MD Simulations of the P53 oncoprotein structure
... We have performed a comparative analysis of the wildtype and mutant versions between the mouse (mouW, mouM) p53 proteins. For the mouse p53 structures, we have examined the effect of the Arg-273His (R273H) mutation on the p53-DNA binding domain. Arginine (Arg) is an alpha-amino acid with pKa = 12.48 ...
... We have performed a comparative analysis of the wildtype and mutant versions between the mouse (mouW, mouM) p53 proteins. For the mouse p53 structures, we have examined the effect of the Arg-273His (R273H) mutation on the p53-DNA binding domain. Arginine (Arg) is an alpha-amino acid with pKa = 12.48 ...
A Difference between Rods and Cones in the Renewal of Outer
... the retinal rods of rats and mice. He suggested that it might be the visual pigment (opsin) molecules which were being replaced. Transfer of protein to the outer segment, shortly after its production in rod inner segments in rats, mice, and frogs was confirmed by the author.5 It was also observed th ...
... the retinal rods of rats and mice. He suggested that it might be the visual pigment (opsin) molecules which were being replaced. Transfer of protein to the outer segment, shortly after its production in rod inner segments in rats, mice, and frogs was confirmed by the author.5 It was also observed th ...
Peptide Design Strategy
... hormone receptor (PTH) - every fourth residue Incorporates CH2 residues into backbone, but maintains native sequence sidechains Successfully mimics α-helix NLGKWLNSMERVEWLRKKLQDVHNF ...
... hormone receptor (PTH) - every fourth residue Incorporates CH2 residues into backbone, but maintains native sequence sidechains Successfully mimics α-helix NLGKWLNSMERVEWLRKKLQDVHNF ...
Symbiotic bacteria enable insect to use a nutritionally inadequate diet
... these nutrients; but this has not been demonstrated empirically. We demonstrate here that phloem sap obtained from the severed stylets of pea aphids Acyrthosiphon pisum feeding on Vicia faba plants generally provided inadequate amounts of at least one essential amino acid to support aphid growth. Co ...
... these nutrients; but this has not been demonstrated empirically. We demonstrate here that phloem sap obtained from the severed stylets of pea aphids Acyrthosiphon pisum feeding on Vicia faba plants generally provided inadequate amounts of at least one essential amino acid to support aphid growth. Co ...
Aromatic amino acid metabolism
... : anthranilate synthase, : anthranilate phosphoribosyl transferase, : N-(5’-phosphoribosyl)- anthranilate isomerase, ...
... : anthranilate synthase, : anthranilate phosphoribosyl transferase, : N-(5’-phosphoribosyl)- anthranilate isomerase, ...
Phosphorylation of Single Stranded RNA Virus Proteins and
... how eukaryotic proteins are phosphorylated by the host enzymatic machinery and are essential for maintaining cell viability and function. The focus of this review is phosphorylation of viral proteins, mediated by activated host kinases. Viruses, being obligate parasites, have evolved to utilize the ...
... how eukaryotic proteins are phosphorylated by the host enzymatic machinery and are essential for maintaining cell viability and function. The focus of this review is phosphorylation of viral proteins, mediated by activated host kinases. Viruses, being obligate parasites, have evolved to utilize the ...
29.9 Tanaka
... cell. But specific nutrients, wastes and metabolites can pass through the membranes of organelles and cells to reach their destination. In addition, many important biological processes are regulated at membrane surfaces, through interactions between peripheral and integral membrane proteins. The com ...
... cell. But specific nutrients, wastes and metabolites can pass through the membranes of organelles and cells to reach their destination. In addition, many important biological processes are regulated at membrane surfaces, through interactions between peripheral and integral membrane proteins. The com ...
hotspots
... essential for recognition and binding to other proteins • This small subset of essential residues is referred to as “hotspots” • If mutated, these residues hamper proteinprotein interaction ...
... essential for recognition and binding to other proteins • This small subset of essential residues is referred to as “hotspots” • If mutated, these residues hamper proteinprotein interaction ...
Regulation of Galactoside Transport by the PTS
... is not conserved well in four MelBs of enteric bacteria, sequences of which have been reported so far. Furthermore, E. coli PTS can regulate MelBs from S. typhimurium and K. pneumoniae (unpublished result). Therefore, we proposed that C-terminal region of the MelB protein is at least one of the inte ...
... is not conserved well in four MelBs of enteric bacteria, sequences of which have been reported so far. Furthermore, E. coli PTS can regulate MelBs from S. typhimurium and K. pneumoniae (unpublished result). Therefore, we proposed that C-terminal region of the MelB protein is at least one of the inte ...
the Golgi Apparatus as the central station of the
... 2. The endocytic pathway. This is the route by which soluble and membrane components enter into the cell. This includes: 2.1. The receptor-mediated endocytosis. The molecules that enter into the cell first bind to either a cell surface receptor or to a receptor stored in intracellular compartments ...
... 2. The endocytic pathway. This is the route by which soluble and membrane components enter into the cell. This includes: 2.1. The receptor-mediated endocytosis. The molecules that enter into the cell first bind to either a cell surface receptor or to a receptor stored in intracellular compartments ...
Characterization of a Novel Peripheral Nervous System Myelin
... MAG overexpression in mixed Schwann cell neuron cultures also provide support for the hypothesis that MAG is involved in axon-Schwann cell interactions (Owens et al., 1990) . Protein zero (PO), MBP, and MAG are the major protein components of PNS myelin (reviewed in Morell et al ., 1989; Lemke, 198 ...
... MAG overexpression in mixed Schwann cell neuron cultures also provide support for the hypothesis that MAG is involved in axon-Schwann cell interactions (Owens et al., 1990) . Protein zero (PO), MBP, and MAG are the major protein components of PNS myelin (reviewed in Morell et al ., 1989; Lemke, 198 ...
Chem 309 Video Tutorial Schedule for Fall 2013
... Introduction to Proteins, Carbohydrates, Lipids and Bioenergetics (16:15) Video Tutorial Lecture Notes Chirality (31:16) Video Tutorial Lecture Notes Proteins and Enzymes Part 2: Chirality and Amino Acids (19:33) Video Tutorial Lecture Notes Proteins and Enzymes Part 8: Introduction to Enzymes (14:5 ...
... Introduction to Proteins, Carbohydrates, Lipids and Bioenergetics (16:15) Video Tutorial Lecture Notes Chirality (31:16) Video Tutorial Lecture Notes Proteins and Enzymes Part 2: Chirality and Amino Acids (19:33) Video Tutorial Lecture Notes Proteins and Enzymes Part 8: Introduction to Enzymes (14:5 ...
Introduction
... 1. The general characteristics and biological functions of proteins and peptides. 2. Amino acid composition of proteins and peptides: structure, classification and physical and chemical properties of amino acids. 3. The formation of peptide bonds. Levels of protein structure. Chemical bonds in prote ...
... 1. The general characteristics and biological functions of proteins and peptides. 2. Amino acid composition of proteins and peptides: structure, classification and physical and chemical properties of amino acids. 3. The formation of peptide bonds. Levels of protein structure. Chemical bonds in prote ...
role of the proteolytic enzymes in the living organisms - IJIIT
... bonds of polypeptides. The classification of exopeptidases is based on their actions on substrates while the endopeptidases are divided by their active sites. AMINOPEPETIDES Aminopeptidases act at a free N terminus of the polypeptide chain and liberate a single amino acid residue, a dipeptide, or a ...
... bonds of polypeptides. The classification of exopeptidases is based on their actions on substrates while the endopeptidases are divided by their active sites. AMINOPEPETIDES Aminopeptidases act at a free N terminus of the polypeptide chain and liberate a single amino acid residue, a dipeptide, or a ...
Steven`s project - The University of Texas at Dallas
... Using the downloaded software The downloaded software is much more difficult to use and does not contain user friendly GU interfaces. Whenever possible a novice user should opt for the on line version as described above. However, if you intend to repack proteins quite regularly, or need to repack i ...
... Using the downloaded software The downloaded software is much more difficult to use and does not contain user friendly GU interfaces. Whenever possible a novice user should opt for the on line version as described above. However, if you intend to repack proteins quite regularly, or need to repack i ...
Topological studies suggest that the pathway of the protons through
... TID-reactive residues in F0• The labeling profilein Fig. 58 was obtaincd after reaction with Neurospora crassa mitochondria in the presence of an oligomycin concentration 10-fold higher than necessary for maximal inhibition. The identical group of residues was TID-reactive in the presence and in the ...
... TID-reactive residues in F0• The labeling profilein Fig. 58 was obtaincd after reaction with Neurospora crassa mitochondria in the presence of an oligomycin concentration 10-fold higher than necessary for maximal inhibition. The identical group of residues was TID-reactive in the presence and in the ...
Effect of essential and non-essential amino acid addition to a
... proline (Table 2). The effect of the addition of nonessential amino acids to diet E was negligible, even though the endogenous flow of most AA tended to decrease. In comparison with diet NF, the endogenous flow of total N in diets E and E+N was reduced by about 30%. This reduction was mainly due to ...
... proline (Table 2). The effect of the addition of nonessential amino acids to diet E was negligible, even though the endogenous flow of most AA tended to decrease. In comparison with diet NF, the endogenous flow of total N in diets E and E+N was reduced by about 30%. This reduction was mainly due to ...
Biochemical Thermodynamics - Illinois Institute of Technology
... All have the same handedness at the alpha carbon The opposite handedness gives you a Damino acid – There are D-amino acids in many organisms – Bacteria incorporate them into structures of their cell walls – Makes those structures resistant to standard proteolytic enzymes, which only attack amino a ...
... All have the same handedness at the alpha carbon The opposite handedness gives you a Damino acid – There are D-amino acids in many organisms – Bacteria incorporate them into structures of their cell walls – Makes those structures resistant to standard proteolytic enzymes, which only attack amino a ...
HIGHLY VISCOUS DOUGH FORMING PROPERTIES OF MARAMA PROTEIN
... strong protein network. Marama protein, thus, appeared to have some structural stability, but only when small deformations were applied. The complex viscosity (ŋ*) decreased at increasing frequency for marama protein, which was similar to gluten (Table 2). According to a review by Tunick (2011), bre ...
... strong protein network. Marama protein, thus, appeared to have some structural stability, but only when small deformations were applied. The complex viscosity (ŋ*) decreased at increasing frequency for marama protein, which was similar to gluten (Table 2). According to a review by Tunick (2011), bre ...
Early and late endosomal compartments of Entamoeba histolytica
... importance of the E. histolytica endo-lysosomal and secretory systems in nutrition and invasion of the organism, relatively little is known about the molecular factors governing these systems including the associated proteins which may regulate endocytic or secretory function. In other eukaryotes, t ...
... importance of the E. histolytica endo-lysosomal and secretory systems in nutrition and invasion of the organism, relatively little is known about the molecular factors governing these systems including the associated proteins which may regulate endocytic or secretory function. In other eukaryotes, t ...
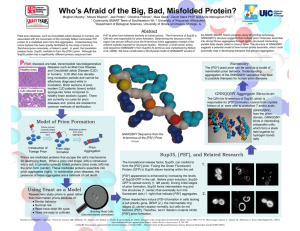
Poster
... Fatal prion diseases, such as Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in humans, are associated with the conversion of the normally folded mammalian PrP protein to a misfolded prion form that aggregates. Understanding how prions behave has been greatly facilitated by the study of prions in Saccharomyces cerevisia ...
... Fatal prion diseases, such as Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in humans, are associated with the conversion of the normally folded mammalian PrP protein to a misfolded prion form that aggregates. Understanding how prions behave has been greatly facilitated by the study of prions in Saccharomyces cerevisia ...
Document
... Gel Filtration Resin. When starting protein purification, technicians sometimes use a gel-filtration (size-exclusion) column first. They know the molecular weight of their protein, so they can often eliminate several contaminant proteins by a quick run through a sizing column. ...
... Gel Filtration Resin. When starting protein purification, technicians sometimes use a gel-filtration (size-exclusion) column first. They know the molecular weight of their protein, so they can often eliminate several contaminant proteins by a quick run through a sizing column. ...
Thulashie Sivarajah
... Under normal conditions, Src is only active at certain times. However, mutated Src kinases that are missing tyrosine 527 are active all the time. This leads to several cancers and diseases including Colon, Breast Cancers, Arthrosclerosis, Psoriasis, and Restnoises. Bivalent inhibitors are inhibitors ...
... Under normal conditions, Src is only active at certain times. However, mutated Src kinases that are missing tyrosine 527 are active all the time. This leads to several cancers and diseases including Colon, Breast Cancers, Arthrosclerosis, Psoriasis, and Restnoises. Bivalent inhibitors are inhibitors ...
Protein

Proteins (/ˈproʊˌtiːnz/ or /ˈproʊti.ɨnz/) are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within living organisms, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific three-dimensional structure that determines its activity.A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than about 20-30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides, or sometimes oligopeptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues in a protein is defined by the sequence of a gene, which is encoded in the genetic code. In general, the genetic code specifies 20 standard amino acids; however, in certain organisms the genetic code can include selenocysteine and—in certain archaea—pyrrolysine. Shortly after or even during synthesis, the residues in a protein are often chemically modified by posttranslational modification, which alters the physical and chemical properties, folding, stability, activity, and ultimately, the function of the proteins. Sometimes proteins have non-peptide groups attached, which can be called prosthetic groups or cofactors. Proteins can also work together to achieve a particular function, and they often associate to form stable protein complexes.Once formed, proteins only exist for a certain period of time and are then degraded and recycled by the cell's machinery through the process of protein turnover. A protein's lifespan is measured in terms of its half-life and covers a wide range. They can exist for minutes or years with an average lifespan of 1–2 days in mammalian cells. Abnormal and or misfolded proteins are degraded more rapidly either due to being targeted for destruction or due to being unstable.Like other biological macromolecules such as polysaccharides and nucleic acids, proteins are essential parts of organisms and participate in virtually every process within cells. Many proteins are enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions and are vital to metabolism. Proteins also have structural or mechanical functions, such as actin and myosin in muscle and the proteins in the cytoskeleton, which form a system of scaffolding that maintains cell shape. Other proteins are important in cell signaling, immune responses, cell adhesion, and the cell cycle. Proteins are also necessary in animals' diets, since animals cannot synthesize all the amino acids they need and must obtain essential amino acids from food. Through the process of digestion, animals break down ingested protein into free amino acids that are then used in metabolism.Proteins may be purified from other cellular components using a variety of techniques such as ultracentrifugation, precipitation, electrophoresis, and chromatography; the advent of genetic engineering has made possible a number of methods to facilitate purification. Methods commonly used to study protein structure and function include immunohistochemistry, site-directed mutagenesis, X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry.