Lipid transfer and metabolism across the endolysosomal
... PPARγ co-activator 1α (PGC1α) [2]. It is therefore not surprising that, in addition to classical lysosomal storage diseases, disfuction of lysosomal–autophagic pathways has been associated to a variety of other disease conditions, including metabolic, infectious, immune and common neurodegenerative ...
... PPARγ co-activator 1α (PGC1α) [2]. It is therefore not surprising that, in addition to classical lysosomal storage diseases, disfuction of lysosomal–autophagic pathways has been associated to a variety of other disease conditions, including metabolic, infectious, immune and common neurodegenerative ...
FREE Sample Here
... Ans: Living things are composed primarily of macromolecules, polymers of simple compounds of just a few different types. The properties of these polymers are determined by their sequence of monomers and these can be combined in many different ways. Diversity is thus achieved through the nearly limit ...
... Ans: Living things are composed primarily of macromolecules, polymers of simple compounds of just a few different types. The properties of these polymers are determined by their sequence of monomers and these can be combined in many different ways. Diversity is thus achieved through the nearly limit ...
FREE Sample Here
... Ans: Living things are composed primarily of macromolecules, polymers of simple compounds of just a few different types. The properties of these polymers are determined by their sequence of monomers and these can be combined in many different ways. Diversity is thus achieved through the nearly limit ...
... Ans: Living things are composed primarily of macromolecules, polymers of simple compounds of just a few different types. The properties of these polymers are determined by their sequence of monomers and these can be combined in many different ways. Diversity is thus achieved through the nearly limit ...
McFil: metabolic carbon flow in leaves
... synthesis of isopentanyl diphosphate, which then isomerises and/or polymerises to form ...
... synthesis of isopentanyl diphosphate, which then isomerises and/or polymerises to form ...
A study of archaeal enzymes involved in polar lipid
... Archaetidylcholine (AC), archaetidylserine (AS), archaetidylglycerol (AG) and archaetidylinositol (AI) have been identified in archaeal membranes as the counterparts of the phosphatidyl derivatives, PC, PS, PG and PI. As in Eukarya and Bacteria, an archaebacterium does not always utilize all of the ...
... Archaetidylcholine (AC), archaetidylserine (AS), archaetidylglycerol (AG) and archaetidylinositol (AI) have been identified in archaeal membranes as the counterparts of the phosphatidyl derivatives, PC, PS, PG and PI. As in Eukarya and Bacteria, an archaebacterium does not always utilize all of the ...
Bio426Lecture28Apr10
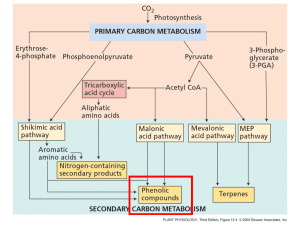
... What’s a phenolic compound? A secondary product that contains a phenol group - a hydroxyl functional group on an aromatic ring. ...
... What’s a phenolic compound? A secondary product that contains a phenol group - a hydroxyl functional group on an aromatic ring. ...
Biological Networks Underlying Abiotic Stress Tolerance in
... comprehensive reviews on proteomics of abiotic stresses in crop plants [5,6] as well as more specialized reviews dedicated to specific stress factors, crops or cellular fractions such as reviews on salinity proteomics [7–9], subcellular proteomics of crop plants exposed to stress [10], proteomics of ...
... comprehensive reviews on proteomics of abiotic stresses in crop plants [5,6] as well as more specialized reviews dedicated to specific stress factors, crops or cellular fractions such as reviews on salinity proteomics [7–9], subcellular proteomics of crop plants exposed to stress [10], proteomics of ...
Preparation of Translationally Competent tRNA by Direct Chemical
... with the ability to perform precise structure-function studies with proteins, beyond that which can be performed with the 20 natural amino acids.1-3 This is usually achieved through nonsense suppression, in which the site of interest is mutated to a stop codon, and an aminoacyl-tRNA bearing the appr ...
... with the ability to perform precise structure-function studies with proteins, beyond that which can be performed with the 20 natural amino acids.1-3 This is usually achieved through nonsense suppression, in which the site of interest is mutated to a stop codon, and an aminoacyl-tRNA bearing the appr ...
Articulins and epiplasmins - Journal of Cell Science
... epiplasm generally reveals many different molecular mass bands, with a pronounced interspecific variation in banding pattern, even among closely related species that are nearly identical morphologically (see, for example, Williams et al., 1984). Polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) directed a ...
... epiplasm generally reveals many different molecular mass bands, with a pronounced interspecific variation in banding pattern, even among closely related species that are nearly identical morphologically (see, for example, Williams et al., 1984). Polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) directed a ...
The Early Interaction of the Outer Membrane Protein PhoE with
... cross-linking approach, the latter protein was found to interact with nascent PhoE chains as short as 57 amino acids (1–3). Subsequently, at a late co-translational or early post-translational stage the precursor protein interacts with SecB (4 – 6). This SecB䡠precursor complex is then targeted to Se ...
... cross-linking approach, the latter protein was found to interact with nascent PhoE chains as short as 57 amino acids (1–3). Subsequently, at a late co-translational or early post-translational stage the precursor protein interacts with SecB (4 – 6). This SecB䡠precursor complex is then targeted to Se ...
Lethal protein produced in response to competition
... in Streptococcus pneumoniae, some cells in a population are killed by their siblings or close relatives in a process linked to induction of competence (5). The release of DNA from lysed cells (allolysis) may increase genetic diversity when there is variation in the population. Additionally, the incr ...
... in Streptococcus pneumoniae, some cells in a population are killed by their siblings or close relatives in a process linked to induction of competence (5). The release of DNA from lysed cells (allolysis) may increase genetic diversity when there is variation in the population. Additionally, the incr ...
TAR-RNA binding by HIV-1 Tat protein is
... Nolte’s 38mer L-RNA, originally developed as a ligand for L-arginine, is sequence-wise unrelated to TAR and binds to a short peptide (12 residues) corresponding to the basic region of HIV-1 Tat protein with a Kd of 26 µM. In contrast, our competition binding experiments demonstrate that the affinity ...
... Nolte’s 38mer L-RNA, originally developed as a ligand for L-arginine, is sequence-wise unrelated to TAR and binds to a short peptide (12 residues) corresponding to the basic region of HIV-1 Tat protein with a Kd of 26 µM. In contrast, our competition binding experiments demonstrate that the affinity ...
Introduction Milk is the exclusive nutrient source for the neonate. ... practices and availability of highly selected sows have allowed for...
... pathways other than protein synthesis may account for a significant portion of the BCAA taken up by the gland (Hurley & Bryson, 1997 Illinois Swine Research Report). Alternative fates of BCAA in the mammary gland, depending upon the amino acid, may include synthesis of cellular protein, synthesis of ...
... pathways other than protein synthesis may account for a significant portion of the BCAA taken up by the gland (Hurley & Bryson, 1997 Illinois Swine Research Report). Alternative fates of BCAA in the mammary gland, depending upon the amino acid, may include synthesis of cellular protein, synthesis of ...
Recombinant N-terminal Nucleotide
... 5 mM, and the activity was monitored at 30 °C with NBD1–581 aliquots (50 –100 mg of protein), by recording NADH disappearance at 340 nm for 5–10 min. Fluorescence—Experiments were performed at 25.0 6 0.1 °C using a SLM-Aminco 8000C spectrofluorometer with spectral band widths of 2 nm and 4 nm, respe ...
... 5 mM, and the activity was monitored at 30 °C with NBD1–581 aliquots (50 –100 mg of protein), by recording NADH disappearance at 340 nm for 5–10 min. Fluorescence—Experiments were performed at 25.0 6 0.1 °C using a SLM-Aminco 8000C spectrofluorometer with spectral band widths of 2 nm and 4 nm, respe ...
CMBI
... – How do the proteins encoded in genomes interact with each other to produce cells and phenotypes ? – To predict such functional interactions between proteins as there exist e.g. in metabolic pathways, signalling pathways or protein complexes ...
... – How do the proteins encoded in genomes interact with each other to produce cells and phenotypes ? – To predict such functional interactions between proteins as there exist e.g. in metabolic pathways, signalling pathways or protein complexes ...
Role for Adenosine Triphosphate in Regulating the Assembly and
... which probably represents an SDS-resistant form. Such SDS-PAGE-resistant oligomers can often be detected upon analysis of other multimeric integral membrane proteins (Silverberg and Marchesi, 1978; Doms and Helenius, 1986). Taken together, the sedimentation and cross-linking results showed that the ...
... which probably represents an SDS-resistant form. Such SDS-PAGE-resistant oligomers can often be detected upon analysis of other multimeric integral membrane proteins (Silverberg and Marchesi, 1978; Doms and Helenius, 1986). Taken together, the sedimentation and cross-linking results showed that the ...
Molecular architecture of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
... (blue) superimposed on to a model of a 2:1 subcomplex of E3BP-didomain (green/magenta, lime/yellow) and E3 (orange). ...
... (blue) superimposed on to a model of a 2:1 subcomplex of E3BP-didomain (green/magenta, lime/yellow) and E3 (orange). ...
Structural Basis of Wnt Recognition by Frizzled
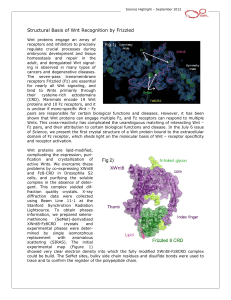
... showed very clear electron density into which the fully modified XWnt8-Fz8CRD complex could be build. The SeMet sites, bulky side chain residues and disulfide bonds were used to trace and to confirm the register of the polypeptide chain. ...
... showed very clear electron density into which the fully modified XWnt8-Fz8CRD complex could be build. The SeMet sites, bulky side chain residues and disulfide bonds were used to trace and to confirm the register of the polypeptide chain. ...
ProteoChem`s Current Catalogue.
... molecules without adding additional spacer arm atoms. Homobifunctional crosslinkers have the same reactive group on both ends of the spacer arm (i.e., Amine Reactive-Amine Reactive); while heterobifunctional crosslinkers have different reactive groups on each end of a spacer arm (i.e., Sulfhydryl Re ...
... molecules without adding additional spacer arm atoms. Homobifunctional crosslinkers have the same reactive group on both ends of the spacer arm (i.e., Amine Reactive-Amine Reactive); while heterobifunctional crosslinkers have different reactive groups on each end of a spacer arm (i.e., Sulfhydryl Re ...
Lecture - Ch 25-7
... – It is either an inorganic ion or a small organic molecule called a coenzyme – Coenzymes are reactants that undergo a chemical change during the reaction and ...
... – It is either an inorganic ion or a small organic molecule called a coenzyme – Coenzymes are reactants that undergo a chemical change during the reaction and ...
Full Text PDF - Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. publishers
... other important mitochondrial enzymes, was found to be oxidized, and the concentration of its substrate a-ketoglutarate was increased in Abcd1 - spinal cord (Fig. 3A). Thus, we hypothesized that KGDHC activity was most likely to be decreased in Abcd1-null mice, even if the steady-state level of a-ke ...
... other important mitochondrial enzymes, was found to be oxidized, and the concentration of its substrate a-ketoglutarate was increased in Abcd1 - spinal cord (Fig. 3A). Thus, we hypothesized that KGDHC activity was most likely to be decreased in Abcd1-null mice, even if the steady-state level of a-ke ...
THE RDOA-DEPENDENT PHOSPHOPROTEOME PROFILE OF Salmonella enterica
... mutants suggested that RdoA kinase activity affects a wide range of cell functions, which could be the result of both direct and indirect phosphorylation of targets. In a search for RdoA’s target(s), the phosphoproteome profile of wild-type and rdoA null S. enterica was examined through phosphoprote ...
... mutants suggested that RdoA kinase activity affects a wide range of cell functions, which could be the result of both direct and indirect phosphorylation of targets. In a search for RdoA’s target(s), the phosphoproteome profile of wild-type and rdoA null S. enterica was examined through phosphoprote ...
Protein

Proteins (/ˈproʊˌtiːnz/ or /ˈproʊti.ɨnz/) are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within living organisms, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific three-dimensional structure that determines its activity.A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than about 20-30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides, or sometimes oligopeptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues in a protein is defined by the sequence of a gene, which is encoded in the genetic code. In general, the genetic code specifies 20 standard amino acids; however, in certain organisms the genetic code can include selenocysteine and—in certain archaea—pyrrolysine. Shortly after or even during synthesis, the residues in a protein are often chemically modified by posttranslational modification, which alters the physical and chemical properties, folding, stability, activity, and ultimately, the function of the proteins. Sometimes proteins have non-peptide groups attached, which can be called prosthetic groups or cofactors. Proteins can also work together to achieve a particular function, and they often associate to form stable protein complexes.Once formed, proteins only exist for a certain period of time and are then degraded and recycled by the cell's machinery through the process of protein turnover. A protein's lifespan is measured in terms of its half-life and covers a wide range. They can exist for minutes or years with an average lifespan of 1–2 days in mammalian cells. Abnormal and or misfolded proteins are degraded more rapidly either due to being targeted for destruction or due to being unstable.Like other biological macromolecules such as polysaccharides and nucleic acids, proteins are essential parts of organisms and participate in virtually every process within cells. Many proteins are enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions and are vital to metabolism. Proteins also have structural or mechanical functions, such as actin and myosin in muscle and the proteins in the cytoskeleton, which form a system of scaffolding that maintains cell shape. Other proteins are important in cell signaling, immune responses, cell adhesion, and the cell cycle. Proteins are also necessary in animals' diets, since animals cannot synthesize all the amino acids they need and must obtain essential amino acids from food. Through the process of digestion, animals break down ingested protein into free amino acids that are then used in metabolism.Proteins may be purified from other cellular components using a variety of techniques such as ultracentrifugation, precipitation, electrophoresis, and chromatography; the advent of genetic engineering has made possible a number of methods to facilitate purification. Methods commonly used to study protein structure and function include immunohistochemistry, site-directed mutagenesis, X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry.