 0.2% acetic acid (adjusted to pH 2.0 with HCl) and ferredoxin. Pigments and theelectron acceptors ...
paper describing HSSP
... values for single residues, pairs of residues, short oligopeptides or short sequence patterns. Both kinds of methods are severely limited by the size of the database in which one performs searches or from which one derives structural preferences. For example, in order to have on the average 5 occurr ...
... values for single residues, pairs of residues, short oligopeptides or short sequence patterns. Both kinds of methods are severely limited by the size of the database in which one performs searches or from which one derives structural preferences. For example, in order to have on the average 5 occurr ...
PDF
... synthesis at various times after the initiation of maturation. The addition of cycloheximide to extrafollicular oocytes during the first 4h after initiation invariably blocks nuclear breakdown (percentage of metaphase oocytes <5 % in all groups from 0-4 h). On the other hand over 50 % of oocytes und ...
... synthesis at various times after the initiation of maturation. The addition of cycloheximide to extrafollicular oocytes during the first 4h after initiation invariably blocks nuclear breakdown (percentage of metaphase oocytes <5 % in all groups from 0-4 h). On the other hand over 50 % of oocytes und ...
Relationship between Hot Spot Residues and Ligand Binding Hot
... analog of the MSCS method that has been shown to accurately identify fragment binding hot spots at PPI surface sites.31 Computational mapping places molecular probessmall organic molecules that vary in size and shapeon a dense grid around the protein, finds favorable positions using empirical free ...
... analog of the MSCS method that has been shown to accurately identify fragment binding hot spots at PPI surface sites.31 Computational mapping places molecular probessmall organic molecules that vary in size and shapeon a dense grid around the protein, finds favorable positions using empirical free ...
Carbon isotope analysis of bulk keratin and single amino acids from
... 1-cm sections from subjects with long hair. Each measurement thus reflects the dietary input over approximately 1 month.14 Subjects were asked about their diets and stated that they did not change their diet significantly over the period of hair growth (approximately 18 months); thus any isotopic va ...
... 1-cm sections from subjects with long hair. Each measurement thus reflects the dietary input over approximately 1 month.14 Subjects were asked about their diets and stated that they did not change their diet significantly over the period of hair growth (approximately 18 months); thus any isotopic va ...
GRE BIOCHEMISTRY TEST PRACTICE BOOK
... area. If, however, your subscores differ by more than a few points, you may take this as an indication that your lower score shows weakness, and you may wish to concentrate your review efforts on topics in that area. It is important to realize that the conditions under which you tested yourself were ...
... area. If, however, your subscores differ by more than a few points, you may take this as an indication that your lower score shows weakness, and you may wish to concentrate your review efforts on topics in that area. It is important to realize that the conditions under which you tested yourself were ...
Transcription - Shippensburg University
... • Three properties of RNA enable it to function as an enzyme – It can form a three-dimensional structure because of its ability to base pair with itself – Some bases in RNA contain functional groups – RNA may hydrogen-bond with other nucleic acid molecules ...
... • Three properties of RNA enable it to function as an enzyme – It can form a three-dimensional structure because of its ability to base pair with itself – Some bases in RNA contain functional groups – RNA may hydrogen-bond with other nucleic acid molecules ...
Identification of a novel N-terminal hydrophobic sequence that
... Zweytick et al., 2000). We have proposed that the machinery responsible for lipid accumulation deserves special status as an organelle, and suggested the name adiposome for this cellular compartment. Thus, in response to an increase in cellular fatty acid or cholesterol, adiposomes package esterifie ...
... Zweytick et al., 2000). We have proposed that the machinery responsible for lipid accumulation deserves special status as an organelle, and suggested the name adiposome for this cellular compartment. Thus, in response to an increase in cellular fatty acid or cholesterol, adiposomes package esterifie ...
The CamSol Method of Rational Design of Protein Mutants with
... represents also a major biotechnological issue, preventing many proteins to be produced at economically convenient yields [13,20,22]. Effective experimental approaches to improve protein solubility during recombinant expression include the use of weak promoters, modified growth media, low temperatur ...
... represents also a major biotechnological issue, preventing many proteins to be produced at economically convenient yields [13,20,22]. Effective experimental approaches to improve protein solubility during recombinant expression include the use of weak promoters, modified growth media, low temperatur ...
and paralogue-specific functions of acyl-CoA
... eukaryotic species examined, and on the basis of both the primary, secondary and tertiary structure it is also highly conserved in eukaryotes [15]. The three-dimensional structure shows that ACBD1 consists of four α-helices, which fold as a skewed updown-down-up helix bundle [16]. This arrangement y ...
... eukaryotic species examined, and on the basis of both the primary, secondary and tertiary structure it is also highly conserved in eukaryotes [15]. The three-dimensional structure shows that ACBD1 consists of four α-helices, which fold as a skewed updown-down-up helix bundle [16]. This arrangement y ...
Facing extremes: archaeal surface-layer (glyco)proteins
... chains, with sulfated glucuronic acid moieties attached to asparagine-linked glucose residues predominating and a single chain of a sulfated repeating unit pentasaccharide linked through N-acetylgalactosamine positioned at the 2-asparagine position of the protein (Lechner & Wieland, 1989). It remain ...
... chains, with sulfated glucuronic acid moieties attached to asparagine-linked glucose residues predominating and a single chain of a sulfated repeating unit pentasaccharide linked through N-acetylgalactosamine positioned at the 2-asparagine position of the protein (Lechner & Wieland, 1989). It remain ...
Document
... acid soluble pool and the second one residue called acid insoluble fraction. Thousands of organic compounds are in acid soluble pool. 10. List any four functions of protein. Ans. A. collagen forms intercellular ground substance B. Insulin acts as hormone. C. Antibody fights against infectious agents ...
... acid soluble pool and the second one residue called acid insoluble fraction. Thousands of organic compounds are in acid soluble pool. 10. List any four functions of protein. Ans. A. collagen forms intercellular ground substance B. Insulin acts as hormone. C. Antibody fights against infectious agents ...
Reivew, Hemoglobin
... Transport and Removal of CO2 Blood transports two forms of CO2 to the lungs: carbamino-hemoglobin and H2CO3/HCO3- (carbonic acidconjugate base pair) 1. Carbamino-hemoglobin: exposure to low pCO2 results in the reversal of the carbamination reaction by mass action and O2 binding is again favored. ...
... Transport and Removal of CO2 Blood transports two forms of CO2 to the lungs: carbamino-hemoglobin and H2CO3/HCO3- (carbonic acidconjugate base pair) 1. Carbamino-hemoglobin: exposure to low pCO2 results in the reversal of the carbamination reaction by mass action and O2 binding is again favored. ...
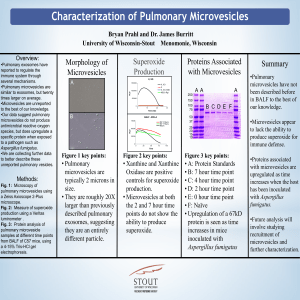
Bryan 2012 Research Day Poster
... reported to regulate the immune system through several mechanisms. •Pulmonary microvesicles are similar to exosomes, but twenty times larger on average. •Microvesicles are unreported to the best of our knowledge. •Our data suggest pulmonary microvesicles do not produce antimicrobial reactive oxygen ...
... reported to regulate the immune system through several mechanisms. •Pulmonary microvesicles are similar to exosomes, but twenty times larger on average. •Microvesicles are unreported to the best of our knowledge. •Our data suggest pulmonary microvesicles do not produce antimicrobial reactive oxygen ...
Variations in amino acid composition in bacterial single stranded
... from three taxonomically distant species, Helicobacter pylori, (Epsilonproteobacteria), Escherichia coli (Gammaproteobacteria), and Streptomyces coelicolor (Actinobacteria). These species with solved SSB structures were selected since they possess 38 %, 50 % and 72 % GC ratio in their genomes, respe ...
... from three taxonomically distant species, Helicobacter pylori, (Epsilonproteobacteria), Escherichia coli (Gammaproteobacteria), and Streptomyces coelicolor (Actinobacteria). These species with solved SSB structures were selected since they possess 38 %, 50 % and 72 % GC ratio in their genomes, respe ...
Differential display proteomic analysis of Picea meyeri pollen
... identical to those already reported in the NCBInr database. Nevertheless, many genes for abundant proteins appeared to be highly conserved in plants. Among the proteins identified, 16 (30%) were previously reported in conifers; 37 (70%) were highly homologous with those of other plants. ...
... identical to those already reported in the NCBInr database. Nevertheless, many genes for abundant proteins appeared to be highly conserved in plants. Among the proteins identified, 16 (30%) were previously reported in conifers; 37 (70%) were highly homologous with those of other plants. ...
Review sheet – Chapter 3 Understand that organic compounds are
... Understand dehydration and hydrolysis reactions – which one builds up polymers and which one breaks them down; how? Know that a polymer and an unlinked monomer have a hydroxyl group (OH) on one end and an H atom on the other end; how does this facilitate water removal or addition? Understand that hy ...
... Understand dehydration and hydrolysis reactions – which one builds up polymers and which one breaks them down; how? Know that a polymer and an unlinked monomer have a hydroxyl group (OH) on one end and an H atom on the other end; how does this facilitate water removal or addition? Understand that hy ...
Carbohydrates - the Complex Carbohydrate Research Center
... • Amino sugars of glucose and galactose occur commonly in glycoconjugates ...
... • Amino sugars of glucose and galactose occur commonly in glycoconjugates ...
Creation/Evolution - Geoscience Research Institute
... has passed into protein it cannot get out again. The transfer of information from nucleic acid to nucleic acid, or from nucleic acid to protein, may be possible, but transfer from protein to protein, or from protein to nucleic acid, is impossible. Information means here the precise determination of ...
... has passed into protein it cannot get out again. The transfer of information from nucleic acid to nucleic acid, or from nucleic acid to protein, may be possible, but transfer from protein to protein, or from protein to nucleic acid, is impossible. Information means here the precise determination of ...
ANP 204 Main Text - National Open University of Nigeria
... glucose but for a change in the positions of OH group on carbon 2 and 4 for mannose and galactose respectively. The carbon atoms involved are ...
... glucose but for a change in the positions of OH group on carbon 2 and 4 for mannose and galactose respectively. The carbon atoms involved are ...
Calcium, a signaling molecule in the endoplasmic reticulum?
... below this level, it is unlikely that Ca21 binding to the high-affinity Ca21 binding, proline-rich domain of calreticulin and calnexin regulate these protein–carbohydrate interactions (Fig. 1). It is not clear at present which Ca21-binding site is essential for the lectin-like activity of calreticul ...
... below this level, it is unlikely that Ca21 binding to the high-affinity Ca21 binding, proline-rich domain of calreticulin and calnexin regulate these protein–carbohydrate interactions (Fig. 1). It is not clear at present which Ca21-binding site is essential for the lectin-like activity of calreticul ...
The Effect of Detergents on Amino Acid Liberation by
... were detected in the media of MYRJ 45-grown cultures but not in MYRJ 52-grown cultures were all branched-chain aliphatic types (valine, leucine and isoleucine). A transport system may therefore exist in A . variabilis which is specific for these amino acids and which is disrupted by MYRJ 45 but not ...
... were detected in the media of MYRJ 45-grown cultures but not in MYRJ 52-grown cultures were all branched-chain aliphatic types (valine, leucine and isoleucine). A transport system may therefore exist in A . variabilis which is specific for these amino acids and which is disrupted by MYRJ 45 but not ...
Free amino acid content in infant formulas
... The total FAA content for CMF (523-864 mmol/L) was considerably lower than for SPF and PHF. While the most abundant FAAs in CMF were taurine (61-74 percent) and glutamic acid (13-17 percent), the two CMFs differed most in proline content: 7 percent in CMF-1 versus none in CMF-2. CMF-1 also containe ...
... The total FAA content for CMF (523-864 mmol/L) was considerably lower than for SPF and PHF. While the most abundant FAAs in CMF were taurine (61-74 percent) and glutamic acid (13-17 percent), the two CMFs differed most in proline content: 7 percent in CMF-1 versus none in CMF-2. CMF-1 also containe ...
Protein

Proteins (/ˈproʊˌtiːnz/ or /ˈproʊti.ɨnz/) are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within living organisms, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific three-dimensional structure that determines its activity.A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than about 20-30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides, or sometimes oligopeptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues in a protein is defined by the sequence of a gene, which is encoded in the genetic code. In general, the genetic code specifies 20 standard amino acids; however, in certain organisms the genetic code can include selenocysteine and—in certain archaea—pyrrolysine. Shortly after or even during synthesis, the residues in a protein are often chemically modified by posttranslational modification, which alters the physical and chemical properties, folding, stability, activity, and ultimately, the function of the proteins. Sometimes proteins have non-peptide groups attached, which can be called prosthetic groups or cofactors. Proteins can also work together to achieve a particular function, and they often associate to form stable protein complexes.Once formed, proteins only exist for a certain period of time and are then degraded and recycled by the cell's machinery through the process of protein turnover. A protein's lifespan is measured in terms of its half-life and covers a wide range. They can exist for minutes or years with an average lifespan of 1–2 days in mammalian cells. Abnormal and or misfolded proteins are degraded more rapidly either due to being targeted for destruction or due to being unstable.Like other biological macromolecules such as polysaccharides and nucleic acids, proteins are essential parts of organisms and participate in virtually every process within cells. Many proteins are enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions and are vital to metabolism. Proteins also have structural or mechanical functions, such as actin and myosin in muscle and the proteins in the cytoskeleton, which form a system of scaffolding that maintains cell shape. Other proteins are important in cell signaling, immune responses, cell adhesion, and the cell cycle. Proteins are also necessary in animals' diets, since animals cannot synthesize all the amino acids they need and must obtain essential amino acids from food. Through the process of digestion, animals break down ingested protein into free amino acids that are then used in metabolism.Proteins may be purified from other cellular components using a variety of techniques such as ultracentrifugation, precipitation, electrophoresis, and chromatography; the advent of genetic engineering has made possible a number of methods to facilitate purification. Methods commonly used to study protein structure and function include immunohistochemistry, site-directed mutagenesis, X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry.